Sdlc
- 1. Software Development Life Cycle(SDLC) ● Overview ● Objective ● Development Phases ● Life cycle Model ● Agile SDLC ● Strength & weakness ● conclusion
- 2. 1.Overview ● It is a process used to develop information systems and user ownership ● A framework that describes the activities performed at each stage of a software development project ● High quality system ● Reaches completion with cost and time ● Have various model like Waterfall,spiral,RAD,Agile
- 4. 3.Development Phase The development phase in SDLC are # Requirement analysis # Design # Coding # Testing # Operation & Maintainance
- 5. Requirement Analysis ● It invovles 'breaking down' the system for * analysis of situation * analysis of project goals ● It can be done by individuals or team members
- 6. Design ● It takes the initial input ● For each requirements design elements will be produced ● It describes the software features and includes hierarchy diagrams,screen layout diagrams ● The output of ths stage describe the new system as a collection of modules or subsytems
- 7. Coding ● Modular & subsystem programming code will be accomplished during this stage ● It is interlinked with the testing stage ● Here overall coding will be tested
- 8. Testing ● Here the code are tested at various levels ● Most common testing are unit,system and user acceptance. ● Types of testing are # White box testing # Black box testing # Regression testing
- 10. Operation & Maintenance ● The deployment includes changes and enhancements ● Maintaining is the important aspect of SDLC
- 11. 4.Life cycle models Different types of life cycle model available are ● Waterfall model ● Prototyping model ● Rapid Application Development(RAD) ● Spiral model
- 12. 5.Waterfall model ● It is the classical system development model ● Requirementsdefines needed information,function,behaviour,performance and interface ● Designdata structures,software architedtures,interface representations,algorithmic details ● Implementationsource code,database,documentation,testing
- 13. waterfall(cont.) Various stages of waterfall model
- 14. Waterfall(cont.) Strength Weakness ● Minimizes planning ● Inflexible overhaed ● Only final stage ● Structure minimizes produces wasted effort documentation ● Works well for ● Backing up to address technically weak or mistake is difficult inexperinced staff
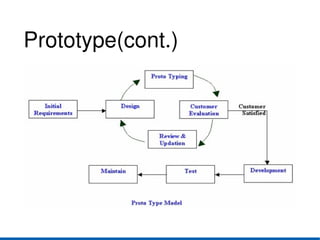
- 15. 6.Prototyping Model ● It uses multiple iterations or requirement,analysis,design ● After each iteration,the result is evaluted by the customer ● When the user is satisfied,the prototype code is brought up to the standards needed for afinal product.
- 16. Prototype(cont.)
- 17. Prototyping(cont.) Strength Weakness ● Customers can see ● It is impossible to steady progress know how long it will ● This is useful when take requirements are ● There is no way to changing rapidly know the no.of iterations will be required
- 18. 7.Spiral Model ● It is riskreduction oriented model ● It breaks the whole projects into mini projects ● For projects with risky elements,its beneficial. ● Each cycle invovles the same sequence as the steps as the waterfall process model
- 19. Spiral(cont.)
- 20. Spiral(cont.) Strength Weakness ● Early iterations of the ● Complicated project are cheapset ● Require attentive & ● Risk decreases knowledgable ● All iterations meets management the project needs
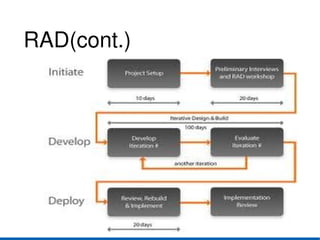
- 21. 8.RAD model ● RAD is a concept that products can be developed faster and higher quality through: Gathering requirements using workshops Prototyping and early,reiterative user testing of designs the reuse of software components
- 22. RAD(cont.)
- 23. RAD(cont.) Strength Weakness ● Reduces the ● Require higly skilled development time engineers ● Reusability ● Both the customer & ● Speed developer should be commited to complete ● Easy to work with ● If it is difficult to modularize,its not work well
- 24. 9.Agile SDLC ● Speed up or bypass on one or more life cycle phases ● Used for time critical application ● Usually less formal and reduced scope ● Used in organizations that employ disciplined methods
- 25. Some Agile Methods ● Adaptive software development(ASD) ● Feature driven development(FDD) ● Crystal clear ● Extreme programming(XP) ● Scrum ● RAD
- 26. 10.Strength & Weakness of SDLC Strength Weakness ● Control ● Increased ● Monitor large projects development time & cost ● Detailed steps ● Rigidity ● Easy to maintain ● Hard to estimate project overruns
- 27. My conclusion ● RAD model can be used in mashups as a life cycle development model because: # Speed process # customer can be involved upto delivery of projects # user requirements can be added or modified at any time during the project
- 28. conclusion(cont.) #It reduces the development time # work can be modularized # can support multi platform like PHP,Python,Perl.. So RAD may be the right option to work with PHP for Mashups