Sds-Page
- 1. Sodium Dodecylsulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis(SDS-PAGE) BY: JANE LOH JENNY ONG
- 2. Overview a. Introduction b. Principle of Sds-page c. Gel preparation d. Process of Sds-page e. Visualization of protein f. Applications g. Advantages and disadvantages h. Conclusion i. References
- 3. Introduction Standard test that used to determine the charged molecules, mainly proteins and nucleic acids. Widely used in biochemistry, forensics, genetics and molecular biology. Laemmli system of SDS-PAGE was first introduced in 1970s.
- 4. Principle Separates protein in an electric field Migrate through a liquid or semisolid medium when subjected to an electric field from anode to cathode terminal Molecules flow at different rates depend on the molecular size of proteins
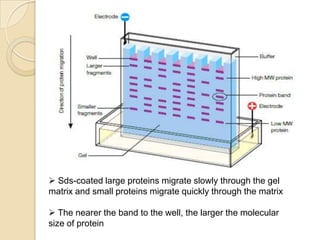
- 5. Sds-coated large proteins migrate slowly through the gel matrix and small proteins migrate quickly through the matrix The nearer the band to the well, the larger the molecular size of protein
- 6. What is SDS? negatively charged detergent sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) used to denature and linearize the proteins coated the proteins with negatively charged
- 7. What is PAGE? SDS-PAGE is differentiated into two systems Continuous sds-page Discontinuous sds-page Polyacrylamide is used to form a gel, a matrix of a pores which allow the molecules migrate at different rates.
- 8. Polyacrylamide gel The size of pores is determined by the concentration of acrylamide. The higher the concentration, the smaller the size of pores. Discontinuos Sds-Page consists of two different gels. Stacking gel (top gel)-4% of acrylamide Separating gel (bottom gel)- range from 5 to 15%of acrylamide
- 9. Why polyacrylamide used for a gel? Chemically inert Electrically neutral Hydrophillic Transparent for optical detection
- 10. Preparation of GEL 1. Clean the plates and combs. 2. Set-up the plates on the rack. 3. Pour the separating gel. 4. Pour the stacking gel. 5. Gel storage.
- 11. Process of SDS-PAGE 1. Boil the samples for 10 minutes to completely denatures the proteins. 2. Assemble the gel into the apparatus. 3. Pour the buffer solution into the chamber. 4. Load 20uL of samples into the well. 5. After that, run electrophoresis by connecting the current supplies.
- 12. Visualization of protein bands Visualizes the band under UV light Types of Stains: 1. Coomassie Blue Traditional method requires staining followed by destaining to remove background gel staining. Most common and least sensitive Limited to ~100ng of protein 2. Silver Stain o Most sensitive test o Detection limit: 0.1-1.0ng of protein
- 13. A. Staining band with Western blot; B. Coomassie blue stain; C. Silver stain
- 14. Applications Determine purity of protein samples Determine molecular weight of protein Identifying disulfide bonds between protein Quantifying proteins Blotting applications
- 15. Advantages & disadvantages Advantages Disadvantages Migration is proportional to the molecular weight Poor band resolution due to high alkaline operating pH Highly sensitive test, separates 2% difference in mass Acrylamide gel is potent neurotoxin chemical Require small amount of samples Gel preparation is difficult and require longer time Stable chemically cross- linked gel Highly cost
- 16. Video of SDS-PAGE Procedure Source origin: Labtricks.com
- 17. Conclusion Sds-page is a technique that used to separate proteins according to their molecular size through the gel. Proteins are unfolded and migrate from cathode to anode terminal at different rates. Molecular weight is determined by compare the result with a standard curve of relative motility of standard proteins
- 18. References Introduction to Agarose and Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Matrices, written by Patricia Barril and Silvia Nates Discontinuous polyacrylamide gel eletrophoresis of DNA fragments. Methods in molecular biology. Written by Budowle, B. Allen, 1991.
- 19. Questions 1) SDS-PAGE has been used (a)To analyze different types of proteins in a biological sample (b)To characterize membrane proteins in their native conformation (c)To characterize the enzyme activities in the lysosome (d)To isolate nuclear DNA 2) In an SDS-PAGE experiment, proteins are separated on the basis of their 3) In an SDS-PAGE gel (a) Proteins are denatured by SDS (b)Proteins have the same charge to mass ratio (c)Smaller proteins migrate more rapidly through the gel (d)All the above