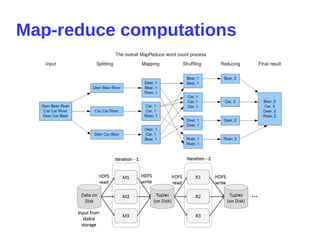
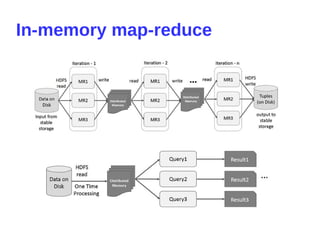
SE2016 BigData Vitalii Bondarenko "HD insight spark. Advanced in-memory Big Data analytics with Microsoft Azure"
- 1. Vitalii Bondarenko Data Platform Competency Manager at Eleks Vitaliy.bondarenko@eleks.com HDInsight: Spark Advanced in-memory BigData Analytics with Microsoft Azure
- 2. Agenda ● Spark Platform ● Spark Core ● Spark Extensions ● Using HDInsight Spark
- 3. About me Vitalii Bondarenko Data Platform Competency Manager Eleks www.eleks.com 20 years in software development 9+ years of developing for MS SQL Server 3+ years of architecting Big Data Solutions ● DW/BI Architect and Technical Lead ● OLTP DB Performance Tuning ● Big Data Data Platform Architect
- 5. Spark Stack ● Clustered computing platform ● Designed to be fast and general purpose ● Integrated with distributed systems ● API for Python, Scala, Java, clear and understandable code ● Integrated with Big Data and BI Tools ● Integrated with different Data Bases, systems and libraries like Cassanda, Kafka, H2O ● First Apache release 2013, this moth v.2.0 has been released
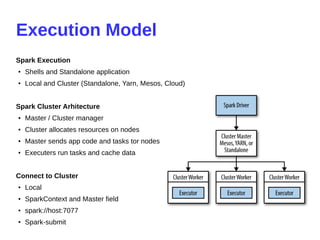
- 8. Execution Model Spark Execution ● Shells and Standalone application ● Local and Cluster (Standalone, Yarn, Mesos, Cloud) Spark Cluster Arhitecture ● Master / Cluster manager ● Cluster allocates resources on nodes ● Master sends app code and tasks tor nodes ● Executers run tasks and cache data Connect to Cluster ● Local ● SparkContext and Master field ● spark://host:7077 ● Spark-submit
- 9. DEMO: Execution Environments ● Local Spark installation ● Shells and Notebook ● Spark Examples ● HDInsight Spark Cluster ● SSH connection to Spark in Azure ● Jupyter Notebook connected to HDInsight Spark
- 10. Spark Core
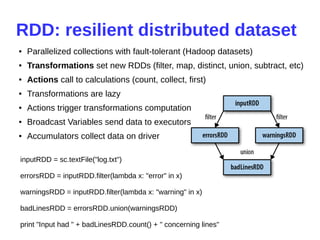
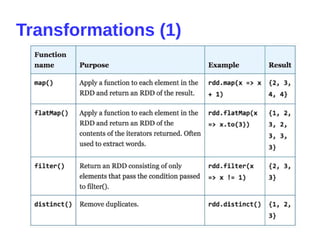
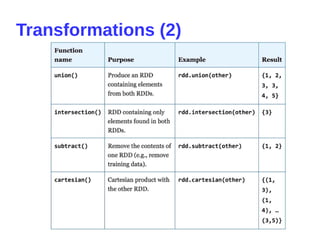
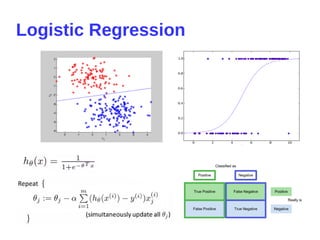
- 11. RDD: resilient distributed dataset ● Parallelized collections with fault-tolerant (Hadoop datasets) ● Transformations set new RDDs (filter, map, distinct, union, subtract, etc) ● Actions call to calculations (count, collect, first) ● Transformations are lazy ● Actions trigger transformations computation ● Broadcast Variables send data to executors ● Accumulators collect data on driver inputRDD = sc.textFile("log.txt") errorsRDD = inputRDD.filter(lambda x: "error" in x) warningsRDD = inputRDD.filter(lambda x: "warning" in x) badLinesRDD = errorsRDD.union(warningsRDD) print "Input had " + badLinesRDD.count() + " concerning lines"
- 12. Spark program scenario ● Create RDD (loading external datasets, parallelizing a collection on driver) ● Transform ● Persist intermediate RDDs as results ● Launch actions
- 13. Persistence (Caching) ● Avoid recalculations ● 10x faster in-memory ● Fault-tolerant ● Persistence levels ● Persist before first action input = sc.parallelize(xrange(1000)) result = input.map(lambda x: x ** x) result.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY) result.count() result.collect()
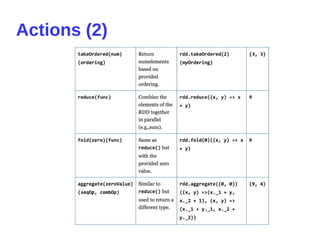
- 16. Actions (1)
- 17. Actions (2)
- 18. Data Partitioning ● userData.join(events) ● userData.partitionBy(100).persist() ● 3-4 partitions on CPU Core ● userData.join(events).mapValues(...).reduceByKey(...)
- 19. DEMO: Spark Core Operations ● Transformations ● Actions
- 20. Spark Extensions
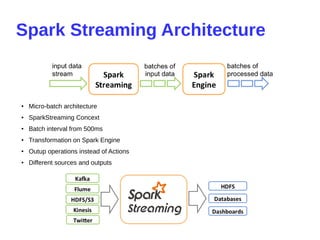
- 21. Spark Streaming Architecture ● Micro-batch architecture ● SparkStreaming Concext ● Batch interval from 500ms ● Transformation on Spark Engine ● Outup operations instead of Actions ● Different sources and outputs
- 22. Spark Streaming Example from pyspark.streaming import StreamingContext ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 1) input_stream = ssc.textFileStream("sampleTextDir") word_pairs = input_stream.flatMap( lambda l:l.split(" ")).map(lambda w: (w,1)) counts = word_pairs.reduceByKey(lambda x,y: x + y) counts.print() ssc.start() ssc.awaitTermination() ● Process RDDs in batches ● Start after ssc.start() ● Output to console on Driver ● Awaiting termination
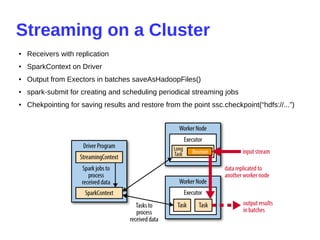
- 23. Streaming on a Cluster ● Receivers with replication ● SparkContext on Driver ● Output from Exectors in batches saveAsHadoopFiles() ● spark-submit for creating and scheduling periodical streaming jobs ● Chekpointing for saving results and restore from the point ssc.checkpoint(“hdfs://...”)
- 24. Streaming Transformations ● DStreams ● Stateless transformantions ● Stagefull transformantions ● Windowed transformantions ● UpdateStateByKey ● ReduceByWindow, reduceByKeyAndWindow ● Recomended batch size from 10 sec val ipDStream = accessLogsDStream.map(logEntry => (logEntry.getIpAddress(), 1)) val ipCountDStream = ipDStream.reduceByKeyAndWindow( {(x, y) => x + y}, // Adding elements in the new batches entering the window {(x, y) => x - y}, // Removing elements from the oldest batches exiting the window Seconds(30), // Window duration Seconds(10)) // Slide duration
- 25. DEMO: Spark Streaming ● Simple streaming with PySpark
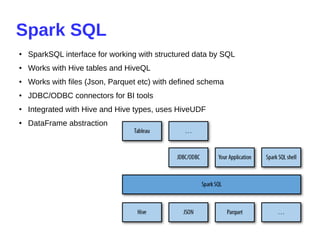
- 26. Spark SQL ● SparkSQL interface for working with structured data by SQL ● Works with Hive tables and HiveQL ● Works with files (Json, Parquet etc) with defined schema ● JDBC/ODBC connectors for BI tools ● Integrated with Hive and Hive types, uses HiveUDF ● DataFrame abstraction
- 27. Spark DataFrames ● hiveCtx.cacheTable("tableName"), in-memory, column-store, while driver is alive ● df.show() ● df.select(“name”, df(“age”)+1) ● df.filtr(df(“age”) > 19) ● df.groupBy(df(“name”)).min() # Import Spark SQLfrom pyspark.sql import HiveContext, Row # Or if you can't include the hive requirementsfrom pyspark.sql import SQLContext, Row sc = new SparkContext(...) hiveCtx = HiveContext(sc) sqlContext = SQLContext(sc) input = hiveCtx.jsonFile(inputFile) # Register the input schema RDD input.registerTempTable("tweets") # Select tweets based on the retweet CounttopTweets = hiveCtx.sql("""SELECT text, retweetCount FROM tweets ORDER BY retweetCount LIMIT 10""")
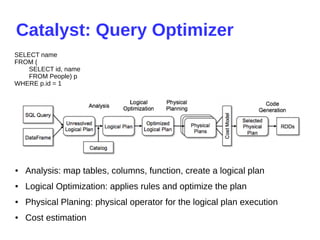
- 28. Catalyst: Query Optimizer ● Analysis: map tables, columns, function, create a logical plan ● Logical Optimization: applies rules and optimize the plan ● Physical Planing: physical operator for the logical plan execution ● Cost estimation SELECT name FROM ( SELECT id, name FROM People) p WHERE p.id = 1
- 29. DEMO: Using SparkSQL ● Simple SparkSQL querying ● Data Frames ● Data exploration with SparkSQL ● Connect from BI
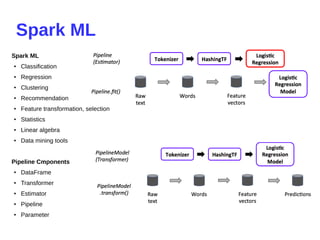
- 30. Spark ML Spark ML ● Classification ● Regression ● Clustering ● Recommendation ● Feature transformation, selection ● Statistics ● Linear algebra ● Data mining tools Pipeline Cmponents ● DataFrame ● Transformer ● Estimator ● Pipeline ● Parameter
- 32. DEMO: Spark ML ● Training a model ● Data visualization
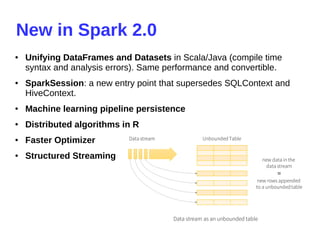
- 33. New in Spark 2.0 ● Unifying DataFrames and Datasets in Scala/Java (compile time syntax and analysis errors). Same performance and convertible. ● SparkSession: a new entry point that supersedes SQLContext and HiveContext. ● Machine learning pipeline persistence ● Distributed algorithms in R ● Faster Optimizer ● Structured Streaming
- 34. New in Spark 2.0 spark = SparkSession .builder() .appName("StructuredNetworkWordCount") .getOrCreate() # Create DataFrame representing the stream of input lines from connection to localhost:9999 lines = spark .readStream .format('socket') .option('host', 'localhost') .option('port', 9999) .load() # Split the lines into words words = lines.select( explode( split(lines.value, ' ') ).alias('word') ) # Generate running word count wordCounts = words.groupBy('word').count() # Start running the query that prints the running counts to the console query = wordCounts .writeStream .outputMode('complete') .format('console') .start() query.awaitTermination() windowedCounts = words.groupBy( window(words.timestamp, '10 minutes', '5 minutes'), words.word ).count()
- 35. HDInsight: Spark
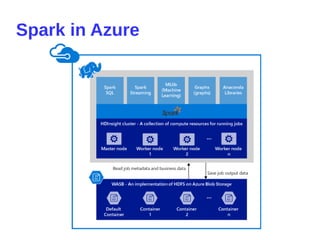
- 36. Spark in Azure
- 37. HDInsight benefits ● Ease of creating clusters (Azure portal, PowerShell, .Net SDK) ● Ease of use (noteboks, azure control panels) ● REST APIs (Livy: job server) ● Support for Azure Data Lake Store (adl://) ● Integration with Azure services (EventHub, Kafka) ● Support for R Server (HDInsight R over Spark) ● Integration with IntelliJ IDEA (Plugin, create and submit apps) ● Concurrent Queries (many users and connections) ● Caching on SSDs (SSD as persist method) ● Integration with BI Tools (connectors for PowerBI and Tableau) ● Pre-loaded Anaconda libraries (200 libraries for ML) ● Scalability (change number of nodes and start/stop cluster) ● 24/7 Support (99% up-time)
- 38. HDInsight Spark Scenarious 1. Streaming data, IoT and real-time analytics 2. Visual data exploration and interactive analysis (HDFS) 3. Spark with NoSQL (HBase and Azure DocumentDB) 4. Spark with Data Lake 5. Spark with SQL Data Warehouse 6. Machine Learning using R Server, Mllib 7. Putting it all together in a notebook experience 8. Using Excel with Spark
- 39. Q&A