Sect 9.2
- 1. 6 th Grade Science Chapter 9 Sun-Earth-Moon System Notes Section 9.2
- 2. If the Moon rotates on its axis why can’t we see the back side of the moon? The moon takes 29.5 days to make one rotation on its axis. The moon takes 29.5 days to make one revolution around the Earth. What is the Moon’s most obvious effect on Earth? The Moon’s most obvious effect on Earth is the ocean tides. Key Questions 1 The Tadpole Galaxy
- 4. Synchronous rotation of the moon
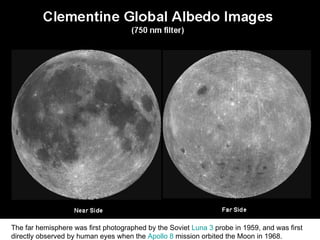
- 5. The far hemisphere was first photographed by the Soviet Luna 3 probe in 1959, and was first directly observed by human eyes when the Apollo 8 mission orbited the Moon in 1968.
- 7. Bay of Fundy - Canada
- 8. What is a new Moon? A new Moon is when the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun. The Moon is dark and rises and sets with the Sun. What is a full Moon? A full Moon is when the Earth is between the Moon and the Sun. The Moon is completely bright and rises when the Sun sets. Key Questions 2 The Sombrero Galaxy
- 10. Full Moon Rising
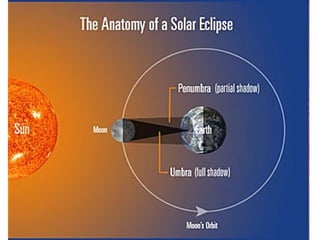
- 11. What are the phases of the Moon? New, Waxing crescent, 1 st quarter, Waxing gibbous, Full, Waning gibbous, 3 rd quarter, Waning crescent. What causes an eclipse to occur? Eclipses occur when Earth or the Moon temporarily blocks the sunlight from reaching the other- Solar Eclipse and Lunar Eclipse. Key Questions 3
- 16. What is an umbra and prenumbra? The umbra is the darkest part of the moon’s shadow. The prenumbra is a lighter part of the moon’s shadow. What are the Moon’s surface features? The Moon has craters from impacts with meteorites. It also has dark, flat regions called maria formed from igneous rock. Key Questions 4
- 19. Project Apollo
- 20. Explain how the Sun, Moon, and Earth are positioned relative to each other during a new moon and how this alignment changes to produce a full moon. Describe what phase the Moon must be in to have a lunar eclipse. A solar eclipse. Define the terms umbra and penumbra and explain how they relate to eclipses. Explain why lunar eclipses are more common than solar eclipses and why so few people ever have a chance to view a total solar eclipse. What do the surface features and their distribution on the Moon’s surface tell you about its history? Questions Section 9.2