Session 1 PMP 4th edition
- 1. Engineer Mohamed Esmat Abdelrazek PMP Project Management professional
- 2. PMP CertificatePMBOK 4th Edition
- 4. Project Framework & initiation
- 5. ?What is a project Temporary endeavor undertaken to create a uniqe service or product or result Temporary: means definite beginning and definite end Uniqe :different design, different location , different circumstance …etc Progressive elaboration: “continuously improving and detailing a plan as more detailed and specific information and more accurate estimates become available as the project progresses,
- 6. operationproject 1-temporary 1-permenant 2-unique 2-repetitive VS example example Constructing a building Production line
- 7. ?What is Project Management the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements
- 8. Project manager Personal skills performance knowledge
- 9. :Who is Stakeholder ? Stakeholders are the people involved in or affected by project activities
- 10. • stakeholders - Customer (owner) - Sponsor - consultant - Consumer (doctors) - Government authorities - Suppliers - Project team Hospital Construction Project
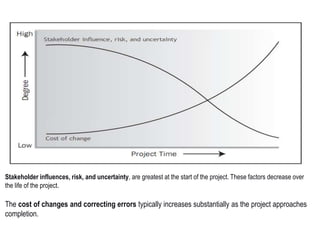
- 12. CHARACTERISTICS OF PROJECT LIFE CYCLE • Cost and staffing levels are low at the start, peak as the work is carried out, and drop rapidly as the project draws to a close.
- 13. Stakeholder influences, risk, and uncertainty, are greatest at the start of the project. These factors decrease over the life of the project. The cost of changes and correcting errors typically increases substantially as the project approaches completion.
- 14. Project Management Process Groups Mapped to the Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle
- 15. - The Process Groups are seldom either discrete or one-time events; they are overlapping activities that occur throughout the project.
- 16. Process Interactions •Inputs • Document s or documentable items that will be acted upon Tools & Techniques Mechanisms applied to inputs to create output Outputs Document s or documentable items that are a result of a process
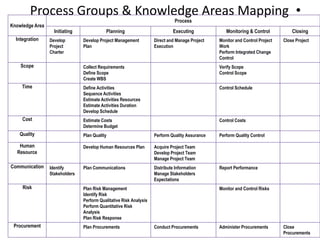
- 17. •Process Groups & Knowledge Areas Mapping Knowledge Area Process Initiating Planning Executing Monitoring & Control Closing Integration Develop Project Charter Develop Project Management Plan Direct and Manage Project Execution Monitor and Control Project Work Perform Integrated Change Control Close Project Scope Collect Requirements Define Scope Create WBS Verify Scope Control Scope Time Define Activities Sequence Activities Estimate Activities Resources Estimate Activities Duration Develop Schedule Control Schedule Cost Estimate Costs Determine Budget Control Costs Quality Plan Quality Perform Quality Assurance Perform Quality Control Human Resource Develop Human Resources Plan Acquire Project Team Develop Project Team Manage Project Team Communication Identify Stakeholders Plan Communications Distribute Information Manage Stakeholders Expectations Report Performance Risk Plan Risk Management Identify Risk Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis Plan Risk Response Monitor and Control Risks Procurement Plan Procurements Conduct Procurements Administer Procurements Close Procurements
- 18. • Projects are means of – Achieving organization’s strategic plan. • Projects are result of one or more of the following : Market demand Strategic opportunity/business need Legal requirements Ecological Impacts Social need Projects and Strategic Planning
- 20. :ManagementProgram Group of related Projects in a coordinated way to obtain benefits and control :Portfolio Management collection of projects or programs and other work that are grouped together to facilitate effective management of that work to meet strategic business objectives
- 21. Project Management Office (PMO) * A department that centralizes the management of projects. Roles of PMO •Project Support: Provide project management guidance to project managers in business units. •Project Management Process/Methodology: Develop and implement a consistent and standardized process. •Training: Conduct training programs or collect requirements for an outside company A primary function of a PMO is to support project managers in a variety of ways
- 22. Thank you