Session rural marketing final
- 2. Defining Rural India Organisation Definition Limitations • rural not defined NSSO (Census) Population less than 5000 • Population density < 400 / Sq Km • 75 percent of the male working population is engaged in agriculture •No Municipal corporation / board Planning Commission • Towns upto 15,000 population are considered Town characteristics rural not defined
- 3. Cont’d LG Electronics All places other than the 7 metros Only clarifies what are the cities NABARD All locations with a population upto 10, 000 considered “ rural” Village & town characteristics not defined Sahara Commercial establishments located in areas servicing less than 1000 population Population characteristics unknown FMCG COS Any area with primarily agricultural based occupation and with a population of less than 20,000 as rural Source: The Rural Marketing Book- Text & Practice, Kashyap. P and Raut. S ( 2007)
- 4. (Cont.) Durables & Agri-input cos Population upto 20,000 is rural Marketing Parlance Organised distribution & media reach ends Urban, Rural & Rurban Jha, 2003 Rurban being the overlap between urban & rural
- 5. Size of the market Largely Untapped Too crowded Urban Market Income on the rise/disposable income Reasons for Going Rural BOP_Rural.wmv Income from other than agriculture Great success stories HLL 50% Colgate 50% LG 50% Asian Paints 60% Dabur 40% Videocon 40% Cadbury’s 25% Hero Hona 40% Sorce ORG Marg and Fransis Kanoi
- 6. Encouraging Indicators/Initiatives for Rural Market Growth Scientific methods – major impetus to Production of food grains Initiatives taken by banks for more branches and Kisan credit card to buy seeds, fertilizers, consumer goods on installment basis Reputed Companies helping in changing lifestyles – Levers Britania ,Dabur, LG, Honda,Videocon Government Policies – White Revolution – Milk products Yellow Revolution (poultry and edible oils); Blue Revolution – Aqua culture Employment Schemes – JRY(Jawahar Rojgar Yojna, PMRY,Small Industries Training, Rural Electrification, Spend on Health and Sanitation, Medical and Health, Primary Education, Credit card for farmers; Waiver of Loans Initiatives by leading organization in spreading awareness Hindustan Levels Shakti, ITC Reliance etc; Media creating an impact-creating awareness levels
- 7. Low per capita income/ Low disposable income Inadequate fixed income (daily wages) PROBLEMS IN RURAL MARKETING Majority – depends on Agricultural Income Acute dependence on monsoon Consumption linked to harvest Infrastructure problems Roads, power Low awareness Too many languages Communication- difficult & expensive Geographic Spread Digging for Diamond
- 8. Profile of the Rural Consumer >Low Literacy Level >Low Income Level p.doc >Massive Geographic Spread & heterogeneous market Urban population concentrated 3200 cities town Rural scattered over 630000 villages >Reference Group Health Workers Doctors Teachers Panchayat Members Rural Bank Managers District Managers Occupation – Principal Farming Trading Handicrafts Cattle & Poultry Farming >Media Habits Fond of music T.V Radio Video Films Generally they have a lot of reservation/inhibition rigid in their behaviour
- 9. RURAL CONSUMER CLASS The Affluent Class The Middle Class The Poor RURAL CONSUMER BEHAVIOR How does an individual decide to spread his Available resources (time,money effort) on Consumption-related products. That is – what they buy why they buy when they buy where they buy it how often they buy it how often they use it Very Rich Well Off Aspirant Poor Climbers
- 10. Simple Model of Rural Consumer Behaviour Need Recognition Pre Purchase Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Decision Post purchase behaviour
- 11. Factors that Influence Rural Behaviour Attitude Stimuli Inputs to any senses Products Package Commercials Brand image Reference Information cues about the characteristics of the product Exposure Eg IFB had not adequately educated farmers about the washing machine -they thought It was a churn for making large quantities of lassi (prosperous village of Punjab) >Consumer belief Consumer feelings Perception Depends on Interpretation Iodex – muscular pain reliever used on animals after hard days work in MP Godrej hair dye on Buffaloes To make them look better in Village haats in Raichur
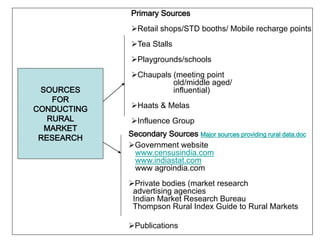
- 13. Primary Sources Retail shops/STD booths/ Mobile recharge points Tea Stalls Playgrounds/schools SOURCES FOR CONDUCTING RURAL MARKET RESEARCH Chaupals (meeting point old/middle aged/ influential) Haats & Melas Influence Group Secondary Sources Major sources providing rural data.doc Government website www.censusindia.com www.indiastat.com www agroindia.com Private bodies (market research advertising agencies Indian Market Research Bureau Thompson Rural Index Guide to Rural Markets Publications
- 14. Thomson Rural Market Index (TRMI): • Hindustan Thompson Associates ltd. developed TRMI – guide to segment markets in the rural areas in 1972 – improved it in 1986, they compiled a data out of 335 districts based on 10 variables. – Thomson Rural market Index.doc
- 15. SEGMENTATION Very Varied –hence proper segmentation very essential Geographic: Region Village size Climate North, East, West and South Demographic Age Family Size Gender Income Occupation Education Caste Psychographics (consists of psychological: sociology: anthropological) Lifestyle Rigid ,changing attitude, urban influence Personality Authoritarian, Ambitious Behavioral Occasions Regular, special occasion Benefits User status regular user, first time user, non user Usage rate Light, medium, heavy Loyalty None, medium, strong Attitude to Product ( positive, negative, hostile) Different variables could be used.. multilevel segmentation
- 16. Approaches for segmenting the rural markets • Size of village Population (ORG-MARG) – Class I villages (>5,000) – Class II villages (1,000-5,000) – Class III villages (<1,000) • Based on location w.r.t nearby town – Villages nearby Urban Centres – Villages in Developing Districts – Immobile & self-sufficient Asiatic villages • Based on size of Farmland – – – – – Marginal farmer (upto 1 hectares) Small farmer (1 hectares-2 hectares) Small & Marginal farmers (2 hectares-4 hectares) Medium Farmer (4-10 hectares) Large Farmer (> & equal to 10 hectares)
- 17. Approaches for segmenting the rural markets (cont.) • Based on Sociological Characteristics – – – – – – • • Proprietors of Land Rich Farmers Small & Marginal Farmers Tenant Farmers Agricultural Labourers Artisans & Others Oglivy Rural has divided India into 56 distinct socio-cultural regions Income – Rural rich/Around Urban area/Above poverty line/below poverty line • NCAER – Destitutes (<16,000), Aspirants (16,000-22,000);Climbers (Till 45,000); Consumers (Till 2,15,000) & Very rich
- 18. Approaches for segmenting the rural markets (cont.) • Based on Development Level – R1/R2/R3/R4product categories & R1.doc • Based on Age Group Perspectives – Pre-Independence – Pain of Nation Building – Pain of Liberalization (1985 onwards) – Liberalization Children (1990 onwards) – Millennium Children (1997 onwards)
- 19. DEVELOPMENTAL MARKETING Developmental marketing is a process through which awareness is created >could be demonstration >could be presentation >Free samples >could be through eg tie up with Bank tie up with Petrol/Diesel pumps (Hyundai did with IOC and PNB and SBI subsidiaries >30% sale of Hyndai from Rural/Semi Urban areas) Awareness Trial Purchase Post-Purchase Satisfaction Colgate – program Operation Jagruti Switch from Charcoal to Colgate tooth powder HLL Free samples of Lifebuoy Cavin Kare – Free sample of Chik Champoo Marico Industries – Parachute coconut oil “Sudhata ki pehchan” –smell to differentiate between real and spurious
- 21. Rural Product Product to be marketed with the requirements of the Rural Consumer should not be an extension of urban offerings (Philips launched Free Power Radio – does not require Battery/electricity you wind it with a lever and radio runs For approximately 30 min. FMCG (HLL, Dabur, Marico, Colgate=Palmolive Coke, Pepsi) Consumer Durables TV ,Fridge, Fan, Presssure Cooker, Cycle, Two wheelers, Sewing machines, watch, mixer grinder, radio, music system, Fans, Washing machines (Philips, LG, Videocon, Onida ) Services Telecom, Banking, Health care ,Insurance (Airtel, BSNL, SBI, PNB,Dena bank,) Classification Of Rural Products Product Life Cycle (PLC) Agri-inputs Seeds, pesticides, tractors (Rallis India, Bayer,) Take Off Launch Maturity Decline
- 22. Corporate Responses to Fakes • Look-alikes- Spell-alikes & Duplicates • Prices range from MRP to 60 % of MRP • Margins range from 60 % to 300 % • Legal action – awareness programmes – New Package Development
- 24. RURAL DISTRIBUTION Physical Distribution Channel of Distribution PHYSICAL DISTRIBUTION Transportation Warehousing Communication Transportation Railways, Roads ,Waterways, Animals Communication ITC using internet, Mobile users by fisherman Warehousing (Three Tier Rural Warehousing Set Up) Central/State Warehousing Cooperatives Rural Godowns
- 25. Levels of Distribution Level Partner Location 1 Company Depot/ C & FA National/ State level 2 Distributor/ Van Operator/ Super Stockist/ Rural Distributor District level 3 Sub Distributor/ retail Tehsil HQ, towns and Stockist/ sub large villages stockist/star seller 4 Wholesaler Feeder towns, large villages, haats 5 Retailer Villages, haats The Great Rural Mall Hindi.mpg
- 26. Distribution Adaption( Indicative) • • • • Hub and Spoke Model, Example: Coca Cola Use of Affinity groups, Example: Project Shakti Haat Activation, Example: Colgate Syndicated distribution, Example: Cavin Care & Amrutanjan • Use of marketing co-operatives, Example: Warna Bazaar in Rural Areas • Mobile traders, Example: FMCG companies ITC e-Chaupal.wmv
- 27. TRAITS OF A RURAL SALESPERSON Hardworking Have Empathy Enthusiastic Common to both Urban & Rural Sales person Perseverance Knowledge Attitude Skills Additional traits for making it Big in Rural Areas Willingness to work in Rural Areas Adopting to cultural differences Down to earth approach Fluent in local language Developmental approach – Create not only Communicate
- 28. RURAL COMMUNICATION Effective Communication goes a long way in establishing the right Messages and thereby more interaction with Potential Customers Communication, however, is not complete if there is no feedback It is very important to re enforce messages in Rural areas Factors Affecting Rural Communication Literacy level Media Habits Traditional approach High resistance – more so initially Lavish at occasions (eg Marriage) Purchasing power also depending on weather- the crops Inequitable distribution of wealth Too many languages Culture
- 29. Promotion- Adaptations for Rural Markets Conventional Non- Conventional Personalised Television Haat and Mela Direct mailer Radio Folk Media( puppet and magic show) POS (demonstration, leaflet) Press Video Van Word of mouth Cinema Mandi Interpersonal communication Outdoor: Wall Painting, Hoarding Animator
- 30. Melas & Haats Melas 1. 25,000 melas 2. Companies can concentrate on the top 100 melas Haat 1. Periodic markets located in larger villages(> 40,000) 2. 10 – 50 villages are serviced 3. Pushkar Mela in Rajasthan 3. Sunday markets are most popular 4. Organised by the state 4. Average number of outlets is 315 veterinary department 5. Product sales, promotion, demonstration and database generation 6. Cultural activities and rural sports and average daily sales is about Rs 2 lakhs 5. Traders participate in at least 4 haats 6. 81 percent of the visitors are repeat customers