Share point 2013 and sql server 2012 what to choose
- 1. SharePoint 2013 & SQL Server 2012 A talk about what SQL Server version you want to use from a SharePoint 2013 perspective
- 3. Introduction
- 4. Our talk of today…
- 5. What version of SQL Server?
- 6. What version of SQL Server?
- 7. What version of SQL Server?
- 8. What version of SQL Server?
- 9. Agenda The agenda of the presentation
- 10. Agenda
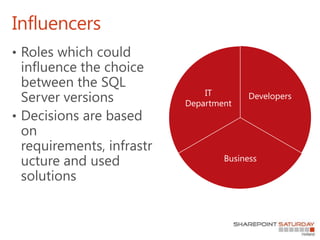
- 11. The choices you have What are the requirements for SharePoint 2013?
- 12. The choices you have SQL Server 2008 • Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 or Windows Server 2012 and higher • Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 • All 64 bit SQL Server 2012 • Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 or Windows Server 2012 and higher • Microsoft SQL Server 2012 • All 64 bit
- 13. Dependencies What has influence on the choice between the two SQL Server versions?
- 16. Infrastructure
- 18. Knowledge level
- 19. Costs
- 20. And then?
- 21. Software level The advantages of SQL Server 2012 at software level
- 23. Advantages – Mixed Licenses
- 24. Infrastructure level The advantages of SQL Server 2012 at infrastructure level
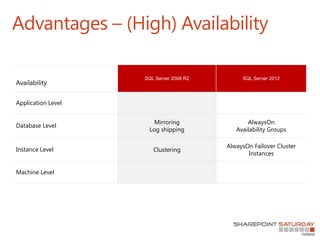
- 25. Availability Application Level Database Level Mirroring Log shipping AlwaysOn Availability Groups Instance Level Clustering AlwaysOn Failover Cluster Instances Machine Level Advantages – (High) Availability
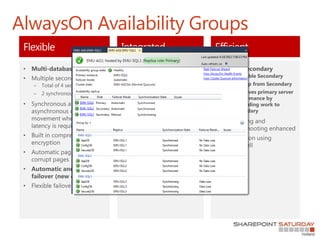
- 26. AlwaysOn
- 29. AlwaysOn SQL Failover Cluster Instances
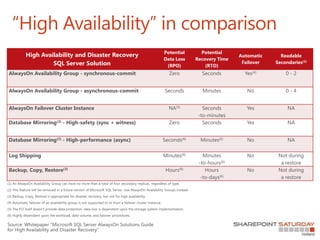
- 30. “High Availability” in comparison High Availability and Disaster Recovery SQL Server Solution Potential Data Loss (RPO) Potential Recovery Time (RTO) Automatic Failover Readable Secondaries(1) AlwaysOn Availability Group - synchronous-commit Zero Seconds Yes(4) 0 - 2 AlwaysOn Availability Group - asynchronous-commit Seconds Minutes No 0 - 4 AlwaysOn Failover Cluster Instance NA(5) Seconds -to-minutes Yes NA Database Mirroring(2) - High-safety (sync + witness) Zero Seconds Yes NA Database Mirroring(2) - High-performance (async) Seconds(6) Minutes(6) No NA Log Shipping Minutes(6) Minutes -to-hours(6) No Not during a restore Backup, Copy, Restore(3) Hours(6) Hours -to-days(6) No Not during a restore Source: Whitepaper “Microsoft SQL Server AlwaysOn Solutions Guide for High Availability and Disaster Recovery”
- 31. Advantages – Cross-Cluster Migration
- 32. Advantages – Windows Azure Blob Storage
- 33. Advantages – Windows Azure Blob Storage
- 34. Advantages – BLOB storage
- 35. Functional level The advantages of SQL Server 2012 at functional level
- 36. Advantages – Report Server
- 37. Advantages – Power Pivot
- 38. Advantages – Power View
- 39. Wrap up
- 40. Wrap up
- 41. THANK YOU
Editor's Notes
- There is already sql 2014 ;-) http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/sqlserver/sql-server-2014.aspx
- Hardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2012http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143506.aspxHardware and Software Requirements for Installing SQL Server 2008 R2http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143506(v=sql.105).aspxHardware and software requirements for SharePoint 2013http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc262485.aspx#section4
- http://mmman.itgroove.net/2013/05/sharepoint-2013-access-services/
- Supporthttp://support.microsoft.com/lifecycle/?LN=en-ie&C2=1044SQL Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 2Support ends 12 months after the next service pack releases or at the end of the product's support lifecycle, whichever comes first. For more information, please see the service pack policy at http://support.microsoft.com/lifecycle/#ServicePackSupport.LicensesSQL Server 2012 Standard - Core-Based or Server+CALSQL Server 2012 Business Intelligence - Server+CALSQL Server 2012 Enterprise - Core-BasedLook for SQL_Server_2012_Licensing_Reference_Guide.pdfMicrosoft to move to license-by-core for SQL Server 2012ratio of 4 cores per physical processor the end cost for you shouldn’t changehttp://www.networkworld.com/community/blog/microsoft-move-license-core-sql-server-2012xVelocityxVelocity is Microsoft’s family of in-memory and memory-optimized data management technologies in SQL Server 2012.The xVelocity columnstore index feature is memory-optimized because it stores data in memory in a special representation built for fast processing, rather than simply in disk page images, like traditional database systems use
- Much improved BI features such as Power View. Power View is a graphical interface which sits on-top of previously structured data. Being based on Silverlight, it is used to significantly enhance the appearance of reports. It’s quite intuitive. It can cross-reference related data. So if your report is structured by day, you can quickly reorganize it to be by person or by geographical area.Reporting Services can be directly accessed within SharePoint 2013. It runs 30-60% faster going thru SharePoint. Reporting Services for 2012 can automatically alert users when data underlying a report has changed. So if you’re using a report that’s a week old, and sales have slipped 20% since last week, RS can send an alert before you unknowing use it.Data in SharePoint (SQL, Excel, PowerPoint, RS) can be presented in asingle dashboard.Because of enhancements in both SQL Server 2012, and in SharePoint 2013, report data is tightly integrated from initial storage to final presentation. So, a user can retrieve SQL Server data into an Excel spreadsheet, structure it via PowerPivot, create a report displaying that data via Power View and display it to PowerPoint. All without leaving SharePoint. Appropriately structured data can have its organization changed in PowerPoint, even if the data is still in SQL – that’s power, err Power View.
- WSFC = Windows Server Failover ClusteringSQL Server 2012 AlwaysOnhttps://www.simple-talk.com/sql/database-administration/sql-server-2012-alwayson/Many people believe AlwaysOn is the best new feature of 2012. Always on is like mirroring on steroids. In fact, mirroring is “deprecated” in 2012. Nasty word that. Things do age out; I think I just mentioned that. Before 2012, the mirror copy of a mirrored database could not be read. It just existed. You almost had to rely on System Manager to prove it even existed. If your system required more than one database to function, then you might find out you were having to access two different databases in two different servers to do your processing. Failovers were by individual databases. So even if you created more than one mirror, if it failed over and the related mirror didn’t failover, you might be offline while you manually failed over the second mirror. In this case, Heaven help you if you hadn’t setup your logins and permissions properly on two separate servers.AlwaysOn (AO for short) enables you to have up to four read-only copies of the primary databases. Presumably these might be geographically dispersed. AO enables you to combine multiple databases in a single failover group, called an Availability Group (awkward to say, but nice to have.) You can even choose between having Synchronous vs Asynchronous connections, but there I go again, digressing. We’ll save that for another Byte…
- Answering Questions with the AlwaysOn Dashboardhttp://www.sqlskills.com/blogs/joe/answering-questions-with-the-alwayson-dashboard/
- AlwaysOn Failover Cluster Instances (SQL Server)http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189134.aspx
- RPO = Recovery Point ObjectiveRTO = Recovery Time Objective
- Cross-Cluster Migration of AlwaysOn Availability Groups for OS UpgradeBeginning with SQL Server 2012 SP1, AlwaysOn Availability Groups supports cross-cluster migration of availability groups for deployments to a new Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC) cluster. A cross-cluster migration moves one availability group or a batch of availability groups to the new, destination WSFC cluster with minimal downtime. The cross-cluster migration process enables you to maintain your service level agreements (SLAs) when upgrading to a Windows Server 2012 cluster. SQL Server 2012 SP1 (or a later version) must be installed and enabled for AlwaysOn on the destination WSFC cluster. The success of a cross-cluster migration depends on thorough planning and preparation of the destination WSFC cluster. For more information, see the "Cross-Cluster Migration of AlwaysOn Availability Groups for OS Upgrade" white paper. This paper will be posted in October 2012 on the Microsoft White Papers (SQL Server 2012) download page.
- SQL Server Backup and Restore with Windows Azure Blob Storage Servicehttp://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj919148.aspxThis feature released in SQL Server 2012 SP1 CU2, enables SQL Server backup and restore directly to the Windows Azure Blob service. This feature can be used to backup SQL Server databases on an on-premises instance or an instance of SQL Server running a hosted environment such as Windows Azure Virtual Machine. Backup to cloud offers benefits such as availability, limitless geo-replicated off-site storage, and ease of migration of data to and from the cloud. In this release, you can issue BACKUP or RESTORE statements by using tsql or SMO. Back up to or restore from the Windows Azure Blob storage service by using SQL Server Management Studio Backup or Restore Wizard is not available in this release.Flexible, reliable, and limitless off-site storage: Storing your backups on Windows Azure Blob service can be a convenient, flexible, and easy to access off-site option. Creating off-site storage for your SQL Server backups can be as easy as modifying your existing scripts/jobs. Off-site storage should typically be far enough from the production database location to prevent a single disaster that might impact both the off-site and production database locations. By choosing to geo replicate the Blob storage you have an extra layer of protection in the event of a disaster that could affect the whole region. In addition, backups are available from anywhere and at any time and can easily be accessed for restores.Backup Archive: The Windows Azure Blob Storage service offers a better alternative to the often used tape option to archive backups. Tape storage might require physical transportation to an off-site facility and measures to protect the media. Storing your backups in Windows Azure Blob Storage provides an instant, highly available, and a durable archiving option.No overhead of hardware management:There is no overhead of hardware management with Windows Azure services. Windows Azure services manage the hardware and provide geo-replication for redundancy and protection against hardware failures.Currently for instances of SQL Server running in a Windows Azure Virtual Machine, backing up to Windows Azure Blob storage services can be done by creating attached disks. However, there is a limit to the number of disks you can attach to a Windows Azure Virtual Machine. This limit is 16 disks for an extra large instance and fewer for smaller instances. By enabling a direct backup to Windows Azure Blob Storage, you can bypass the 16 disk limit.In addition, the backup file which now is stored in the Windows Azure Blob storage service is directly available to either an on-premises SQL Server or another SQL Server running in a Windows Azure Virtual Machine, without the need for database attach/detach or downloading and attaching the VHD.Cost Benefits: Pay only for the service that is used. Can be cost-effective as an off-site and backup archive option. See the Windows Azure Billing Considerations section for more information and links.
- SQL Server Backup and Restore with Windows Azure Blob Storage Servicehttp://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj919148.aspxThis feature released in SQL Server 2012 SP1 CU2, enables SQL Server backup and restore directly to the Windows Azure Blob service. This feature can be used to backup SQL Server databases on an on-premises instance or an instance of SQL Server running a hosted environment such as Windows Azure Virtual Machine. Backup to cloud offers benefits such as availability, limitless geo-replicated off-site storage, and ease of migration of data to and from the cloud. In this release, you can issue BACKUP or RESTORE statements by using tsql or SMO. Back up to or restore from the Windows Azure Blob storage service by using SQL Server Management Studio Backup or Restore Wizard is not available in this release.Flexible, reliable, and limitless off-site storage: Storing your backups on Windows Azure Blob service can be a convenient, flexible, and easy to access off-site option. Creating off-site storage for your SQL Server backups can be as easy as modifying your existing scripts/jobs. Off-site storage should typically be far enough from the production database location to prevent a single disaster that might impact both the off-site and production database locations. By choosing to geo replicate the Blob storage you have an extra layer of protection in the event of a disaster that could affect the whole region. In addition, backups are available from anywhere and at any time and can easily be accessed for restores.Backup Archive: The Windows Azure Blob Storage service offers a better alternative to the often used tape option to archive backups. Tape storage might require physical transportation to an off-site facility and measures to protect the media. Storing your backups in Windows Azure Blob Storage provides an instant, highly available, and a durable archiving option.No overhead of hardware management:There is no overhead of hardware management with Windows Azure services. Windows Azure services manage the hardware and provide geo-replication for redundancy and protection against hardware failures.Currently for instances of SQL Server running in a Windows Azure Virtual Machine, backing up to Windows Azure Blob storage services can be done by creating attached disks. However, there is a limit to the number of disks you can attach to a Windows Azure Virtual Machine. This limit is 16 disks for an extra large instance and fewer for smaller instances. By enabling a direct backup to Windows Azure Blob Storage, you can bypass the 16 disk limit.In addition, the backup file which now is stored in the Windows Azure Blob storage service is directly available to either an on-premises SQL Server or another SQL Server running in a Windows Azure Virtual Machine, without the need for database attach/detach or downloading and attaching the VHD.Cost Benefits: Pay only for the service that is used. Can be cost-effective as an off-site and backup archive option. See the Windows Azure Billing Considerations section for more information and links.
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb500435FileStream data type. Most SharePoint data is in the form of Binary Large Objects, blobs for short. Blobs are far and away the fastest way to store documents. In effect, it’s just copying a file to a disk. You don’t have to format it or create rows or keep indexes like you do with data. Until now, though, the problem with blobs is that they were o/s files which were added by SQL. SQL could always find them, but then so could anyone else with the appropriate permissions. And they could read them. This gave DBAs and system administrators much insecurity. Filestreams are handled differently. They are still just files, but they are stored with the SQL Server shell and can only be accessed by going through SQL Security. So they are very secure. FileStream datatypes should dramatically speed up document insertion and retrieval
- Reporting ServicesReporting Services can be directly accessed within SharePoint 2013. It runs 30-60% faster going thru SharePoint. Reporting Services for 2012 can automatically alert users when data underlying a report has changed. So if you’re using a report that’s a week old, and sales have slipped 20% since last week, RS can send an alert before you unknowing use it.Data in SharePoint (SQL, Excel, PowerPoint, RS) can be presented in asingle dashboard.
- What’s new in PowerPivot in Excel 2013http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/excel-help/whats-new-in-powerpivot-in-excel-2013-HA102893837.aspx#_Toc335818194SharePoint 2013 PowerPivot Component Overviewhttp://www.sharepointdoug.com/2013/04/powerpivot-component-overview.htmlExploring PowerPivot for Exel and PowerView in SQL Server 2012http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODvV9ku-R58Reporting Services can be directly accessed within SharePoint 2013. It runs 30-60% faster going thru SharePoint. Reporting Services for 2012 can automatically alert users when data underlying a report has changed. So if you’re using a report that’s a week old, and sales have slipped 20% since last week, RS can send an alert before you unknowing use it.Data in SharePoint (SQL, Excel, PowerPoint, RS) can be presented in asingle dashboard.Filter data when importing. You can import data in both Excel and PowerPivot, but when importing data in PowerPivot, you can filter out unnecessary data to import just a subset.Rename tables and columns as you import data in PowerPivot.Manage the model and create relationships using drag and drop in the Diagram View.Apply formatting (to be used in Power View and PivotTable reports).Define your own calculated fields to use throughout a workbook.Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to use in PivotTables.Create user-defined hierarchies to use throughout a workbook.Define perspectives.Author your own calculations by writing advanced formulas that use the Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) expression language.Use other more advanced data and modeling operations.
- Demohttps://spdemoportiva.sharepoint.com/sites/BICenter/Dashboards/Customer%20Satisfaction%20Dashboard.aspxUsername: admin@spdemoportiva.onmicrosoft.com Password: pass@word1
- Much improved BI features such as Power View. Power View is a graphical interface which sits on-top of previously structured data. Being based on Silverlight, it is used to significantly enhance the appearance of reports. It’s quite intuitive. It can cross-reference related data. So if your report is structured by day, you can quickly reorganize it to be by person or by geographical area.https://businessintelligencedemoportal.com/sites/contosoenergy/SitePages/pvrsample.aspxBecause of enhancements in both SQL Server 2012, and in SharePoint 2013, report data is tightly integrated from initial storage to final presentation. So, a user can retrieve SQL Server data into an Excel spreadsheet, structure it via PowerPivot, create a report displaying that data via Power View and display it to PowerPoint. All without leaving SharePoint. Appropriately structured data can have its organization changed in PowerPoint, even if the data is still in SQL – that’s power, err Power View.
- Demohttps://spdemoportiva.sharepoint.com/sites/bicenter/Dashboards/Executive%20Reports.aspxUsername: admin@spdemoportiva.onmicrosoft.com Password: pass@word1 More demos of Power View availablehttp://blogs.msdn.com/b/oneclickbi/archive/2011/12/27/more-demos-of-power-view-available.aspx