Six Sigma Recruiting
- 1. Six Sigma Recruiting © The Talent Buzz
- 2. Six Sigma Recruiting… … is a problem solving methodology … performance is the statistical term for a process that produces fewer than 3.4 defects or errors per million opportunities … improvement is when the key outcomes of a business or work process are improved dramatically, often by 70% or more … is a general purpose approach to minimizing mistakes and maximizing value … helps organization achieve breakthrough improvements, not incremental © The Talent Buzz
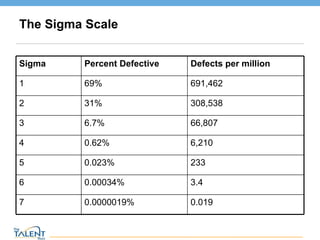
- 3. The Sigma Scale © The Talent Buzz Sigma Percent Defective Defects per million 1 69% 691,462 2 31% 308,538 3 6.7% 66,807 4 0.62% 6,210 5 0.023% 233 6 0.00034% 3.4 7 0.0000019% 0.019
- 4. How Good Is Good? © The Talent Buzz 99% Good (3.8 Sigma) 99.9996% Good (Six Sigma) 20,000 lost articles of mail per hour 7 articles of lost mail per hour 5,000 incorrect surgical operations per week 1.7 incorrect surgical operations per week 2 short or long landings at major airports daily 1 short or long landing at major airports every 5 years 11.8 million shares incorrectly traded on the NYSE every day 4,021 shares incorrectly traded on the NYSE every day 3 warranty claims for every new automobile 1 warranty claim for every 980 new automobiles No electricity for 7 hours each month One hour without electricity every 34 years
- 5. Ready to Launch a Six Sigma Project? Must have significant financial or strategic value Produce results that significantly exceed the amount of resources and effort required to obtain improvements Improve performance by greater than 70% over existing levels © The Talent Buzz
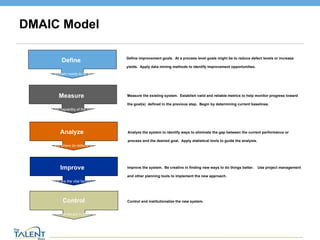
- 6. DMAIC Model Define What problem needs to be solved Measure What is the capability of the process? Analyze When and where do defects occur? Improve What are the vital factors? Control What controls can be put in place to sustain? Define improvement goals. At a process level goals might be to reduce defect levels or increase yields. Apply data mining methods to identify improvement opportunities. Measure the existing system. Establish valid and reliable metrics to help monitor progress toward the goal(s) defined in the previous step. Begin by determining current baselines. Analyze the system to identify ways to eliminate the gap between the current performance or process and the desired goal. Apply statistical tools to guide the analysis. Improve the system. Be creative in finding new ways to do things better. Use project management and other planning tools to implement the new approach. Control and institutionalize the new system. © The Talent Buzz
- 7. Project Considerations Align with the business or HR strategy Complete project assumptions Define process parameters Define in and out of scope Determine the milestones Accurate cost benefit analysis Consider guiding principles and organizational drivers Address all constraints Your business case starts with a problem statement Then is reversed into a goal statement Select the right team Defined the roles Engage the team Define What problem needs to be solved © The Talent Buzz
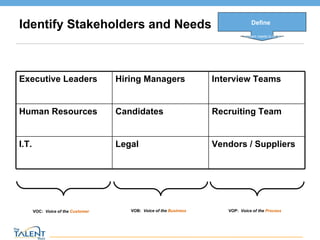
- 8. Identify Stakeholders and Needs Define What problem needs to be solved VOC: Voice of the Customer VOB: Voice of the Business VOP: Voice of the Process © The Talent Buzz Executive Leaders Hiring Managers Interview Teams Human Resources Candidates Recruiting Team I.T. Legal Vendors / Suppliers
- 9. Develop Project Timeline Define What problem needs to be solved © The Talent Buzz
- 10. Complete Cost Benefit Analysis Process Improvement Opportunities Operating Environment Opportunities + Effectiveness Gains Efficiency Gains = Measure What is the capability of the process? © The Talent Buzz
- 11. Designing A Capacity Model Measure What is the capability of the process? © The Talent Buzz
- 12. Assessing Current Results Measure What is the capability of the process? © The Talent Buzz
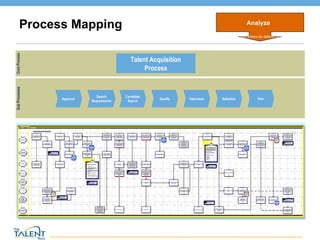
- 13. Process Mapping Core Process Talent Acquisition Process Sub Processes Approval Search Requirements Candidate Search Interviews Qualify Selection Hire Analyze When and where do defects occur? © The Talent Buzz
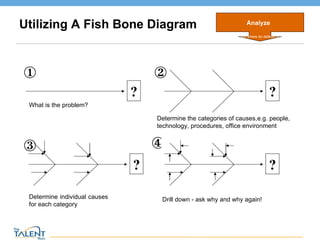
- 14. Utilizing A Fish Bone Diagram Analyze When and where do defects occur? © The Talent Buzz ? What is the problem? ? Determine the categories of causes,e.g. people, technology, procedures, office environment ? Determine individual causes for each category ? Drill down - ask why and why again!
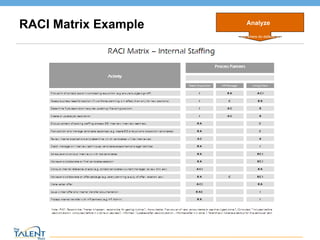
- 15. Tool: RACI Matrix RACI is an Acronym for the following words ... R = Responsible “The person who has to make something happen… responsible for doing it ” A = Accountable “The person who has the power of veto… accountable to see that it gets done ” C = Consulted “The person who is included before a decision/action is taken… consulted before it is done or decided ” I = Informed “ The person who is updated after a decision/action has been taken… informed after it is done ” Analyze When and where do defects occur? © The Talent Buzz
- 16. RACI Matrix Example Analyze When and where do defects occur? © The Talent Buzz
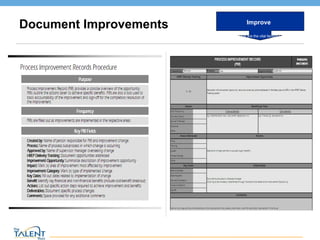
- 17. Document Improvements Improve What are the vital factors? © The Talent Buzz
- 18. Communication Planning Improve What are the vital factors? © The Talent Buzz
- 19. Change Management Focus Areas Why we need to change Dynamics of change Individual responses Reactions Managers role Nine Key Strategies Committed leadership Compelling vision Ownership Continuous improvement Open dialogue Explicit values Measurement and rewards Coaching and training Celebrations Current State Transition State Desired Outcome Improve What are the vital factors? © The Talent Buzz
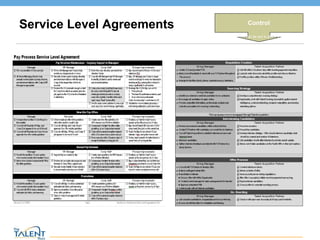
- 20. Service Level Agreements Control What controls can be put in place to sustain? © The Talent Buzz
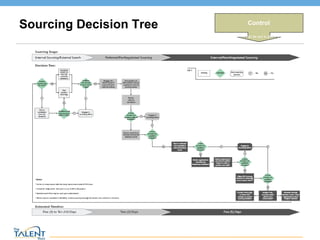
- 21. Sourcing Decision Tree Control What controls can be put in place to sustain? © The Talent Buzz
- 22. Project Successes and Highlights Capital Impact Decreased cost per hire by 46% Decreased time to fill by 27% Improved % staffed ratio from 92% to 98% Decreased interview to hire ratio by 44% Increased quality of hire by 39% Soft Benefits Dramatically increased client satisfaction and perception Significantly enhanced candidate experience Sourced and hired higher candidate talent Minimized legal risks and exposures © The Talent Buzz
- 23. Six Sigma Within Recruiting What do you need to improve? Quality Cost Time Experience Ratio Is Six Sigma recruiting realistic? How to apply the principles? What about innovation? © The Talent Buzz
- 24. Best Practices For Your Project Set stretch goals Nothing is sacred Engage your clients Focus on change management Put your faith in the data Minimize handoffs Align projects with key goals Celebrate successes Unleash everyone’s potential Consider RPO, and outsourcing options © The Talent Buzz
- 25. Avoiding Pitfalls With Your Project Not allowing enough time Who’s the leader Scope creep But we’re different Overtraining Blindly believing your measurement system Not leveraging technology © The Talent Buzz
- 26. What Really Matters Recruiting leadership with the vision and talent to drive transformational change A team with domains of expertise in recruiting, who have the influential skills to implement change with clients A proven methodology Sound, proven project management approach Creating an engaging experience for your clients © The Talent Buzz
- 27. Contact & Connect Contact / Connect with Jason Buss LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/jbuss Twitter: www.twitter.com/jjbuss Facebook: www.facebook.com/jasonbuss Foursquare: www.foursquare.com/user/jjbuss Gmail: bussjj (at) gmail.com Skype: bussjj www.TheTalentBuzz.com © The Talent Buzz
Editor's Notes
- As you have gone through defining the overall project, you also need to identify your stakeholders and their needs. This can be done several ways, both formally and informally. - Formally by engaging these groups as part of the project team, or as a project “gating review” team - Or more informally through historic survey data or client feedback In Six Sigma, there are 3 “voices” you need to consider: VOC: Generally speaking, these are the customer requirements or requests VOB: The voice of profitability or ROI. VOP: This is the overall ability of your process to meet the requirements and needs of your customers and the business. It also has a heavy component looking at what resources are required to successfully run a specific process.
- The next phase of the DMAIC model is Measure… This is where you are measuring your existing system or process, as well as looking at baselines for your measurement. A complete CBA is required to get the necessary approvals to secure funding, or receive approvals to move forward with your project. Process Improvement Opportunities: - Reducing the number of handoffs in HR - On-line employment application and background check authorization Operating Environment Opportunities: - Creating a centralized staffing model - Creating a competitive talent sourcing capability Effectiveness: - SLA, managing client expectations - Exceptional candidate experience Efficiency: - Technology - Cost per hire
- Objective: To determine major causes, potential root causes and potential solution options Purpose: To identify the cause of a problem by applying the experience and expertise of a group in structured brainstorming. Also used to brainstorm possible ways to cause a desired effect to happen Instructions: 1. Name the problem or effect to be analyzed and write it at the head of a fishbone diagram 2. Determine appropriate cause categories. These are the bones of the fish 3. Brainstorm potential causes in each category 4. Identify the cause-and-effect relationship between factors in each category 5. Construct the fishbone diagram 6. Use data gathering or team consensus to narrow down and select most likely cause(s) for further investigation and/or solution generation Duration: 60-120 minutes