Slide share london excellence workshop on service excellence 25 october 2005
- 1. 1 Service Excellence – the key to Customer Retention 25 October 2005 Royal Commonwealth Society London “London Excellence” Dr. Ted Marra Strategic Partner, Symbia
- 2. 2 Symbia – who we are Founded in 1994 as an independent professional services company » Management consulting » Interim Management » Technical Services Primary areas of expertise » Customer Relationship Management (B2B) » Performance Management » Procurement S-Cat prime contractor for Business & Management Consultancy Working across public and private sector
- 3. 3 Who we deliver to: Some of our clients
- 4. 4 Who you are Where you are from Why you are here Very Short Introductions
- 5. 5 Group Activity At your tables, share with your colleagues what you believe best describes your senior management’s beliefs or attitudes about service in your organisation Group discussion
- 6. 6 Attitude about the job Attitude about the company Employee behaviour Merchandise Value Service Helpfulness Customer impression Customer recommendations Employee retention Customer retention Return on assets Operating margin Revenue growth A COMPELLING PLACE TO WORK A COMPELLING PLACE TO INVEST A COMPELLING PLACE TO SHOP 5 UNIT INCREASE IN EMPLOYEE ATTITUDE 1.3 UNIT INCREASE IN CUSTOMER IMPRESSION 0.5% INCREASE IN REVENUE GROWTH DRIVES DRIVES The service-profit chain at Sears
- 7. 7 Service Excellence Basic Model Service Excellence Recovery Stronger Relationships Prevention + Understand Assess Negotiate Be an Advocate Prepare Listen & Learn Be a Resource Be an Advocate Apply Quality Techniques The Systematic Cycles of Customer Engagement
- 8. 8 Customer Relationship Strategies Customer “Sensing” Processes Vision, Business Plan and Key Business Objectives CRM Customers Touch Points • Sales •Delivery •Service •Others CustomerFocusedCulture Feedback The Customer System of an Organisation
- 9. 9 Managing the Customer Relationship: Customer Experience and Touch Points (B2B) Sales Process Delivery Customer Purchase Decision Customer Purchase Consideration System Design Installation Repair Service / Maintenance First Invoice Order Submission Credit Review Purchase Cycle Customer Purchase Consideration Training Technical Support Account Maintenance “Telecommunications”
- 10. 10 Group Activity At your tables, identify the moments of truth or touch points that occur between your customers and your organisation » Identify the ones where you believe your organisation delivers its best service » Identify the ones where you customers would say they experience the most pain (highest level of difficulty) Share these with those at your table Group discussion
- 11. 11 The Two Costs of Doing Business Whenever a customer comes to do business with your organisation they always incur two costs. What are they? 1. E_________ 2. E_________
- 12. 12 Behavioural Research Data Poor service loses customers » Problem Experience Impacts Customer Loyalty: Before the problem 70%-95% and 40%-75% after a problem. So what is your recovery capability? » Nearly 67% of the time, the reason a customer reduces or stops doing business with you and goes to a competitor is because of poor service (B2C) » Nearly 70% of the time, business to business customers stop doing business or reduce purchases is that they perceive your organisation is “not easy to do business with” (B2B) “It costs six to twenty times as much to get a new customer as it does to keep an existing one”
- 13. 13 A “Best Practice” Complaint and Enquiry Management Process Customer Initiation Contact Process Fulfillment Process Validation Process Management Process Escalation Process Closed Loop The Recovery System
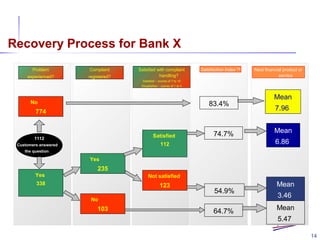
- 14. 14 Mean 7.96 Problem experienced? No 774 Yes 338 Satisfaction Index TM Next financial product or service 1112 Customers answered the question Complaint registered? No 103 74.7% Not satisfied 123 Satisfied with complaint handling? Satisfied – scores of 7 to 10 Dissatisfied – scores of 1 to 4 Yes 235 Satisfied 112 64.7% 54.9% Mean 6.86 Mean 5.47 Mean 3.46 83.4% Recovery Process for Bank X
- 15. 15 Understanding your customers o Basic needs o Wants o Sources of value A Critical Success Factor for Achieving Service Excellence
- 16. 16 Value should be measured in terms of “benefits” perceived by the customer » Image/reputation/brand strength » Process » People » Product » Service » Technology » Support The Seven Sources of Value
- 17. 17 Group Activity At your tables, identify the following » The 2 most important basic needs of your customers » The item you believe would be at the top of your customer’s “wish list” » One key way you could add more value in your customer relationships Share these with those at your table Group discussion
- 18. 18 Group Activity At your tables, identify the following » The three most critical components of service excellence – the ones which form the base capability of an organisation to be able to deliver excellent service consistently Discuss them briefly with those at your table Group discussion
- 19. 19 Service Excellence Characteristics/Scope Benefits Innovation Service Excellence People Process Service Easy to do business (simple) Responsive/Short cycle time Knowledge Skills Behaviours Attitudes Capability HR Systems Alignment
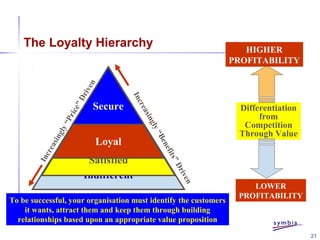
- 20. 20 Loyalty is the state in which the desired set of customer needs, wants and benefits are provided throughout the business relationship resulting in being the preferred and recommended supplier in all relevant product and service areas
- 21. 21 The Loyalty Hierarchy Indifferent Satisfied Loyal Secure Increasingly“Benefits”Driven Increasingly“Price”Driven Differentiation from Competition Through Value LOWER PROFITABILITY HIGHER PROFITABILITY To be successful, your organisation must identify the customers it wants, attract them and keep them through building relationships based upon an appropriate value proposition
- 22. 22 Group Activity At your tables, discuss the following » What should be your organisation’s action plan for change if it is serious about achieving service excellence? That is, what do you have to do or do differently to achieve service excellence? » What are the barriers and how do you overcome them? Group discussion
- 23. 23 Questions?
- 24. 24 Adjourn and Thank You!
- 26. 26 Possible Attitudes or Beliefs of Management Regarding Service (see journal article) Service is viewed as a cost – not in terms of benefits Oh, but at least we’re the “best of a bad lot” Excellent service is a “nice to have” They don’t see that poor service will cost far more in the end than their investment in achieving excellent service Lack of education of management e.g., the service-profit chain Service is viewed as operational – not strategic Customer satisfaction measurement often does not include anything other than the basic needs of customers – and not touching on their wants or value adds Customer service management are sometimes viewed as second class citizens
- 27. 27 Model of Organisational Performance Employee Orientation Customer Focus Excellence Work Environment/Values Attitudes Behaviors Organisational Performance Continuous Improvement Desired Outcomes: • Customer Retention • Employee Retention • Financial Results • Business Excellence Employee Performance (“Excellence”) Employee Mindset (“Paradigms”) Critical Success Factors (“Drivers”)
- 28. 28 Behavioural Research Data In a business to business environment, you usually do not know there is a problem until it is too late! Those customers who do not complain are your least loyal, yet easiest and least costly to retain. » You must find a way to invite them to speak with you about their issue
- 29. 29 The Tip of the Iceberg 5% 60% 35% Complain to Field Level/ District/Sales Office/ Plant/Mill/Chain Partner Encounter a problem, but do not complain No News is not necessarily good News! 65% 30% to 50% Call Centre Why do some people NOT complain? Complain to Head Office
- 30. 30 Defining “Basic” Needs Areas where you must be routinely flawless in delivery (six sigma!) Failure on a “basic need” results in: » Disproportionately high levels of dissatisfaction » Recurring problems of a “basic” nature can quickly lead to customer disengagement Customers tend to be more less tolerant to perceived gaps between your performance and that of a competitor on “basic needs”
- 31. 31 Defining “Wants” The true “wants” of the customer go to the next level above “needs”. Meeting “wants” usually results in satisfying the customer or even delighting them » It may or may not ensure loyalty Customers easily articulate their needs » Determining “wants” requires more effort You must tap into the customer’s “wish list”
- 32. 32 Defining Value Value is an intangible or tangible benefit which the customer perceives that the competition is either unwilling or unable to provide. It is a true source of differentiation & competitive advantage Pre-requisite: “routinely perfect in delivering on the basic needs” (zero defects)
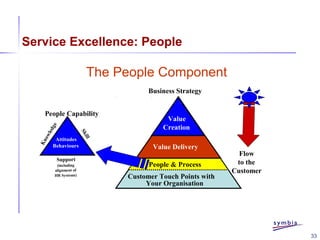
- 33. 33 Service Excellence: People The People Component Customer Touch Points with Your Organisation People & Process Value Delivery Value Creation People Capability Attitudes Behaviours Knowledge Skill Support (including alignment of HR Systems) Business Strategy Flow to the Customer
Editor's Notes
- CHERYL WIDTH AND BREADTH OF INDUSTRY COVERAGE AND EXP…RET BANK, GOVT, TRANSPORT, MILITARY, LOGISTICS Perf Mgn – MoD, B&B, RBoS LUL – BRM, Barclays Procurement – Home Office