Social Change: Social Media's role in Business
- 1. Social Change: Social media’s role in business May 2012 Flickr: Robert S. Donovan
- 2. Today’s roadmap • What is social media? • Is it right for my organization? • What about privacy, security and legal concerns? • How do I convince my boss and colleagues of the benefits? • Where do I get started? Flickr: Max Mayorov
- 3. Learning Objectives • Recognize and apply social media terms and principles • Realize the potential social media benefits to your organization • Understand the principles of change management • Envision how change management can encourage social media adoption within your organization Flickr: gutter
- 4. Today’s ground rules • Ask questions! • Engage, Engage, Engage • We will provide this PPT after the class • We’ll take breaks as needed • There are links throughout this presentation, view it in presentation mode to click on these additional resources Flickr: Victor1558 4
- 5. What is social media? Social media are “primarily Internet-based tools for sharing and discussing information. The term most often refers to activities that integrate technology, social interaction, and the construction of words, pictures, videos, and audio.” -Wikipedia 5
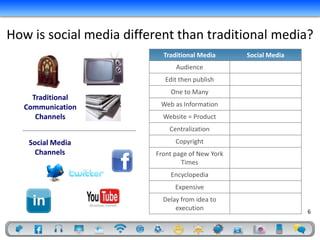
- 6. How is social media different than traditional media? Traditional Media Social Media Audience Edit then publish One to Many Traditional Communication Web as Information Channels Website = Product Centralization Social Media Copyright Channels Front page of New York Times Encyclopedia Expensive Delay from idea to execution 6
- 7. How is social media different than traditional media? Traditional Media Social Media Audience People Edit then publish Publish then edit One to Many Many to Many Traditional Web as Information Participatory Web Communication Channels Website = Product Website = Service Centralization Decentralization Social Media Copyright Open Source Channels Front page of New York Front page of Digg Times Encyclopedia Wikipedia Expensive Inexpensive Delay from idea to Quick execution and execution feedback 7
- 8. 8
- 9. Social media is NOT: just facebook 9
- 10. So what is social media? creation participation Collaboration authenticity connecting idea sharing community 10 Flickr: takomabibelot
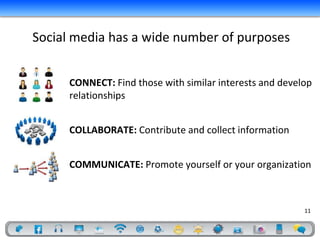
- 11. Social media has a wide number of purposes CONNECT: Find those with similar interests and develop relationships COLLABORATE: Contribute and collect information COMMUNICATE: Promote yourself or your organization 11
- 12. Why integrate social media into health? • Increases the reach to diverse audiences • Allows for engagement and real- time feedback • Enables relationship building and collaboration • Empowers people to make healthier and safer decisions • Provides an opportunity to correct misinformation 12
- 13. Social media channels 13
- 14. Social media channels STRENGTH WEAKNESS Blog + Conversational and personal - Legal implications for inaccuracy + Direct line to an organization - Comments may require moderation + Real-time , location-based updates - Breaking news can be inaccurate Microblogging + Reaches mobile audiences - Requires regular use and potentially engagement Social networking + Conversational and personal - Legal implications for inaccuracy + Popular portals for health information - Lack of control Mobile + Most personal way to engage - Applications are expensive to develop + Text messages and applications (apps) - Texting requires a strong sign-up plan Video sharing + Easily shared and embedded - Comments may require moderation + Contributes to Google rankings - Expensive, time-consuming to create + Wide variety of ways to disseminate - Expensive to develop Widgets your web content (eCards, widgets, ads, QR codes and more ) - Require strong promotion plans 14
- 15. Social media by the numbers 15
- 16. Your addressable audience is massive 311M Americans living in the US 232M of them are internet users 16
- 17. Social Media Revolution 2011 17
- 18. Social networking statistics • 800+ M active users • >50% of active users log in daily • 250 M photos uploaded daily • 350 M users access Facebook • 135+ M members in 200 through mobile devices countries • 4 B searches generated • 2 M company pages • 180,000+ websites use LinkedIn Share button to send content to LinkedIn 18
- 19. Blogging and Micro-blogging statistics Blogging • 164+ million blogs • 2/3 bloggers are male (66%) • 27% blog full time • 57% of bloggers are between 25 to 44 years old Micro-blogging • 200+ million users • 450K accounts created daily • 24% of users check it several times a day • 88% audience penetration 19
- 20. 50% 81% • 50% of people globally use a • 81% of people globally have computer – a mobile phone – • 3.3 billion people • 5.3 billion people Source: ICT Facts and Figures, “The World in 2011” as reported on CNN; and PEW RESEARCH CENTER, “Cell Phones, Computers 20 Increasingly common,” Q62 and Q65. Based on median % across the 16 nations where 2002, 2007, and 2010 data are available.
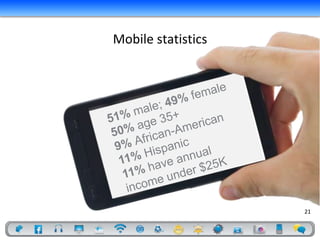
- 21. Mobile statistics 21
- 22. Mobile internet use will soon exceed desktop Mobile Internet Users Desktop Internet Users 2000 1600 global internet 1200 users (mm) 800 400 0 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 22
- 23. Social media in health communication 23
- 24. Consumers who use social media for healthcare information 24
- 25. The social life of health information Survey statistics are based on 74% of adults who use the internet: • 59% searched for health related information • 25% read commentary or experiences about health issues • 19% watched an online video about health issues • 13% have gone online to find others who might have health concerns similar to theirs 25
- 26. Social media successes in health communication 26
- 27. YouTube: Breast cancer awareness • A single video upload causes an Internet sensation – “Pink Glove Dance” with 13.4 million views to date. – Sequel with 450,000 views – Medline increased awareness of their kind donation and has contributed $750,000 to the National Breast Cancer Foundation 27
- 28. LiveStrong raised millions to fight cancer • In 2004, a little yellow bracelet changed the cancer cause and raised $25.1 million in 6 months • 80 million bracelets sold to date • Brand recognition and strong social media presence • LiveStrong Young Adult Alliance SMASH website 28
- 29. Social media and your website 29
- 30. So what do I get out of social media? 551,516 likes 5-7 posts per week >100 comments per post 50 videos posted 62,919 channel views 325,542 video views 39,877 followers ~30 tweets per week 30
- 31. Reinforcing messages enhances credibility Source: 2011 Edelman Trust Barometer. Accessed from http://www.edelman.com/trust/2011/uploads/Trust%20Executive%20Summary.PDF on May 29, 2011. 31
- 32. Enterprise 2.0: The other social media 32
- 33. Enterprise 2.0 – social media inside the firewall Enterprise 2.0 “aims to help employees, customers and suppliers collaborate, share, and organize information via Web 2.0 technologies. -Wikipedia 33
- 34. E2.0 – also known as Social Business Tool Purpose Intranet • Knowledge management • Content organization • Training • Technical support • Administrative functions (travel, vacation, etc.) Blogs • Leadership or SME information sharing and employee engagement Profile pages • Connecting colleagues Discussion forums • Sharing ideas/expertise across the office or the world Wikis • Internal, real-time collaboration Ideation • Idea generation, voting, and implementation RSS Feeds • Get email updates when new content appears Tagging • Makes content searchable and shareable 34
- 35. E2.0 Statistics 61% of businesses surveyed in US, Canada and Europe had at least one social media tool available to some or all employees Of organizations with at least one Intranet 2.0 tool: • 75% have blogs • 65% have discussion forums Resources: • 63% have instant messaging • 38% spent <$10,000 • 61% have wikis • 34% spent $10,000 - $99,999 • 60% have user commenting • 28% spent >$100,000 • 56% have RSS • 51% have tagging 35 Source: 2011 Prescient Digital Media The Social Intranet Study
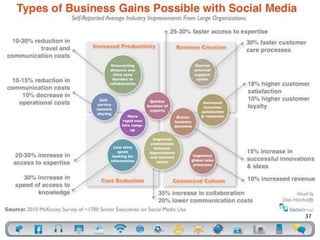
- 36. What can E2.0 do for your organization? • Raise morale • Improve collaboration • Engage the workforce • Share knowledge/expertise • Recruit and retain talent • Increase efficiency • Train staff • Encourage fun! 36
- 37. 37
- 38. If this stuff is so great, why doesn’t everyone use it? Barriers • 18% Lack of Executive support • 18% Bigger priorities • 12% Lack of IT support • 10% Policy concerns • 10% Other • 9% Apathy • 9% Business case 38 Source: 2011 Prescient Digital Media The Social Intranet Study
- 39. “Yeah, great, but this doesn’t help me bring this stuff to my organization!” 39
- 40. So you want to start a revolution? 40
- 42. If you’re going to start a revolution… you better use the right strategy Change Management: A structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from a current state to a desired future state - Wikipedia 42
- 43. Is your organization clamoring for social media? We need to: • Change perceptions about… • Keep employees informed… • Engage and motivate our employees… • Disseminate information in an emergency… • Find and recruit new talent… • Train our employees… 43
- 44. Is your landscape ready? Does your organization have a business need that social media can Does your boss understand help address? this is NOT a ‘build it and they will come’ scenario? WHAT IS YOUR BOSS’ MOTIVATION – GET PROMOTED, GROW THE DEPARTMENT, ENGAGE A WORLDWIDE WORKFORCE, COAST INTO RETIREMENT? Is your environment conducive to change? 44
- 45. Social media is a long-term investment The adoption curve could take Where are you? months or years to evolve… Where is your organization? 45
- 46. Why do good ideas so often fail? Because they: • Don’t have a sense of urgency • Don’t have leadership buy-in • Don’t have a clear vision • Don’t have an effective communications strategy • Allow obstacles to derail the change • Don’t create short term wins • Declare victory too soon • Neglect to anchor changes into the culture 46
- 47. 47
- 48. What about these guys? 48
- 49. Bottom line: This is NOT build it and they will come! 49
- 50. Social media and health care 50
- 51. Case study: Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation 51
- 52. Key benefits from Glaser case study Results: 1. Greater access to information 2. Increased collaboration as employees learn each other’s abilities and interests 3. Leadership blog led to a perception of increased transparency 4. Information shared openly without fear of adverse consequences 5. Huge improvement in the exchange of ideas between employees Measuring Success: • Improved company morale • Anecdotal evidence from employees who say they are now more efficient, more effective and more productive 52
- 53. Keys to success Critical Success Factors • Involve team members early on before building your strategy, determining the design, branding or naming, or selecting a technology solution • Create many learning opportunities for employees • Engage leadership and staff at all levels throughout the process • Keep initial goals simple and attainable • Manage expectations of staff and management 53
- 54. What’s next for Glaser? • Single sign-on • Mobile integration • Integration of video and legacy systems • Enhanced training and education programs • Adding collaborative team spaces will: • Allow more sharing and encourage content creation • Increase idea exchange and sharing among work groups The key? Constant evolution – keep asking your users what they want and give it to them! 54
- 55. So is E2.0 right for my organization? 55
- 56. Before you can answer that, consider these… Resources Technology Processes • Time • Complexity • Knowledge • Money • Cost management • Labor • Compatibility • Employee • Infrastructure • Infrastructure training Unsuccessful attempts can either be a learning experience or create strong negative feelings 56
- 57. But don’t forget the most important part… • Involve the team • Solve their problems • Listen to their feedback, especially the bad!! • Know how they currently collaborate • Know their key issues (silos, regional differences, etc.) • Leverage their expertise 57
- 58. Wow, this sounds expensive! 58
- 59. So how do I actually DO this? 59
- 60. What are the key points to convey about social media? • Social Media is another tool to reach internal and external stakeholders • Research is an imperative first step to developing a strategy • Define your audience, monitor their social media usage, build your strategy • It MUST be integrated into the Communications Plan to be successful • Marketing, branding and messaging must be consistent with all other communications efforts • It is a commitment, and needs to be managed consistently to yield results 60
- 61. The risks and benefits of social media Benefits Risks of NOT embracing • Real time information sharing • Poor collaboration decreases efficiency • Proactive monitoring to avoid • Getting blindsided by news or situations escalating information • Correct biased or wrong information • Proliferating misinformation • An innovative, solutions driven culture • Loss of innovation and participation • Increased trust and authenticity • Lack of trust or authenticity • Improved morale through • Decreased morale as people think their transparency ideas aren’t valued • Engaged stakeholders become brand • Disengaged or disinterested ambassadors stakeholders won’t advocate for you 61
- 62. So how do I make an impact? • Be who you are • Know your environment (IT, security, legal) • Know your resources (time, money, partnerships) 62
- 63. The steps to smart social media 1. Listen! 2. Determine your objective 3. Define your audience 4. Research the channels they use 5. Create launch, promotion and evaluation plans 6. Link evaluation to business objectives 7. Integrate with all outreach 8. Use major events to increase awareness and participation 63
- 64. How do I integrate social media into my communication strategy? By answering the following: • What are my resources? • Who is my audience? • What social media tools do they use? • How can I integrate social media with my media plan, conference strategy, partner outreach, website, etc.? • How do I ensure collaboration so the social media team stays in the loop? 64
- 65. Critical success factors to adopting Social Media 1. Obtain leadership buy-in 10. Answer WIIFM 2. Convene the right team 11. Collaborate with IT, Privacy, Legal 3. Develop a shared understanding of 12. Design a strong governance process the problem 13. Educate and train 4. Know your culture 14. Integrate with existing outreach 5. Build relationships 15. Evolve, evolve, evolve 6. Define your business goals 16. Leverage your friends and partners 7. Research your audience and the 17. Gather feedback tools 18. Measure progress against 8. Benchmark peers to track progress benchmarks and business goals 9. Set realistic expectations 65
- 66. Social media measurement 66
- 67. 67
- 68. Focus on achieving outcomes, not just outputs • Are people using the platform to do their jobs more effectively? • Is employee morale improving? • Is the staff working more efficiently? • Are you capturing innovative ideas and implementing them? • Is employee engagement increasing? • Have formerly siloed departments begun to collaborate? 68
- 69. Lessons learned • Watch trends, study demographics and use this presentation to build your strategy • Listen, share, and learn • Promote, evaluate, and develop long-term strategy • Keep content fresh and engaging – Don’t just do it, do it right! • Be as conversational as you can 69
- 70. Discussion 70
- 71. Resources to learn more Strategy and Plans • CDC Health Communicator’s Social Media Toolkit, HowTo.gov, Mayo Clinic Center for Social Media Keep Current • Mashable, Social Media Examiner Research and Stats • Socialbakers.com, Pew Internet & American Life Project, Neilson, eMarketer, Quantcast, Siteanalytics, Hubspot, comscore, Technorati, Google Insights Healthcare • Fierce Mobile Healthcare, Dose of Digital and Healthcare Social Media, iHealthBeat, thehealthdigital.com, eHowHealth 71
- 72. Appendix 72
- 73. 10 Do’s of Social Media Be honest and transparent as you communicate online Offer compelling content (e.g., interviews with leadership, photos of events, videos of speeches, links) to your stakeholders Communicate in a way that reflects positively on your organization Respond to questions in a timely fashion with valuable resources Set expectations with visible policies (e.g., comments, disclaimers of endorsement/linking, only tweeting from 9am-5pm) Have a thick skin and consistently ask your stakeholders for feedback Listen to your stakeholders and respond when you can help (e.g., correcting misinformation) Stick to your policies and don’t feel obligated to respond to stakeholders that issue personal attacks or use offensive language Be human and tell compelling stories that resonate with your audience Balance to promote across tools while tailoring for each channel (i.e., do not copy/paste) 73
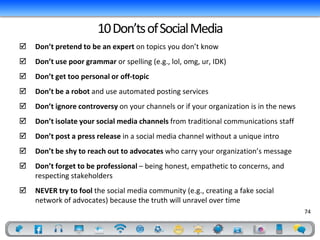
- 74. 10 Don’ts of Social Media Don’t pretend to be an expert on topics you don’t know Don’t use poor grammar or spelling (e.g., lol, omg, ur, IDK) Don’t get too personal or off-topic Don’t be a robot and use automated posting services Don’t ignore controversy on your channels or if your organization is in the news Don’t isolate your social media channels from traditional communications staff Don’t post a press release in a social media channel without a unique intro Don’t be shy to reach out to advocates who carry your organization’s message Don’t forget to be professional – being honest, empathetic to concerns, and respecting stakeholders NEVER try to fool the social media community (e.g., creating a fake social network of advocates) because the truth will unravel over time 74
- 75. Social Media best practices 75
- 76. Blogs are well-known and easily used Blogging Do’s Blogging Don’ts • A web log “Blog” is a conversational online post that allows people to Be conversational Send every post through the approval comment chain • Free to create Tell a story Post your press • Tailored content for a specific audience releases • You are in control of the message Write your own blog Have a ghostwriter • Expands reach to a new audience than Be honest Ignore controversy your website Write in first person Write in third person • Quickly respond to news, legislation, Post often Get discouraged studies, etc. Have a thick skin Disable or filter comments 76
- 77. Micro-blogging lets you send shorts updates to your followers • Individuals use Twitter to connect and share information – Communicate your brand, ideas, organization, or passions – Share information (blogs, videos, websites, etc.) – Promote your ideas, blogs, website, etc. – Ask questions, engage in conversations – Ask opinions or use as a sounding board • Organizations use Twitter to customer service, communications or engaging employees – Promote events, initiatives, and resources – Obtain feedback – Respond to customer concerns, complaints – Engage or recruit employees 77 • Must be committed to posting and responding consistently
- 78. Top ten best practices for writing tweets 1. Keep it short (120 characters) 2. Abbreviate 3. Include links 4. Shorten URLs 5. Make it interesting 6. Use hashtags (#) 7. Follow others 8. Respond and engage 9. Be real! 10. Have fun! 78
- 79. Social networking builds communities • Social networking allows an organization to create an interconnected community 90M • Social networking is more than LinkedIn and Facebook – Google+ 7.5M – Chime.in – Pinterest 135M – Patients Like Me – GovLoop 79 50K
- 80. Top ten social networking best practices 1. Learn about the site/community 2. Consider your resources 3. Develop management, promotion, and evaluation plans 4. Determine clearance procedures 5. Post your commenting policy 6. Post short, interactive comments with videos, images, and links 7. Post consistently and respond to comments 8. Promote national events and current news (when appropriate) to provide fans with topical, timely information 9. Engage partners and encourage cross-promotion 10.Be transparent and engaged! 80
Editor's Notes
- How many people use Facebook? LinkedIn? Twitter? How many have blogged? How many have a company intranet? How many have participated by posting a blog, commenting on a discussion forum, or contributing content in some way?I’m not a guru, ninja, Lean Six, anything! I’m a believer in the power and potential of social media, but I am not a zealot. I realize that social media is a tool, neither more nor less. It is a tool and it can be used for good or bad, and it can be effective and ineffective.But make no mistake, social media is a revolution in the way we communicate. We are often more familiar with someone across the country than we are with our own neighbor. This new type of communication has massive implications:Improve internal collaborationMarket a productServe customers betterCrowd source solutions to vexing problemsCollaborate across cubicles or the world
- Social media as an online conversation. The key word is conversation – that means two-way communication. Wikipedia – who has heard of crowdsourcing? Anyone know what it is? Wikipedia is crowd sourcing – if it were a book it would have more than 22 million pages and take you 123 years to read – oh, and studies prove it’s more accurate than the Encyclopedia Britannica!To understand social media better, let’s discuss the differences between social media and traditional media.
- The conversation is going on with or without you. You can choose to engage, inform and participate, or you can choose to ignore large sections of the American public.In addition, in the public health space there is a LOT of misinformation on the web; you can be part of the solution, providing valuable, factual information and helping people or not – but they’re going to search for the information one way or the other!
- Social media is an online conversation. It is engagement and it can be between two people within an organization, two people who are passionate about the same thing, or two people who have absolutely nothing in common – except their use of social media.It’s power is in its potential to engage and inspire people.
- Each of these channels has specific strengths and weaknesses. You have to not only understand how social media could potentially benefit your business – you have to know what channel is right for you, what resources you’ll need and most importantly what channels your target audience is using.We’ll discuss these the components of a successful social media strategy in a little while, but first some numbers to help you understand the size and scope of social media.
- We are changing the way we interact with each other as well as locating information, developing opinions, making decisions, and ultimately changing behaviors. There are approximately 311 million Americans living in USA.An estimated 232 million of them are Internet users.
- Here is a recap of some of the most important statistics that you just watched:Facebook tops Google for weekly traffic in USAYouTube, which is owned by Google, is the second largest search engine in the world. The #1 search engine is of course Google itself. If Facebook was a country – it would be the 3rd largest country by population with approximately 800+ million users (after China and India who’s population is in the billions) 90% of consumers trust peer recommendations such as Yelp versus 14% who trust advertisement93% of marketers use social media for business purposeshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x0EnhXn5boM
- Smartphone users spend about 18 hours per month using their mobile apps and browsing the mobile web.
- Google projects that mobile internet usage will exceed desktop in a few short years – possibly as soon as 2014.
- Men are more likely than women to turn to Facebook and other social networks for healthcare purposes.Overall, nearly a third of respondents, and 50 percent of those under the age of 35, had used social media for healthcare purposes, which can range from registering a complaint to looking up informational videos on YouTube.
- As you can tell with these statistics, it is becoming more prevalent for adults to research health related information on the Internet. Social networking is especially important because adults are now using these sites to get health information, follow their friends’ personal health experiences via blogs and online groups. Additionally, some of these adults are even raising awareness or money for a health-related issue or cause. Since there is so much misinformation on the web, it is important for you to engage with the public through your website and social media to provide accurate health information. Source: http://www.pewinternet.org/~/media//Files/Reports/2011/PIP_Social_Life_of_Health_Info.pdf
- YouTube is another social media avenue being used to spread the word about breast cancer awareness. In November 2009, a video called “Pink Glove Dance” was created with more than 200 hospital employees of a local medical center in Portland, Oregon dancing to a fun pop song and spreading breast cancer awareness. They were a YouTube success, with 13.4 million views to date. Since the “Pink Glove Dance” video was such an online sensation, Medline, the company that makes the pink gloves and produced the video, decided to make a sequel. The 2010 sequel video reached 450,000+ viewers. In 2011, Medline decided to host an online nationwide competition to find the best Pink Glove Dance video. Hospitals, nursing homes, schools and everyone who wanted to organize a group of people produced hundreds of videos and submitted them on the website. These incredible videos are meant to raise awareness and inspire others to join the cause. The winning video reached over 61,000 votes! Using these mediums is a great way to gain international attention and get people involved in the fight against breast cancer. As an added bonus for breast cancer organizations in particular, the fact that social networking reaches an overall younger audience is greatly beneficial to getting the message out there to the right people at the right time. By encouraging early detection of breast cancer among the younger generation, those who may have the best chances of detecting breast cancer early on are now given a better chance at survival.http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OEdVfyt-mLwhttp://pinkglovedance.com/home/ - Winner:http://pinkglovedance.com/competition/entry-39
- Social Media can drive website trafficDiscuss engagement and empowering your friends, followers, fans, to be brand ambassadors of your messageSusan G. Komen PR Crisis – took away funding for Planned Parenthood, resulting in lower access to free breast screenings for low income women. What happened? Poor communication of a politically charged issue. (People said it was politically motivated since Planned Parenthood provides abortion services.) After the announcement they were all but silent on Facebook, Twitter and in the media. Their slow response, lack of a crisis management plan, and the effective response from Planned Parenthood put Komen on the defensive. They were accused of deleting critical posts on Facebook: Rule #1 perception is reality – rather than engaging and admitting a mistake they let it ride for three days! They didn’t post to Twitter or Facebook for nearly 24 hours!Planned Parenthood immediately began a huge fundraising effort to counteract the funds it lost from SGKAt times the ratio of negative to positive on Twitter was 80-1; 80 negative comments for every 1 positive!By posting other non-related posts SGK just angered and alienated fans who wanted to engage about this decision.Then they released a taped video (not an interview) while Planned Parenthood did live interviews with all the major networksThis began on Tuesday – they apologized on Friday. It took more than 24 hours to respond on social media and when they did respond it was an official statement without follow-on engagement. Why didn’t they say “We hear your anger and frustration. We are discussing the best way to respond to this situation and will get back to you soon.”LESSON? Know how to use social media and always have a crisis communications plan!
- Mention the book “Enterprise 2.0: New Collaborative Tools for Your Organization's Toughest Challenges”By Andrew McAfee
- Great article on 14 reasons why these types of implementations often fail.
- A few things to know:This is a revolution and if you treat it lightly it will never occurIt is a revolution in the way we communicate, interact, share information, and engage. We’re often more familiar with someone across the country than we are with our own neighbors!
- Remember that, it’s not about the tools, it’s about what the tools create: collaboration, engagement, teamwork, etc.The companies that recognized the early implications of social media, embraced the change and sought to lead from the front.
- Part of knowing whether social media is right for your organization is understanding what social media can and can’t do, and then determining if those capabilities social media has align with a business need your organization has.
- Junior staff – get the technology, get what it does for them and will be your early champions – use that to your advantage. Get their feedback on the early versions!!!WIIFM!!Junior staff – networkingMiddle managers – staffingSenior leaders – business developmentWe are designing a web portal that through a user authentication process will enable simultaneous global interactions in a safe, behind-the-firewall employee collaboration platform.ORWe’re creating a secure website where our employees can collaborate, share ideas, and inspire one another.BEST PRACTICES:- Change management plan must mature and continues to use first year strategies for middle and late adopter, - Incorporate metrics early as a monitor of progress and measure of accountability - Consistent use and promotion of best practices and celebrate successes as opportunities for promotionCM Team must walk the walk! Transparency; all development ideas, roadmaps, bugs, and feedback are on the site for all to see and comment on. All areas of the team are active, visible and accessible across the tool. Through this approach we’ve gained trust, champions, and incredible support. Since Hello’s August 2008 launch, more than: 90% of the firm has logged in to the platform80% of staff have contributed original content500 online communities have been establishedCharacteristics of each adoption group were considered in messaging and outreach strategiesDetermine what your early adopters want and give it to themFrom early adopters we learned features perceived as efficient - like blogs for team communication saving email traffic; wiki for meeting agendas, action, collaboration & event planning saving hours, version control and email; forums to drive firm wide conversation From mid to late adopters, we learned the importance of linking how Hello could support staff in daily work - the business applications valuedResistors we didn’t even try to design strategies to engage – they either will or won’t
- Dr. Closed Mind: Engage, persuade, make him part of the team, or marginalize his influence by getting the people around him.The Silo: Involve in the planning; get them onboard EARLY – help them understand that collaboration does mean giving up some control, but it also means better ideas! Talk to them in terms they can relate to!Captain Conservative: Get him involved if possible, otherwise get the right change agents around him to minimalize his delaying tactics.
- Sr. Management turnover led to this even being possibleNeeded political capital, budget; large initial costs, but ultimately it’s more efficient for a large workforceHad a core management team and a content manager – they were the main POC, they were trained, and they became each office’s championInvolved key staffAt 6 months evaluated the platform and gave out Awards to keep interest and show what was possible on the platformIncorporated feedback – button on landing page, people saw evolution of their feedback implemented; Surveys, team meetings; presentations across departmental meetingsIn person trainings; created initial pages for every department to ensure an initial presenceDid grass roots and senior leadership
- Choose your guiding coalition carefully – it’s not always the most senior, sometimes it’s the most influential – either positive or negative!Also, the key here is to give employees a sense of ownership – it will also help them see this as a part of a better way to work, and not just some new thing they have to learn to doUnderstanding what the platform is, why it was created, and how collaboration will improve their work will encourage adoption.If you create a ‘black hole’ of technology development it will breed mistrust and apprehensionSet small achievable goals – build momentum!Staff – this won’t solve your every problem. Management – this won’t happen overnight.
- Strategy – breaking through the cluttera. Taking best practices and making them relevant and practicalb. Implications of social media (security, privacy, etc.)
- The benefits of social media center around connection, collaboration and transparencyBig picture:Social media allows agencies to communicate more effectively with stakeholdersInternally, for example with study centers, social media would allow for exceptional collaborationOne of the biggest risks in NOT doing social media is there’s an online discussion going on all the time and news outlets monitor these channels for stories – so inaccuracies can hurtEXAMPLE: H1N1 virus rumors started on social media and the CDC was able to squash the rumors quickly because they were already using social media