Software development process models
- 2. What is Waterfall Model The waterfall model is a sequential (non-iterative) design process, used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases of conception, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, production/implementation and maintenance.
- 4. When to use the waterfall model: Requirements are very well known, clear and fixed. Product definition is stable. Technology is understood. There are no ambiguous requirements Ample resources with required expertise are available freely The project is short.
- 5. Activities of Waterfall Model •Requirements definition •Requirements Analysis •Design •Development •Testing(unit & system or Integration testing) •Deployment •Maintenance
- 6. Advantages of waterfall model: •It allows for departmentalization and managerial control. •Simple and easy to understand and use. •Easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model – each phase has specific deliverables and a review process. •Phases are processed and completed one at a time. •Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood. •A schedule can be set with deadlines for each stage of development and a product can proceed through the development process like a car in a car-wash, and theoretically, be delivered on time
- 7. Disadvantages of waterfall model: •It does not allow for much reflection or revision. •Once an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go back and change something that was not well-thought out in the concept stage. •No working software is produced until late during the life cycle. •High amounts of risk and uncertainty. •Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects. •Poor model for long and ongoing projects. •Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate to high risk of changing.
- 8. What is Prototype Model? The basic idea in Prototype model is that instead of freezing the requirements before a design or coding can proceed, a throwaway prototype is built to understand the requirements. This prototype is developed based on the currently known requirements. Prototype model is a software development model. By using this prototype, the client can get an “actual feel” of the system, since the interactions with prototype can enable the client to better understand the requirements of the desired system. Prototyping is an attractive idea for complicated and large systems for which there is no manual process or existing system to help determining the requirements.
- 9. Diagram of Prototype model:
- 10. When to use Prototype model: Prototype model should be used when the desired system needs to have a lot of interaction with the end users. Typically, online systems, web interfaces have a very high amount of interaction with end users, are best suited for Prototype model. It might take a while for a system to be built that allows ease of use and needs minimal training for the end user. Prototyping ensures that the end users constantly work with the system and provide a feedback which is incorporated in the prototype to result in a useable system. They are excellent for designing good human computer interface systems.
- 11. Advantages of Prototype model: Users are actively involved in the development Since in this methodology a working model of the system is provided, the users get a better understanding of the system being developed. Errors can be detected much earlier. Quicker user feedback is available leading to better solutions. Missing functionality can be identified easily Confusing or difficult functions can be identified Requirements validation, Quick implementation of, incomplete, but functional, application.
- 12. Disadvantages of Prototype model: Leads to implementing and then repairing way of building systems. Practically, this methodology may increase the complexity of the system as scope of the system may expand beyond original plans. Incomplete application may cause application not to be used as the full system was designed Incomplete or inadequate problem analysis.
- 13. Incremental Model In this model, each module passes through the requirements, design, implementation and testing phases. A working version of software is produced during the first module, so you have working software early on during thesoftware life cycle. Each subsequent release of the module adds function to the previous release. The process continues till the complete system is achieved.
- 15. When to use the Incremental model: This model can be used when the requirements of the complete system are clearly defined and understood. Major requirements must be defined; however, some details can evolve with time. There is a need to get a product to the market early. A new technology is being used Resources with needed skill set are not available There are some high risk features and goals.
- 16. Advantages of Incremental model: Generates working software quickly and early during the software life cycle. This model is more flexible – less costly to change scope and requirements. It is easier to test and debug during a smaller iteration. In this model customer can respond to each built. Lowers initial delivery cost. Easier to manage risk because risky pieces are identified and handled during it’d iteration.
- 17. Disadvantages of Incremental model: Needs good planning and design. Needs a clear and complete definition of the whole system before it can be broken down and built incrementally. Total cost is higher than waterfall.
- 18. Spiral Model The spiral model is similar to the incremental model, with more emphasis placed on risk analysis. The spiral model has four phases: Planning(specification), Risk Analysis, Engineering and Evaluation. A software project repeatedly passes through these phases in iterations (called Spirals in this model).
- 20. When to use Spiral model: •When costs and risk evaluation is important •For medium to high-risk projects •Long-term project commitment unwise because of potential changes to economic priorities •Requirements are complex •New product line •Significant changes are expected (research and exploration)
- 21. Advantages of Spiral model: High amount of risk analysis hence, avoidance of Risk is enhanced. Good for large and mission-critical projects. Strong approval and documentation control. Additional Functionality can be added at a later date. Software is produced early in the software life cycle.
- 22. Disadvantages of Spiral model: Can be a costly model to use. Risk analysis requires highly specific expertise. Project’s success is highly dependent on the risk analysis phase. Doesn’t work well for smaller projects.
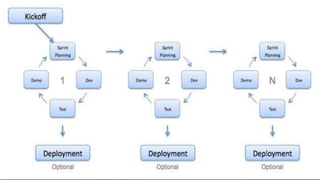
- 23. Agile Model Agile development model is also a type of Incremental model. Software is developed in incremental, rapid cycles. This results in small incremental releases with each release building on previous functionality. Each release is thoroughlytested to ensure software quality is maintained. It is used for time critical applications.
- 25. When to use Agile model: When new changes are needed to be implemented. The freedom agile gives to change is very important. New changes can be implemented at very little cost because of the frequency of new increments that are produced. To implement a new feature the developers need to lose only the work of a few days, or even only hours, to roll back and implement it. Unlike the waterfall model in agile model very limited planning is required to get started with the project. Agile assumes that the end users’ needs are ever changing in a dynamic business and IT world. Changes can be discussed and features can be newly effected or removed based on feedback. This effectively gives the customer the finished system they want or need.
- 26. Advantages of Agile model: Customer satisfaction by rapid, continuous delivery of useful software. People and interactions are emphasized rather than process and tools. Customers, developers and testers constantly interact with each other. Working software is delivered frequently (weeks rather than months).Face-to-face conversation is the best form of communication. Close, daily cooperation between business people and developers. Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design. Regular adaptation to changing circumstances. Even late changes in requirements are welcomed
- 27. Disadvantages of Agile model: In case of some software deliverables, especially the large ones, it is difficult to assess the effort required at the beginning of the software development life cycle. There is lack of emphasis on necessary designing and documentation. The project can easily get taken off track if the customer representative is not clear what final outcome that they want. Only senior programmers are capable of taking the kind of decisions required during the development process. Hence it has no place for newbie programmers, unless combined with experienced resources.