Solving equations
- 1. Solving Equations Russell Shaw GCSE Mathematics February 2010
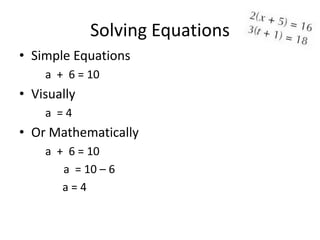
- 2. Solving Equations • Simple Equations a + 6 = 10 • Visually a =4 • Or Mathematically a + 6 = 10 a = 10 – 6 a=4
- 3. Solving Equations • Balancing Method – Keep the balance level – What you do to one side, do to the other • Mathematically: a + 6 = 10 a + 6 – 6 = 10 – 6 a=4
- 4. Solving Equations • Opposite operation – If its “add” on one side carry it over and “subtract” – If its “subtract” on one side carry it over and “add” – If its “multiply” on one side carry it over and “divide” – If its “divide” on one side carry it over and “multiply”
- 5. Solving Equations • Try these: y+3=5 11 = y – 10 2a = 6 p/5 = 3 5t = 20 b/4 = 12
- 6. Solving Equations • Try these: y+3=5 y=2 11 = y – 10 y = 21 2a = 6 a=3 p/5 = 3 p = 15 5t = 20 t=4 b/4 = 12 b = 48
- 7. Solving Equations • Combining operations: 2y + 3 = 21 • Need to get “unknowns” on one side and known on the other 2y = 21 -3 = 18 2y = 18 • Now get the unknown by itself y = 18/2 = 9 • Check your answer 2 x 9 + 3 = 18 + 3 = 21 √
- 8. Solving Equations • Try these: 2y + 5 = 15 11 = 2y – 9 2a - 4 = 6 p/5 + 4 = 14 5t + 5 = 20
- 9. Solving Equations • Try these: 2y + 5 = 15 y=5 11 = 2y – 9 y = 10 2a - 4 = 6 a=5 p/5 + 4 = 14 p = 50 5t + 5 = 20 t=3
- 10. Solving Equations • Brackets: 3(2p + 5) = 45 • Expand the brackets first • Then solve as normal 3 x 2p + 3 x 5 = 45 6p + 15 = 45 6p = 30 p=5 Check!!
- 11. Solving Equations • Letters on both sides: 4(2x – 3) = 2x + 6 • Expand the brackets first 8x – 12 = 2x + 6 • Get the “unknowns” on one side and known on the other 6x = 18 • Then solve as normal x=3
- 12. Solving Equations • Try these: 2y + 3 = 5y – 6 5t + 7 = 3t + 10 2(a + 3) = 7 3(5r + 2) = 12r – 8 6(g + 7) = 3(4g + 2)
- 13. Solving Equations • Try these: 2y + 3 = 5y – 6 y=3 5t + 7 = 3t + 10 t = 3/2 2(a + 3) = 7 a = 1/2 3(5r + 2) = 12r – 8 r = -14/3 6(g + 7) = 3(4g + 2) g=6
- 14. Solving Equations • Word Formulae pay = rate of pay x hours worked + bonus If rate of pay = £7/hour and hours worked = 40 and a bonus of £20 is given, how much is the pay? pay = £7 x 40 + £20 = £280 + £20 = £300 • A word formulae uses words to represent relationships between quantities
- 15. Solving Equations • Algebraic Formulae pay = rate of pay x hours worked + bonus We could represent pay as P, rate of pay as R, hours worked as H and bonus as B So P=RxH+B P = RH + B If R = £8/hour and H = 30 and B = £10, how much is the pay? pay = £8 x 30 + £10 = £240 + £10 = £250 An algebraic formulae uses letters to represent relationships between quantities
- 16. Solving Equations • Try this: – Write a word formula and an algebraic formula for the area of a rectangle – Use your formula to find the area of a rectangle with length = 10 and width = 3
- 17. Solving Equations • More complicated formulae s = ½ a t2 Find s when t = 4 and a = 10 s = ½ x 10 x 42 s = ½ x 10 x 16 s = ½ x 160 s = 80
- 18. Solving Equations • Rearranging to change the subject of a formula – You will need to be able to rearrange formulae. H = (4t + 6)/s – Make t the subject of the formula H = (4t + 6)/s H x s = (4t + 6) 4t + 6 = Hs 4t = Hs – 6 t = (Hs – 6)/4
- 19. Solving Equations • Rearranging to change the subject of a formula • Once you can rearrange you can solve problems – If Perimeter = 30cm and rectangle has length 8 cm and width y cm – find y. • P = 2 x l + 2 x w = 2l + 2w • So P – 2l = 2w • So w = (P – 2l)/2 • w = (30 – 2 x 8) / 2 = 7 cm
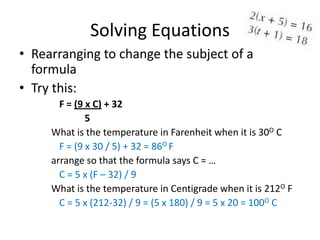
- 20. Solving Equations • Rearranging to change the subject of a formula • Try this: F = (9 x C) + 32 5 What is the temperature in Farenheit when it is 30O C Rearrange so that the formula says C = … What is the temperature in Centigrade when it is 212O F
- 21. Solving Equations • Rearranging to change the subject of a formula • Try this: F = (9 x C) + 32 5 What is the temperature in Farenheit when it is 30O C F = (9 x 30 / 5) + 32 = 86O F arrange so that the formula says C = … C = 5 x (F – 32) / 9 What is the temperature in Centigrade when it is 212O F C = 5 x (212-32) / 9 = (5 x 180) / 9 = 5 x 20 = 100O C
- 22. Solving Equations • Inequalities • Values maybe more than… or less than… • > means greater than • < means less than • ≥ means greater than or equal to • ≤ means less than or equal to
- 23. Solving Equations • Inequalities • Things maybe more than… or less than… • 6 is greater than 4 6 > 4 • 5 is less than 10 5 < 10 • x is greater than or equal to 5 x ≥ 5 • 2 is less than or equal to y 2≤y
- 24. Solving Equations • Inequalities on a number line • We can represent inequalities on a number line. • If the number is “included” – using a ≥ or ≤ symbol – we make the end point a solid circle • x ≥ -1 • If the number is “excluded” – using a > or < symbol – we make the end point an empty circle • x<2
- 25. Solving Equations • Inequalities on a number line • We can represent dual inequalities on a number line. • -3 < x ≤ 4 (-3 is less than x, and x is less than or equal to 4) • -4 ≤ x ≤ 3
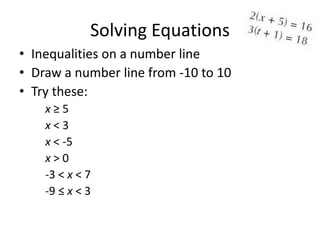
- 26. Solving Equations • Inequalities on a number line • Draw a number line from -10 to 10 • Try these: x≥5 x<3 x < -5 x>0 -3 < x < 7 -9 ≤ x < 3
- 27. Solving Equations • Solving Inequalities • You maybe asked to give the integer solutions to an inequality • -3 < x ≤ 4 -3 is NOT included (<), BUT 4 is included (≤) so the solution is: -2 , -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
- 28. Solving Equations • Solving Inequalities • Find integer solutions to: -2 ≤ n ≤ 1 0<n<5 • Write an inequality for the integers listed: -2, -1 , 0 , 1, 2, 3, 4 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
- 29. Solving Equations • Solving Inequalities • Find integer solutions to: -2 ≤ n ≤ 1 -2, -1, 0, 1 0<n<5 1, 2, 3, 4 • Write an inequality for the integers listed: -2, -1 , 0 , 1, 2, 3, 4 -2 ≤ n < 5 or -1 < n ≤ 4 or .. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 0 < n < 7 or 1 ≤ n < 7 or ..
- 30. Solving Equations (H) • Solving Inequalities • We can solve inequalities – just like equations • Solve 3x + 3 > 18 3x > 18 – 3 = 15 x > 15/3 = 5 x >5 • These can have brackets included too –just like normal equations!
- 31. Solving Equations (H) • Solving Inequalities • We can solve inequalities – just like equations • When solving you can: – Add or subtract same quantity to both sides – Multiply or divide both sides by the same positive quantity • BUT you can’t: – Multiply or divide both sides by a negative quantity
- 32. Solving Equations (H) • Solving Inequalities • You can solve two sided inequalities by treating it as two separate inequalities. • 7 ≤ 3x -2 < 10 So solve: 7 ≤ 3x -2 and 3x -2 < 10 Writing the answer as 3 ≤ x < 4
- 33. Solving Equations (H) • Solving Inequalities • Try these: 3p – 5 ≤ 4 1 + 6b > 7 8 – 2m ≥ 1 – 4m 7 < 4p + 3 ≤ 27 3 < 2q – 7 < 7
- 34. Solving Equations (H) • Solving Inequalities • Try these: 3p – 5 ≤ 4 p≤3 1 + 6b > 7 b>1 8 – 2m ≥ 1 – 4m m ≥ -7/2 7 < 4p + 3 ≤ 27 1<p≤6 3 < 2q – 7 < 7 5<q<7