Stars and solar system
- 2. TOPIC-“ Stars and Solar System ” OBJECTIVE-Creativity, Communication Skills, Scientific Temperament GROUP NAME-“ GALAXY POINTERS ” MEMBERS NAME- Abhimanyu Gupta Anurag Sharma Atul Mishra Saral Upadyaya Tarok Bakshi
- 3. INTRODUCTION On a clear night, we can see many stars. These appear to twinkle when viewed from the earth. Apart from the stars and the moon, we can also sometimes see some other ‘bright objects’ in the night sky. These, however, do not twinkle. They are planets. The word ‘planet’ is of Greek origin and means ‘wanderers’. Unlike the stars which appear almost fixed , the planets keep on changing there positions. There observed brightness is because of the light of the sun reflected by them. In Hindi, planets are known as GRAHAS. We also sometimes observe bright lines of light, flashing across the sky for a very short duration; we call these as shooting stars. The stars, the sun, the moon, the planets and the shooting stars are the main celestial objects that make up the universe. If we look up into the sky on a clear dark night, we can see a faint band of light running across the heavens. This is the MILKY WAY, our own Galaxy. It contains about two hundred billion stars and countless other objects. The stars of this galaxy spread out from its centre like a spiral. Therefore it is, known as SPIRAL GALAXY. All members of this galaxy, including the sun and its solar family, and billions of other stars, revolve around its centre.
- 4. of sun to reach the earth. The sun’s distance from the earth is therefore 14.4 crore kilometers! The color of a star is determined by its surface temperature. Stars, which have a lower temperature, appear red. Those with a high temperature appear white and those with a very high temperature are blue. The size and color of stars changes with brightness and temperature. After the sun, it is the star SIRUS, which is the brightest star in the night sky. The stars, like the sun appear to move from east to west. This is due to the rotation of earth on its axis from west to east. Hence, a star which appears to rise in the evening, appear to set in west in the early morning. Stars are very hot and huge heavenly objects made up of very hot gases. They appear like ‘dots’ only because they are very very far away from us. Their light takes million of years to reach the earth. Distances of stars are, therefore, expressed in terms of a unit called, the light year. One light year is the distance travelled by light in one year. The star nearest to the earth is the Sun. The next nearest star is the ALPHA CENTUARI or PROXIMA CENTUARI. This is at a distance of 4.3 light years from the earth. This means that we get light from this star only 4.3 years after it gets emitted from it! In comparison it takes about 8 minutes only for the light
- 5. The revolution of earth around the sun and its rotation about its own axis is the cause of the same star rising four minutes earlier after each day. This implies that the ‘set up’ of the sky changes every night. The POLE STAR, is also called DHURAV TARA in Hindi. It is a special star present in the northern hemisphere. This star, unlike the other stars, appears to be fixed at one place. In fact, all the stars appear to revolve around the pole star. This is so, because it lies on a line close to the axis of rotation of the earth. Because of this special feature, this star has been very useful to travellers. It helps them to find direction at night. The pole stars defines the north direction. The other directions can then be defined with respect to this direction.
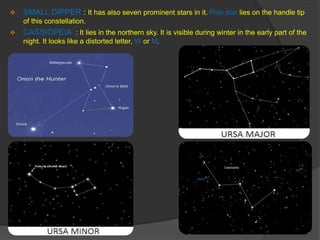
- 6. CONSTELLATIONS A close and careful observation on the stars on a clear night reveals that some of these stars appear to form some kind of patterns that appear to resemble some familiar shapes. Such a group of stars is known as a constellation. Thus, a constellation is a group of stars that appear to form some recognizable pattern or shape in the sky. ORION : In winter evening we observe three bright stars, that are part of there Orion. It has seven bright stars. Four of these appear to be arranged in the form quadrilateral and the other three form a straight line in the middle. One of the largest of a stars, known as Betalgeuse, is situated on one corner of this quadrilateral while another bright star, called Rigel, is located on its opposite corner. BIG DIPPER : The Big Dipper is made up of seven stars in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is also known as Ursa Major or Great Bear. The Hindi name for Big Dipper is Saptrishi. In this constellation, the two stars, at the top, are called pointers. This is because the line joining them, points in the direction of Pole Star.
- 7. SMALL DIPPER : It has also seven prominent stars in it. Pole star lies on the handle tip of this constellation. CASSIOPEIA : It lies in the northern sky. It is visible during winter in the early part of the night. It looks like a distorted letter, W or M.
- 8. THE MOON On a full moon day, the earth lies in between the moon and the sun. On this day, the full face of the moon is visible to us. On a new moon day (nearly fifteen days after the full moon day), the moon is on the other side of the earth, hence, we cannot see it. On the days following the new moon day, the illuminated part of the moon (that is visible from the earth) appears crescent in shape. The size of this illuminated part goes on increasing day by day until its full face becomes visible again on the full moon day. These appearances of moon on different days, are known as the phases of the moon. The moon, is our nearest neighbour in the space. It is a natural satellite of the earth. It has no air and almost no water on it. It does not have any light of its own. Its observed silvery glow is only due to the light of the sun reflected by its surface. Moon takes nearly 29.5 solar days to make one complete revolution around the earth. Although one half of the moon (the half facing the sun) is always illuminated by the sun light, the ‘lighted up’ portion, of the moon appears to change shape (as viewed from the earth). This is due to changes in the relative position of the earth, the sun and the moon. During the first half of the moon’s orbit, the moon’s visible size grows (waxes). During the remaining half of its orbit, the shape of moon appears to decrease (wanes) in size.
- 9. In 1969, the American astronaut, Neil Armstrong landed on the moon for the first time, followed by Edwin Aldrin. They found the Moon’s surface to be dusty and barren. Craters, upto hundreds of kilometres wide, cover its surface. It also has large number of mountain ranges, valleys and lava plains. The Moon does not posses any atmosphere and water and thus, there is no weather. As there is no atmosphere to trap heat, the temperature on the Moon is extreme, ranging from 100ºC at noon to -173ºC at night.
- 10. Our solar system consists of the sun and the eight planets. The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Besides planets, the solar system consists of a large number of minor planets or asteroids, a host of comets and meteors. The gravitational pull (attraction) between the sun and these celestial bodies keep all of them revolving around it. The solar system is dominated by the Sun, which accounts for almost 99.9% of the matter of the whole system. The Sun is also the source of almost all the energy in the solar system. The Earth receives almost all its energy (heat and light) from the sun. The Sun is essentially a sphere of hot gases. The temperature of the bright disc (visible), which is the source of energy for us is about 6,000 K. The disc is called the photosphere. The radius of the Sun is almost 100 times the radius of the earth and its mass is about a million times the mass of the earth.
- 11. PLANETS The name planet has been given to all those (bright) heavenly bodies that revolve around the sun. They look like star s but they do not twinkle. Their observed brightness is only due to the light of the sun reflected by them. There are eight planets in our solar system. They move in elliptical-shaped paths called orbits, around the sun. The eight planets of our solar system, in increasing order of distances from the sun, are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The planets are divided into two categories: 1. The Terrestrial Planets 2. The Jovian Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are the Terrestrial planets. They have solid and rocky surfaces. The Jovian planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets are very large in size and are made up largely of gases.
- 12. Venus (Shukra) Mercury lies closer to the sun than any other planet. It is a dry, hot and virtually airless planet. It has craters like the moon, but its interior is similar to that of the earth. Like the earth, its interior contains iron and other heavy elements. Mercury is much smaller in size than the earth. It is occasionally visible just before sunrise or immediately after sunset. Hence, it is often known as the morning or evening star. Being close to the sun, it takes only 88 earth days to go once around the sun. Venus is the brightest objet in our sky after the sun and the moon. Its bright appearance is due to its cloudy atmosphere which reflects almost three- fourth of the sunlight falling on it. Venus is almost the same size as the earth but rotates relatively slowly around its axis. It rotates from east to west while the earth rotates from west to east. It has no moon or satellite of its own. Venus is even hotter than mercury though it is relatively farther away from the sun. This is because of the high percentage of CO2 in its atmosphere. Venus is also known as a morning or evening star as it is usually visible only during these times. It also shows phases like the moon. Mercury (Budh)
- 13. The earth is very unique and special planet of our solar system. The portion of the earth facing the sun at any time has day; the other portion facing away has night. As the earth rotates on its axis, ‘day and night’ follow one another. The axis of rotation of the earth is known to be tilted with respect to its orbit. It completes one revolution around the sun in nearly 365 ¼ days. When the northern hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it is summer there. At that time, it is winter in the southern hemisphere. radiation from the sun and protects us from its harmful biological effects. The atmosphere also acts like a natural greenhouse. This keeps the temperature of the earth in the range suitable for the continuation of life. The reverse happens when the northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun. Autumn and spring occur when the earth is in between these two extreme position in its orbit. From outer space, earth appears blue and green due to the reflection of light from water and landmasses on its surface. It has a thin atmosphere. Though thin, it plays a very vital role in protecting and preserving life on the earth. It protects us from being hit by smaller bodies of the solar system. It has an ozone layer, which absorbs the ultraviolet Earth (Prithvi)
- 14. Mars (Mangal) Mars usually appears reddish in colour hence, it is also often known as the red planet. Its surface resembles a cold high altitude desert. Its atmosphere consists primarily of CO2, along with small amounts of nitrogen, oxygen, water vapour and other gases. Its surface temperature and surface pressure both are very low. These conditions make it unlikely for water to exits in a liquid state on this planet. The diameter of Mars is only a little more than half of that of earth. It mass is, however, only one- tenth of that of the earth. Mars, therefore, has a low average density as compared to the earth. Mars has two natural satellites or moons named Phobos or Deimos. It is no wonder that earth is the only planet in the solar system that can sustain life on its surface. It fulfills and meets the conditions needed for development and sustenance of life. We can summerize these conditions as: 1. the right size and right distance from the sun so that it has right temperature range and gravity. 2. presence of water on its surface. 3. suitable atmosphere and a blanket of ozone layer.
- 15. Jupiter (Brihaspati) Jupiter is the largest of all planets. Its volume is 1,300 times more than that of the earth. It shows its own colouful bands. These are believed to be due to its strong atmospheric currents and the dense cloud- cover around it. Jupiter consists mainly of hydrogen and helium in gaseous form. Its cloud-cover is made up of methane, in gaseous form, with some ammonia in crystalline form. Till date, Jupiter is known to have 28* moons. Saturn is quite similar to Jupiter in size, mass and composition. It is the second largest planet of the solar family. It is distinguished by its very unique and special system of rings. These rings give it a beautiful appearence. These rings can be seen clearly only with the help of telescope. Saturn is also known to have 30* natural satellites or moons of its own. This planet has the largest numbers of moons amongst all the planets. Saturn (Shani) * The number of moons of the Jovian planets keeps on changing. With the improvement in observing techniques, many new moons may be discovered.
- 16. Uranus (Arun) Uranus is also a very large planet. In fact, it is the third largest planet of the solar system. Its diameter is almost four times of than that of the earth. That means it can contain as many as (nearly) 64 earths in it. Hydrogen and methane have been detected in the atmosphere of this planet. This planet is observed to have blue-green colours. This is believed to be because of the presence methane gas in its cold, clear atmosphere. Its northern hemisphere remains in a four-decade long period of darkness because of the way the planets rotates. So far 21* satellites or moons of Uranus have been discovered. Neptune is very far away from the sun and is visible only through a telescope. It has been named after the Roman sea god Neptune. Neptune has 8* satellite revolving around it. We do not have much detailed information about this planet. This is mainly because of its very large distance from the earth as well as from the sun. Neptune (Varun) * The number of moons of the Jovian planets keeps on changing. With the improvement in observing techniques, many new moons may be discovered.
- 17. Apart from the sun, the eight planets and their associated moons, there also some other minor bodies in the solar system. These are the asteroids, meteors and comets. These are very small planets or planetoids that are found mainly in a belt between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter. Each asteroid has its own orbit. Taken together, the orbits of all of them are spread over a large distance, forming a band. Astronomers have discovered more than 500 asteroids which are larger than 48 km in diameter. Ceres is the largest of the asteroids discovered till now. The name comet means a ‘hairy star’. Comets are relatively small and icy celestial bodies revolving around the sun. When a comet is near the sun, some of the ‘ice’ in it turns into gas. The gas and loose dust, freed from the ice, create a long illuminated tail that streams behind the comet. Approximately, 2,000 comets have been observed over the years. Comets are visible only when they are near the sun. This is because the intense solar heat vaporizes parts of their icy matter an creates their characterised illuminated tail.
- 18. space. When that happens, they get intensely heated up due to the friction resulting from their rapid motion through the earth’s atmosphere. This makes them shine brilliantly like fireballs. Their view then consists of luminous heads followed by a comet like tail of light that may persist for several minutes. We call them as shooting or falling stars. They exist but for a short while because the intense heat vaporizes them off very quickly. There are, however, some meteors that are so large that a part of them is able to reach the surface of the earth. We call such large meteors as meteorites. Study of meteorites, found on the earth, has helped scientists to know more about the nature of the materials from which all celestial bodies, in our solar system, may have been formed. There are a few periodic comets that appear again and again at regular (nearly constant) intervals. The best known of such ‘periodic comets’ is the Halley’s comet. It appears (approximately) after every 76 years. It was last seen in the year, 1986. It is, therefore, next expected to ‘pass by’ the earth in the year, 2062. Meteors are relatively small solid bodies that also revolve around the sun. Some of them, by chance, may enter into the earth’s atmosphere from outer
- 19. Celestial bodies like the earth’s moon, revolving around a planet, are called its natural satellites. Artificial satellites are man-made objects which can be made to revolve around the earth. They are, however, much closer to the earth than the moon. Artificial satellites perform various tasks, such as transmitting radio, telephone and television signals, sending back information for weather forecasting, military surveillance and for locating mineral resources. Satellites, that are being put to maximum use, are the geostationary satellites. A geostationary satellite appears to remain fixed with respect to a particular point on the earth. For such satellites, the time period of their revolution around the earth, equals the time period of rotation of the earth around its own axis (i.e. nearly 24 hours). It is these satellites that have made global audio-visual communication such as practical, and now routine, reality. These satellites stay in the same position relative to the surface of the earth, hence, the broadcasting station does not loose contact with the receiver. Satellites have revolutionized communication by making worldwide telephone links and live broadcast. A satellite receives a microwave signal from a ground station on the earth (amplified) signal back to a receiving station on earth at a different frequency (the down link).