Stem Functions And its modifications
- 2. Before we go any further in this presentation, let’s define a stem. A stem: is generally considered to be the central axis of the plant. supports the leaves and flowers of a plant. has nodes from which new shoots and sometimes new roots can arise. is usually found above-ground, but can be modified and found below-ground as well.
- 3. FUNCTION OF STEMS Stems support leaves and branches. Stems transport water and solutes between roots and leaves. Stems in some plants are photosynthetic. Stems may store materials necessary for life (e.g., water, starch, sugar). In some plants, stems have become adapted for specialized functions.
- 4. Stems support a display of leaves. Stems orient the leaves toward the light with minimal overlap among the leaves. Asclepias - milkweed
- 7. Cacti - stout fleshy stems that are modified for food and water storage and photosynthesis.
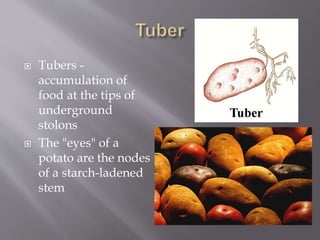
- 8. Tubers - accumulation of food at the tips of underground stolons The "eyes" of a potato are the nodes of a starch-ladened stem
- 9. A corm is a swollen, vertical stem with a papery covering. Gladiolus and Crocus are examples of plants that form corms.Crocus corms
- 10. Bulbs - large buds with a small stem at the lower end surrounded by numerous fleshy leaves, adventitious roots at base Examples include onion, tulip, and lily
- 11. Rhizomes - horizontal stems that grow below the ground with adventitious roots Examples of plants that can produce rhizomes are irises, ferns, and grasses.
- 12. Other plants, like ginger, produce large, thick rhizomes called pachymorphs. The pachymorph rhizome of Ginger
- 13. Honey locust (modified stem) Black Locust (modified leaf stipules)
- 14. Grape Tendrils
- 15. Stolons or runners - horizontal stem that grows above the ground with long internodes Examples of plants that can produce stolons are strawberry and airplane plants
- 16. A stem : supports leaves and branches. transports water and stores food. performs photosynthesis. performs specialized functions in different conditions. Stem Modifications: • Tuber • Stolon • Corm • Tendril • Bulb • Rhizome