Stones
- 1. 10. STONE AND REINFORCED10. STONE AND REINFORCED MASONRYMASONRY
- 2. 2 Chapter 9Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Stone & Concrete Masonry
- 3. 10.1 STONE AND REINFORCED MASONRY -10.1 STONE AND REINFORCED MASONRY - OVERVIEWOVERVIEW 10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY 10.3 QUARRYING AND PRODUCING OF BUILDING STONES10.3 QUARRYING AND PRODUCING OF BUILDING STONES 10.4 TYPES OF STONE MASONRY WALLS AND THEIR10.4 TYPES OF STONE MASONRY WALLS AND THEIR CONSTRUCTIONCONSTRUCTION 10.5 PRECAST CONCRETE MASONRY AND CONSTRUCTION10.5 PRECAST CONCRETE MASONRY AND CONSTRUCTION OF WALLSOF WALLS
- 4. 4 Stone vs BrickStone vs Brick Similarities:Similarities: – Both stackedBoth stacked – Mortar JointsMortar Joints Differences:Differences: – Shape:Shape: » Brick molded - Stone Cut and CarvedBrick molded - Stone Cut and Carved – Physical Properties:Physical Properties: » Brick made/controlled – Stone provided by natureBrick made/controlled – Stone provided by nature
- 5. 10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY Stone Masonry:Stone Masonry: Building stones obtained by quarrying from the rocky strataBuilding stones obtained by quarrying from the rocky strata of earth and reducing it to the required shapes and sizes for constructionof earth and reducing it to the required shapes and sizes for construction Types of rock:Types of rock: (i)(i) IgneousIgneous - Formed as a result of cooling of the molten- Formed as a result of cooling of the molten rock to solid state - It is nonporous, hard, strong and durable -rock to solid state - It is nonporous, hard, strong and durable - GraniteGranite:: Consists mainly of quartz, feldspar, mica, and other colored minerals; colorsConsists mainly of quartz, feldspar, mica, and other colored minerals; colors include black, gray, red, pink, brown, buff, and green -include black, gray, red, pink, brown, buff, and green - Serpentine:Serpentine: MainMain ingredient is serpentine; color ranges from olive green to greenish black, is fineingredient is serpentine; color ranges from olive green to greenish black, is fine grained and densegrained and dense -- BasaltBasalt:: Color ranges from gray to black; used mainly forColor ranges from gray to black; used mainly for paving stones and retaining walls -paving stones and retaining walls - (ii)(ii) SedimentarySedimentary:: Sediments deposited bySediments deposited by the action of water or wind gets consolidated to a rock -the action of water or wind gets consolidated to a rock - SandstoneSandstone:: Sedimentary rock composed of sand sized grains made of silica, iron oxide andSedimentary rock composed of sand sized grains made of silica, iron oxide and clay - Colors include gray, brown, light brown, buff, russet, red, copper, andclay - Colors include gray, brown, light brown, buff, russet, red, copper, and purple -purple - Shale:Shale: Derived from clays and silts; weak along planes and is in thinDerived from clays and silts; weak along planes and is in thin laminations - High in limestone and color varies from black to red, yellow, andlaminations - High in limestone and color varies from black to red, yellow, and blueblue
- 6. 6 GraniteGranite Non-porous, hard, strong, durableNon-porous, hard, strong, durable Color RangeColor Range Surface TexturesSurface Textures SourcesSources Primary UsesPrimary Uses
- 9. -- Shale:Shale: Derived from clays and silts; weak along planes and is in thinDerived from clays and silts; weak along planes and is in thin laminations - High in limestone and color varies from black to red, yellow, andlaminations - High in limestone and color varies from black to red, yellow, and blueblue -- Limestone:Limestone: Sedimentary rock composed of calcite and dolomite - ThreeSedimentary rock composed of calcite and dolomite - Three types: oolitic, dolomitic and crystalline - Has high compressive strength - Usedtypes: oolitic, dolomitic and crystalline - Has high compressive strength - Used for building stones and for paneling -for building stones and for paneling - Metamorphic:Metamorphic: Igneous or sedimentaryIgneous or sedimentary rock transformed by heat and pressure into another rock -rock transformed by heat and pressure into another rock - Marble:Marble: Recrystallized limestone, color varies from white through gray and black, red,Recrystallized limestone, color varies from white through gray and black, red, violet, pink, yellow, and green - Presence of oxides of iron, silica, graphite,violet, pink, yellow, and green - Presence of oxides of iron, silica, graphite, carbonaceous, matter, and mica produce these color variationscarbonaceous, matter, and mica produce these color variations 10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY (Cont’d)(Cont’d)
- 10. 10 Limestone & SandstoneLimestone & Sandstone Porous, relatively weakPorous, relatively weak Color RangeColor Range Surface TexturesSurface Textures SourcesSources Primary UsesPrimary Uses
- 12. -- Quartzite:Quartzite: It is a variety of and stone composed of mainly granularIt is a variety of and stone composed of mainly granular quartz cemented by silica, color varies from brown, buff, tan, ivory, redquartz cemented by silica, color varies from brown, buff, tan, ivory, red through gray -through gray - Schist:Schist: Made of silica with smaller amounts of iron oxideMade of silica with smaller amounts of iron oxide and magnesium oxide - Color varies from blue, green, brown, gold,and magnesium oxide - Color varies from blue, green, brown, gold, white, gray, and red -white, gray, and red - Slate:Slate: Consists mainly of clays and shales - MajorConsists mainly of clays and shales - Major ingredients are silicon dioxide, iron oxide, potassium oxide, magnesiumingredients are silicon dioxide, iron oxide, potassium oxide, magnesium oxide, and sometimes titanium, calcium and sulfur - Slate found inoxide, and sometimes titanium, calcium and sulfur - Slate found in parallel layers, which enables it to be cut into thin sheetsparallel layers, which enables it to be cut into thin sheets 10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY10.2 TYPES OF ROCKS USED IN STONE MASONRY (Cont’d)(Cont’d)
- 14. 14 Marble - Exterior Application
- 16. Produced by blasting or cuttingProduced by blasting or cutting - Irregular-sized stone is produced by- Irregular-sized stone is produced by blasting the rock, the larger pieces are cut into smaller units for use as anblasting the rock, the larger pieces are cut into smaller units for use as an exterior finish, rest is crushed and sorted into various sizes as aggregates -exterior finish, rest is crushed and sorted into various sizes as aggregates - Most of the dimensional stones used in building construction are producedMost of the dimensional stones used in building construction are produced by cutting large blocks in the quarry - Cut with diamond belt saws (12ftby cutting large blocks in the quarry - Cut with diamond belt saws (12ft wide, 2 to 5 ft thick, and 50 ft long); rubber air bags inflated in the saw cutwide, 2 to 5 ft thick, and 50 ft long); rubber air bags inflated in the saw cut to break it away and then the separated rock is lowered onto prepared stoneto break it away and then the separated rock is lowered onto prepared stone chips cushion - Thereafter it is cut into smaller sizes and transported bychips cushion - Thereafter it is cut into smaller sizes and transported by front-end loaders to the mill for further processingfront-end loaders to the mill for further processing 10.3 QUARRYING AND PRODUCING BUILDING10.3 QUARRYING AND PRODUCING BUILDING STONESSTONES
- 17. 17 Types of StoneTypes of Stone FieldstoneFieldstone Rubble StoneRubble Stone Dimension StoneDimension Stone
- 18. 18 Stone Masonry PatternsStone Masonry Patterns Laid in MortarLaid in Mortar RubbleRubble (Unsquare pieces)(Unsquare pieces) AshlarAshlar (Square Pieces)(Square Pieces) Coursed or RandomCoursed or Random OrientationOrientation
- 19. 19
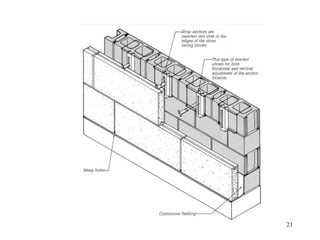
- 20. 10.4.1 Types of Stone Masonry Walls:10.4.1 Types of Stone Masonry Walls: (i)(i) Solid masonry wallSolid masonry wall mademade by laying stone masonry over a prepared bed of mortar, and proceeding in a similar mannerby laying stone masonry over a prepared bed of mortar, and proceeding in a similar manner to increase the height;to increase the height; (ii) Composite wall(ii) Composite wall made of an outer wall of large stone slabs,made of an outer wall of large stone slabs, attached to a backing of structural frame or brick/concrete masonry wall; andattached to a backing of structural frame or brick/concrete masonry wall; and (iii) Cavity(iii) Cavity wallwall made by two different types of masonry wall separated by a cavity, which is eithermade by two different types of masonry wall separated by a cavity, which is either insulated or empty and connected together by metal tiesinsulated or empty and connected together by metal ties 10.4.2 Laying of stone masonry blocks in a wall:10.4.2 Laying of stone masonry blocks in a wall: (a) Rubble(a) Rubble MasonryMasonry - Composed of unsquared pieces of stones; mason has to choose carefully each- Composed of unsquared pieces of stones; mason has to choose carefully each stone so that it can fit into the available space -stone so that it can fit into the available space - (b) Ashlar masonry(b) Ashlar masonry - Made of- Made of squared pieces of stones; mason has to carefully lift the heavy stones by a hoist and lower itsquared pieces of stones; mason has to carefully lift the heavy stones by a hoist and lower it into place -into place - (c) Coursed stone masonry:(c) Coursed stone masonry: has continuous horizontal joints -has continuous horizontal joints - (d)(d) Uncoursed or random masonry :Uncoursed or random masonry : Does not have defined bedding planes for theDoes not have defined bedding planes for the wallwall 10.4 TYPES OF STONE MASONRY WALLS AND THEIR10.4 TYPES OF STONE MASONRY WALLS AND THEIR CONSTRUCTIONCONSTRUCTION
- 21. 21
- 22. 22
- 23. 10.5 PRECAST CONCRETE MASONRY AND10.5 PRECAST CONCRETE MASONRY AND CONSTRUCTION OF WALLSCONSTRUCTION OF WALLS 10.5.1 Precast Concrete Masonry Blocks10.5.1 Precast Concrete Masonry Blocks:: Manufactured by vibrating aManufactured by vibrating a stiff concrete mixture into metal molds, immediately turning it out wet onto astiff concrete mixture into metal molds, immediately turning it out wet onto a rack (so that the mold can be reused immediately) at a rate of 1000 or more unitsrack (so that the mold can be reused immediately) at a rate of 1000 or more units per hour - Racks are cured at an accelerated rate by subjecting them to steam,per hour - Racks are cured at an accelerated rate by subjecting them to steam, either at the atmospheric pressure or for faster curing at higher pressure. Aftereither at the atmospheric pressure or for faster curing at higher pressure. After the units are steam cured, the units are dried to a specific moisture content, andthe units are steam cured, the units are dried to a specific moisture content, and bundled in wooded crates for shipping to the construction sitebundled in wooded crates for shipping to the construction site Made in varying sizes and shapesMade in varying sizes and shapes:: Standard hollow blocksStandard hollow blocks -- 4”x8”x16” long or 4”x8”x8” - 6”x8”x8” or 8”x8”x8”, 10”x8”x16”, or 10”x8”x8”4”x8”x16” long or 4”x8”x8” - 6”x8”x8” or 8”x8”x8”, 10”x8”x16”, or 10”x8”x8” , 12”x8”x16” or 12”x8”x8” -, 12”x8”x16” or 12”x8”x8” - Other shapes:Other shapes: Channel bond beam, Low-webChannel bond beam, Low-web beam, Solid unit, Capping unit, A-block, H block, Header unit, Control jointbeam, Solid unit, Capping unit, A-block, H block, Header unit, Control joint unit, Single Bullnose, etc.unit, Single Bullnose, etc.
- 24. 24 Concrete Masonry UnitsConcrete Masonry Units Manufacturing ProcessManufacturing Process ConfigurationsConfigurations Testing StandardsTesting Standards
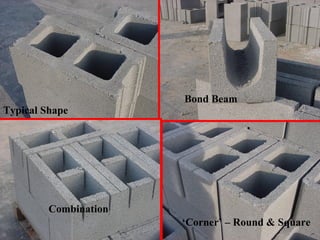
- 25. 25 Typical Shape Bond Beam Combination ‘Corner’ – Round & Square
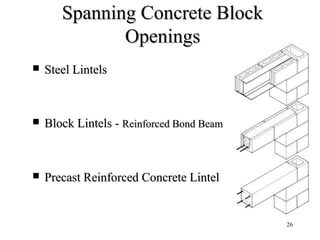
- 26. 26 Spanning Concrete BlockSpanning Concrete Block OpeningsOpenings Steel LintelsSteel Lintels Block Lintels -Block Lintels - Reinforced Bond BeamReinforced Bond Beam Precast Reinforced Concrete LintelPrecast Reinforced Concrete Lintel
- 27. 27 Reinforcing & AnchorageReinforcing & Anchorage Joint ReinforcingJoint Reinforcing – LadderLadder – TrussTruss
- 28. 10.5 PRECAST CONCRETE MASONRY AND10.5 PRECAST CONCRETE MASONRY AND CONSTRUCTION OF WALLSCONSTRUCTION OF WALLS (Cont’d)(Cont’d) -- Masonry gradesMasonry grades:: N - Grade;N - Grade; For general use above or below grade;For general use above or below grade; SS grade:grade: Above grade use only;Above grade use only; Types : Type ITypes : Type I -- Moisture-controlled units forMoisture-controlled units for use where drying shrinkage of units would cause cracking in concrete masonry;use where drying shrinkage of units would cause cracking in concrete masonry; Type IIType II - Non-moisture-controlled units - weights: Normal, medium and light- Non-moisture-controlled units - weights: Normal, medium and light weightsweights 10.5.2 Laying of Concrete Blocks in Walls:10.5.2 Laying of Concrete Blocks in Walls: MortarMortar used in stone masonry is identical to the one used earlier in brickused in stone masonry is identical to the one used earlier in brick masonry constructionmasonry construction Only the face shells of the block are mortaredOnly the face shells of the block are mortared with the webs unsupportedwith the webs unsupported Often reinforced with steelOften reinforced with steel to increase its load bearing capacity and itsto increase its load bearing capacity and its resistance to crackingresistance to cracking Concrete masonry isConcrete masonry is often reinforced with horizontal reinforcement steeloften reinforced with horizontal reinforcement steel,, introducedintroduced as welded grids of small diameter steel rodsas welded grids of small diameter steel rods, that are laid onto the, that are laid onto the bed joints, at the desired vertical intervals.bed joints, at the desired vertical intervals.
- 29. 29 System PropertiesSystem Properties SizesSizes: 10 foot lengths;: 10 foot lengths; width should be 2” lesswidth should be 2” less than wallthan wall ShapesShapes: ladder & truss: ladder & truss ConfigurationsConfigurations: Many: Many variationsvariations MaterialsMaterials: Steel with: Steel with various finishes andvarious finishes and gaugesgauges Ladder Truss
- 31. 31 Layout & Lead Blocks
- 32. 32 Installation of Mortar Bead
- 33. 33 Lay CMU
- 34. 34 Tooled Joints
- 35. 35 Control Joint
- 37. 37 Painted CMU
- 38. 38Splitface, Brick, & Tile