Stretch reflex
- 2. Contents • Objective • Definition • Stretch reflex • Functions of stretch reflex • Home work
- 3. Objective of the class To understand what is stretch Reflex
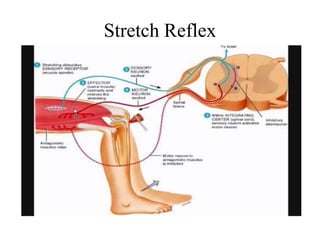
- 4. Definition • It is a muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle. It is a monosynaptic reflex which provides automatic regulation of skeletal muscle length. Features: i. Monosynaptic: a simple reflex involving only one synapse between the sensory and motor neuron. ii. Ipsilateral: the stretch reflex is ipsilateral as it stimulates only the stipulated muscle to respond on the same side and not on the opposite side. iii. Automatic regulation: a sudden change induced in a muscle length or velocity gives signal to the spinal cord, which thus sends return signal to the muscle, thus leading to contraction.
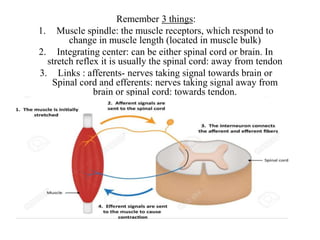
- 5. Remember 3 things: 1. Muscle spindle: the muscle receptors, which respond to change in muscle length (located in muscle bulk) 2. Integrating center: can be either spinal cord or brain. In stretch reflex it is usually the spinal cord: away from tendon 3. Links : afferents- nerves taking signal towards brain or Spinal cord and efferents: nerves taking signal away from brain or spinal cord: towards tendon.
- 6. Functions of stretch reflex • Muscle protection: stretching of spindle increasing muscle length increase in motor neuron activity muscle to contract reduce stretching. • Maintain good posture: it is the consequence of stretch reflex.
- 7. Summary….. a. Define b. 3 things to remember c. 2 Functions
- 9. Reference • Kisner C and Colby. Therapeutic exercise: foundations and techniques.6th ed. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
- 10. Thank You