states of matter
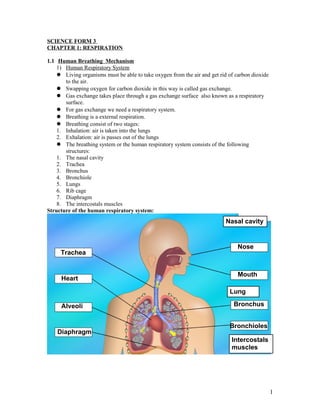
- 1. SCIENCE FORM 3 CHAPTER 1: RESPIRATION 1.1 Human Breathing Mechanism 1) Human Respiratory System Living organisms must be able to take oxygen from the air and get rid of carbon dioxide to the air. Swapping oxygen for carbon dioxide in this way is called gas exchange. Gas exchange takes place through a gas exchange surface also known as a respiratory surface. For gas exchange we need a respiratory system. Breathing is a external respiration. Breathing consist of two stages: 1. Inhalation: air is taken into the lungs 2. Exhalation: air is passes out of the lungs The breathing system or the human respiratory system consists of the following structures: 1. The nasal cavity 2. Trachea 3. Bronchus 4. Bronchiole 5. Lungs 6. Rib cage 7. Diaphragm 8. The intercostals muscles Structure of the human respiratory system: Nasal cavity Trachea Nose Mouth Heart Alveoli Diaphragm Bronchioles Bronchus Intercostals muscles Lung 1
- 2. 2) Structure of the lung The lungs are the respiratory organs. We have a pair of lungs in the thoracic cavity. They are protected by the rib cage. The lungs are connected to the trachea by two tubes. These tubes are right bronchus and left bronchus. The bronchus divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles. The bronchioles end in clusters of tiny air sacs known as alveoli, in the lungs. Flow of air into the lungs: Air is breathed in through the nose and enters the nostrils. The nostrils leads to the nasal cavity. While passing through the nasal cavity the air is warmed up and moistened. Hairs and sticky mucus trap particles inside the nasal cavity. The clean air then enters to the trachea. The trachea branches into two bronchi.Eachs bronchus leads directly into a lung. The bronchus branches into bronchioles. Each bronchiole end in a cluster of air sacs called alveoli/alveolus. The wall of the alveolus is only one-cell thick. It is thin, moist and surrounded by a network of capillaries. The exchange of respiratory gases occurs between the alveolus and capillaries. The path of air into the lungs is summarized: Nasal cavity trachea bronchus bronchiole alveolus 2
- 3. The breathing mechanism Breathing mechanism involves: 1. Inhalation (breathing in) 2. Exhalation (breathing out) During inhalation: 1. The intercostals muscles and the diaphragm contract. 2. The diaphragm moves down wards, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. 3. The intercostals muscles pull the ribs up, expanding the ribs and further increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. 4. These actions lower the air pressure in the alveoli. 5. Air from the outside then rushes in through the nasal cavities, trachea and lungs. The lungs expand. During exhalation: 1. The intercostals muscles relax causing the rib cage to move downwards and inwards. 2. At the same time, the muscles of the diaphragm relax. The diaphragm curves upwards and returns to its original dome shape. 3. These action return the thoracic cavity to its original volume. The air pressure inside the lungs is now higher than the atmospheric pressure outside. 4. The lungs contract and the air is forced out through the respiratory tract. Comparison between inhalation and exhalation: Inhalation Aspect Exhalation Contracts,flattens and is pushed downwards. Diaphragm Relaxes and is pushed upwards. Moves upwards and outwards. Movement of rib cage and the wall of the thoracic cavity. Moves downwards and inwards. Increases Volume of thoracic cavity Decreases Decreases Air pressure in the thoracic cavity. Increases From the atmosphere to the lungs. Movement of air From the lungs to the atmosphere. 1.2 Transport of Oxygen in the Human Body 1. Diffusion of oxygen from the alveolus to the capillaries. The exchange of gases occurs by diffusion in the alveoli. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region where they are highly concentrated to a region where they are less concentrated. Inhaled air which is sucked into the lungs is rich in oxygen. The oxygen concentration in the alveolus higher than the oxygen concentration in the deoxygenated blood in the capillaries. The difference in oxygen concentration makes the oxygen diffuse easily into the blood capillaries. Oxygen in the alveolus diffuses through the walls into the blood. Carbon dioxide and water vapour diffuse from the blood into the alveolus. The characteristics enable oxygen to diffuse through the walls of the alveoli easily and efficiently 1. have very large surface areas and thin walls(only one- cell thick).The inner surfaces of the alveoli are always moist. 2. The outer surfaces of the alveoli are surrounded by a network of blood capillaries. 3
- 4. 2. Oxygen transport Through the breathing process,oxygen from the air flows into our bloodstream. The heart then pumps the oxygenated blood to supply oxygen to the body cells. Body cells need oxygen for cell respiration. Haemoglobin need to carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body. Haemoglobin is a blood pigment. As the oxygen concentration is high in the alveolus,oxygen diffuses into the capillaries.Oxygen then combines with haemoglobin in the red blood cells and forms oxyhaemoglobin. 3. Diffusion of oxygen from the capillaries to the body cells When blood reaches the body cells,oxyhaemoglobin is broken down into haemoglobin and oxygen. The oxygen then diffuses through the walls of the capillaries into the cells. Oxygen is then used to oxidise food to relaese oxygen during cell respiration. At the same time,carbon dioxide from the cells diffuses into the capillaries to be carried back to the lungs. 1.3 The importance of a healthy respiratory system 1. Effects of harmful substances: i. Nicotine in cigarettes cause the following effects: a) Stimulates the production of cells in the trachea and lungs and leads to lung cancer. b) Narrows and hardens the blood vessels.This affects blood flow and causes heart attacks. ii. Tar in tobacco is carcinogenic and can cause lung cancer. iii. Nitrogen dioxide in cigarette smoke forms an acid which can destroy lung tissues. iv. Sulphur dioxide is very soluble in the alveoli and it forms an acid which destroys the lungs. v. Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas,combines with haemoglobin in the red blood cells and prevents oxygen from combining with haemoglobin. vi. Dust and dirt can hinders the exchange of gases. 4
- 5. 2. Diseases of the respiratory system: Air pollution,the presence of harmful microbes in air,smoking and crowded cities cause respiratory diseases.Examples include asthma, influenza, pneumonia, tuberculosis,bronchitis,emphysema and lung cancer. Asthma:condition in which the tubes of the lungs become inflamed.This is because the air tubes are narrower and partially blocked. Influenza:cause by viruses which attack the mucus membranes in the respiratory system.Blocked noses,teary eyes, giddiness, headaches,aches in the limbs,coughs and feverare some of the symptoms of the diseases. Pneumonia:caused by bacteria,viruses and chemical substances in polluted air.The lungs are filled with pus and fluid and the patient will suffer from chest pains,fever and coughs. Tuberculosis:caused by bacterial infection which are carried by water droplets and dust in the air.The patient suffers prolonged coughs and spits out blood in the end stages. Bronchitis:cused by viral infections.Bronchitis makes a person cough and produce a lot of mucus.Bronchitis caused colds and phlegm.This disease makes respiration and gaseous exchange difficult. Emphysema:This disease is linked to smokers and people who work in dust areas.The patient experiences breathing difficulties. Lung cancer: Cause by smoking cigarettes.Air polluted with carcinogen from factories and vehicle emissions,dust and asbestos also cause cancer.Lung cancer is difficult to cure. 3. Improving Air Quality Pollution is mainly caused by irresponsible human behavior and improperly planned activities. We must be responsible for preserving and conserving air quality. Air pollution interferes with the respiratory process. It can cause respiratory diseases which can be fatal. To preserve and conserve the quality of air we must: 1. Support and campaign against open burning of rubbish. 2. Give up the habit of smoking. 3. Reduce the number of vehicles on the road. 4. Avoid the burning of forest for agriculture, housing and industries. 5
- 6. 2. Diseases of the respiratory system: Air pollution,the presence of harmful microbes in air,smoking and crowded cities cause respiratory diseases.Examples include asthma, influenza, pneumonia, tuberculosis,bronchitis,emphysema and lung cancer. Asthma:condition in which the tubes of the lungs become inflamed.This is because the air tubes are narrower and partially blocked. Influenza:cause by viruses which attack the mucus membranes in the respiratory system.Blocked noses,teary eyes, giddiness, headaches,aches in the limbs,coughs and feverare some of the symptoms of the diseases. Pneumonia:caused by bacteria,viruses and chemical substances in polluted air.The lungs are filled with pus and fluid and the patient will suffer from chest pains,fever and coughs. Tuberculosis:caused by bacterial infection which are carried by water droplets and dust in the air.The patient suffers prolonged coughs and spits out blood in the end stages. Bronchitis:cused by viral infections.Bronchitis makes a person cough and produce a lot of mucus.Bronchitis caused colds and phlegm.This disease makes respiration and gaseous exchange difficult. Emphysema:This disease is linked to smokers and people who work in dust areas.The patient experiences breathing difficulties. Lung cancer: Cause by smoking cigarettes.Air polluted with carcinogen from factories and vehicle emissions,dust and asbestos also cause cancer.Lung cancer is difficult to cure. 3. Improving Air Quality Pollution is mainly caused by irresponsible human behavior and improperly planned activities. We must be responsible for preserving and conserving air quality. Air pollution interferes with the respiratory process. It can cause respiratory diseases which can be fatal. To preserve and conserve the quality of air we must: 1. Support and campaign against open burning of rubbish. 2. Give up the habit of smoking. 3. Reduce the number of vehicles on the road. 4. Avoid the burning of forest for agriculture, housing and industries. 5