TECHNOLOGY FOR THE CLASSROOM, DEVICES, MOBILE LEARNING, LEARNING PLATFORMS.pdf
- 1. MAESTRÍA EN ENSEÑANZA DEL IDIOMA INGLÉS, COMO LENGUA EXTRANJERA ENSEÑANZA DEL SIGLO XXI ENFOCADA AL APRENDIZAJE DEL INGLES COMO LENGUA EXTRANJERA BY: • Lic. Jefferson Villalba TECHNOLOGY FOR THE CLASSROOM, DEVICES, MOBILE LEARNING, LEARNING PLATFORMS
- 2. What is the Background? TECHNOLOGY FOR THE CLASSROOM, DEVICES, MOBILE LEARNING, LEARNING PLATFORMS What Does Technology in the Classroom Mean? What Do Technology devices Mean? What Does Mobile learning Mean? What Does Learning Platforms Mean? “It is any tool that teacher uses to convey, enhance the lesson or interact with students”. Robert Z. “It is an educational system that supports, with the help of mobile devices, a continuous access to the learning process”. Carl Mitcham “It is an electronic tool that can be used for creating, storing, or transmitting information in the form of electronic data. ”. Merriam- Webster. “It is a webspace or portal for educational content and resources that offers a student everything they need in one place:” Cynthia Chandler. It includes: phone, laptop or tablets It includes: Speakers, printer and microphone, phone, laptop or tablet, etc.…. It includes: Coursera, Skillshare, Moodle
- 3. What evidence can you present of the usefulness of this topic for 21st century Education? • How does technology help with collaboration in education? • How does technology help with critical thinking? • How does technology help with creativity in education? • How does technology help with communication in education? Communication Group 1 Creativity Group 2 Collaboration Group 4 Critical Thinking Group 3 Focus on the 4Cs TECHNOLOGY FOR THE CLASSROOM, DEVICES, MOBILE LEARNING, LEARNING PLATFORMS -Resources are Open To Everyone. -Increased Precision In Demonstrations. -Increased Communication through websites -Light Speed Research. -Students Learn at Their Speed. -Making Learning Fun. -Assessing Students Properly. It affects critical thinking by helping students apply what they've learned to real- life situations and develop problem- solving skills They can use a set of easy and free tools to make fantastic mind-maps and visual graphs to illustrate a topic or a concept. This tool amplifies student engagement and voice and helps students lead one another to more in-depth reading and greater skill development.
- 4. What happen with the other Cs ? Choices Caring Let the students have choices. It means: • Get students attention • Motivate them • Inspire them TECHNOLOGY FOR THE CLASSROOM, DEVICES, MOBILE LEARNING, LEARNING PLATFORMS
- 5. What are the Goals? Transforming education by using information and communication technologies (ICTs) to improve students’ learning outcomes. Provide students with possibilities to construct and improve knowledge at any time or place.
- 6. What EFL Approach and 21stC. method would you use? Content Based Instruction Content-Based Instruction (CBI) is “an approach to second language teaching in which teaching is organized around the content or information that students will acquire, rather than around a linguistic. Richards & Rodgers An example of CBI lesson using technology for the classroom, devices, mobile learning, learning platforms Preparation The lesson A subject of interest is chosen. Finding suitable sources that deal with different aspects of the subject. It could be websites, reference books, audio, video, interactive lectures, learning platforms. Devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops are needed. Cs: Choices 1. Using small groups 2. Assigning each group a small research task. 3. Groups sharing and comparing information 4. Report or presentation as a learning result. APPROACH
- 7. METHOD GAMAFICATION Involves using game-based elements such as point scoring, peer competition, team work, score tables, to drive engagement, help students assimilate new information and test their knowledge.
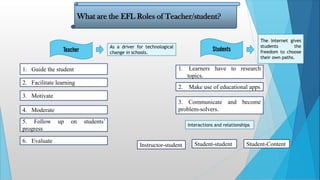
- 8. What are the EFL Roles of Teacher/student? Teacher As a driver for technological change in schools. 1. Guide the student 2. Facilitate learning 3. Motivate 4. Moderate 5. Follow up on students’ progress 6. Evaluate Students 1. Learners have to research topics. The Internet gives students the freedom to choose their own paths. 2. Make use of educational apps 3. Communicate and become problem-solvers. Interactions and relationships Instructor-student Student-student Student-Content
- 9. What about the Material? Digital learning materials Devices • Reading e-books • Listening to podcasts • Using applications for learning purposes: educational videos, educational games, accessing documents or document libraries, participating in online lessons and tutorials, receiving live-streamed lectures, accessing video clips or audio libraries, reading asynchronous publications, participating in virtual learning communities, etc. Smartphones Laptop Tablets PCs
- 10. What Language skills can be developed ?
- 11. The main learning benefits are: • By eliminating the need for learning to happen at a set time and a set place • Learning Οn Multiple Devices. • Affordability and portability • By collaborating with others in the workplace rooms. • By connecting with the world in real time. • Save Time • Higher productivity • Better reaction to complex tasks • Lower stress levels in the students. Learning Flexibility Online Learning Communities Multitasking . • Information is at your fingertips. • Many resources that supports a higher quality of learners’ performance. Better Performance
- 12. Disadvantages Multitasking May Not Be Best Technology Presents Problems • According to a 2012 article in Forbes magazine: “The distractions of daily life combined with the ongoing social and entertainment activities on mobile devices can be detrimental to their classroom performance”. • Many students may be unable to participate in class because their devices are not compatible with the class's software and websites. • Connectivity May Be Limited ("dropped class“) • Eye strain and headaches related to cellphone use. • Mobile students who spend long hours doing required reading from their devices could develop what Allamby calls "screen sightedness." Small screens can be harmful
- 13. What activities would you implement with your learners? • Digital Icebreakers • Audio Projects • Video Projects • Apps for Student Projects • Active Learning with Mobile Devices • Sharing Stories: Motivating Language Learners with Mobile Devices • Digital Storytelling
- 14. How would you incorporate the topic into the assessment process? Diagnostic assessments. Formative assessments. Summative assessments. Peer assessments Types of assessments How To Develop Mobile Learning Assessments Conclude each unit or module with an assessment. Integrate interactive assessments that can be accessed anywhere. Use Google Applications to create online quizzes and exams. TIPS
- 15. Conclusions Mobile learning opens so many doors to new technology and will continue to get more complex as the years go on. Future generations are extremely receptive to utilizing new Technology. The use of mobile technologies places the student at the center of the teaching-learning process, due to this the teacher is only the mediator between content and knowledge. Mobile-learning must be carried out with the collaboration of all the actors involved, stakeholders (educational institutions, teachers, and students) Teachers should monitor the use of smarthphones for academic purposes.
- 16. References • Batista, E., (2000). Palm reading Goes Educational. Retrieved November 19th, 2002 from the World Wide Web: http://www.wired.com/news/culture/0,1284,38065,00. • Harris, Paul (2001). Goin`Mobile. Retrieved November 10th, 2002 from the World Wide Web: http://www.learningcircuits.org/2001/jul2001/harris.html UNESCO. (2017). Retrieved June 22, 2017, from http://www.unesco.org/new/en/unesco/themes/icts/m4ed/ • Leong, D., (2001). History of PDA – The Beginning. Retrieved September 7th, 2002 from the World Wide Web: http://www.pdawear.com/news/article_pda_beginning.htm Mobile / • Cellular Technology (2002). HSCSD (High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data) Data Transfer System, International. Retrieved November 20th, 2002 from the World Wide Web: http://www.mobilecommstechnology.com/projects/hscsd/index.html • Nitsche, K. Acceptance of Mobile, Classroom-Bound E-Learning Systems from the Perspective of Students and Lectures. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, Beijing, China, 15–18 July 2013; pp. 508–509