Textile internship - Raymonds
- 1. TEXTILE INTERNSHIP RAYMONDS –TEXTILE DIVISION (VAPI) BY:- Swarnim Singh
- 2. OBJECTIVE To understand the concept of spun yarn production, grey fabric production, dyeing, printing and finishing of fabric, textile testing and their quality aspects for both technical as well as for commercial purposes.
- 3. Estb. 1925 FIRST POLY-WOOL BLEND in India (1959) MNFD. WOOL/ WOOL BLENDS STARTED MNFG. JEANS, SHIRTS TOTAL TEXTILE SOLUTIONS
- 4. ChairmanandManagingdirector oftheRaymondGroup INTRODUCTON Raymond Group is an Indian branded fabric and fashion retailer, incorporated in 1925. Raymond group is the world's largest producer of worsted suiting fabric. Raymond Limited (Textile Division) has more than 60% market share of the Indian market for worsted suiting fabrics. . It has launched its ‘Technosmart’, ‘Technostretch’ and ‘Technofresh’ in the Techno-series. RAYMOND GROUP DIVISONS TEXTILE ESP. WORSTED SUITING FABRIC AVIATION & COSMETIC S ENGINEERING FILES & TOOLS DENIMS & DESIGNER WEAR PROPHYLACTIC & TOILETRIES
- 6. ORGANISATION STRUCTURE Board of Directors Managing Director Marketing Manager Production HOD Work Manager Supervisor Workmen Finance manager ORGANISATION CHART The installed capacity of Vapi unit is 154 looms and 21840 spindles. The unit has a work force of more than 1900
- 7. VAPI PLANT ABOUT VAPI PLANT 1. Industrial Area 94.4 acres 2. Residential Area 18 acres 3. Rest forest area 4. digital computer-controlled manufacturing System 5. Automated warehouse system 6. Well connected by rail and road. 7. Fabric production: 25 million metre/annum
- 9. DEPARTMENTS AT VAPI DEPARTMENTS Production Designing Service Quality Control Sampling Supply Chain Management a. Raw Material Godown (RMG) b.GreyCombing c. Dyeing d. Recombing e. Spinning f. Yarn Room g. Weaving h. Mending i. Finishing j. Folding k. Warehouse a.Human Resource b. Accounts c. Commercial d.Engineering,Civil, Mechanical, Electrical,Safety, Instrumental e. Store f. Effluent Treatment Plant
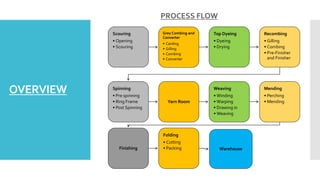
- 10. OVERVIEW PROCESS FLOW Scouring • Opening • Scouring Grey Combing and Converter • Carding • Gilling • Combing • Converter Top Dyeing • Dyeing • Drying Recombing • Gilling • Combing • Pre-Finisher and Finisher Spinning • Pre spinning • Ring Frame • Post Spinning Yarn Room Weaving • Winding • Warping • Drawing in • Weaving Mending • Perching • Mending Finishing Folding • Cutting • Packing Warehouse
- 11. STAGEWISE INDUSTRIAL PROCESS FLOWCHART
- 15. 1. Raymond raw material store RAW WOOL STORED FOR FURTHER PROCESSING
- 16. 2.WOOL SCOURING Wool Scouring is the process of washing raw wool in an alkaline solution (Esteem AJ 80-48) or detergent . It is done to remove impurities like mud, vegetable matter and grease present in the raw wool. 100 60 80 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 GREASE VEGETABLE MATTER MUD Removal of Waste
- 17. Scouring includes mixing, beating, cleaning, and drying Feed Hopper 1 Double Drum Opener Feed Hopper 2 Wing Belt Bowls6 Drum Dryer Stepped Opener Washing and Rinsing Drying
- 18. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF SCOURING MACHINE 1. scouring department capacity -14,000 kg of wool per day 2. Efficiency - 94%. 3. Machine cost- 1.8 cr 4. MACHINE CONSIST OF FOLLWING ACTION– A.MIXING:- Inclined spiked lattice and roller setup - penetrates the raw wool fibers, opens and transport further. B. BEATING- cleans the wool and removes the mud C.. CLEANING -six bowl system – 3 bowl for washing with detergent (ESTEEM 48 – AJ 80) and the last three bowls are used for rinsing the washed fibers D. DRYING - 6 drum dryer & 3 drum stepped opener
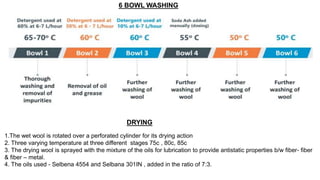
- 19. 6 BOWL WASHING DRYING 1.The wet wool is rotated over a perforated cylinder for its drying action 2. Three varying temperature at three different stages 75c , 80c, 85c 3. The drying wool is sprayed with the mixture of the oils for lubrication to provide antistatic properties b/w fiber- fiber & fiber – metal. 4. The oils used - Selbena 4554 and Selbana 301IN , added in the ratio of 7:3.
- 20. WASHING , RINSING , DRYING
- 21. GREASE RECOVERY MACHINE Dirty water from bowls of scouring machines is pumped to Grease Recovery Machine , which is clean in three level . GREASE • Grease is recovered in drums • Capacity of 180kg • Used by cosmetic companies. MUD • Sent to decanter • Purified using chemicals WATER RECYCLED • Sent to ETP • Water fed back to bowls DIRTY WATER
- 23. 3.GREY COMBING PROCESS FLOW OF GREY COMBING a. The Department has 1.2 carding machines, French manufacturer N. Schlumberger. 2. 3 gill boxes , N. Schlumberger GN8 machines 3. 10 combers ,
- 24. CARDING Carding performs many functions including: removal of vegetable impurities (like burrs) gradual opening of wool fibers Parallel arrangement of fibers as evenly as possible called card sliver.
- 25. CARDING MACHINE
- 26. GILLING The card sliver undergoes three gilling operations that prepare the card sliver for combing. This is done:- • To remove hooks, align, straighten and blend the fibers • To improve sliver uniformity (by doubling) so as to reduce fiber breakage and noil during combing • To reduce any excessive extensibility of the card sliver. • To ensure less chances of fiber breakage during combing. Gilling machine consists of:- • Draw or feed rollers - put uniform tension through the sliver and opens the fibers. • Detaching or delivery rollers- detaches the short fibers. • A nozzle -the gilled sliver is lubricated with SelbanaUN to reduce crimp and maintain friction.
- 27. GILLING MACHINE
- 28. COMBING The result is the sliver consisting of only long wool fibers parallel to each other, combed out noils which are sold to the carpet industry and are utilized in making shawls and blankets
- 29. After combing, sliver is sent to top forming machine. This machine automatically takes a fixed weight of sliver, 8.5Kg and convert it into top which is ready for dyeing. TOP FORMATION
- 30. CONVERTER MACHINE A Converter machine is used to cut polyester tows of continuous filaments into a sliver of shorter length. This process is known as converting . Converting cuts the filaments by passing them between 2 rollers. Result is a top formation of 8.5 kg.
- 31. DYEING Wool and polyester cannot be dyed together as they have different properties and affinity to different dyes. The overall dyeing process takes about 3-4 hours. Parameters Wool Polyester pH 4.5-5 4.5 Temperatur e 90 0C 1200C Dye Metal Complex Acid Dyes Reactive Dyes Disperse Dyes Time 30 minutes (only dyeing) 15 minutes (only dyeing)
- 33. LAB SAMPLING
- 34. Superlab - The Sampling room It has a dyeing machine which runs by automated Computer Color Matching Software (CCM). The Superlab machine consists of eight dyers for lab sampling with the capacity of 20g each. All the shades are given a Shade No. and Reference No. along with blend details on the shade card, SAMPLING ROOM
- 35. BULK DYEING – TOP DYEING
- 36. BULK DYEING – PIECE DYEING
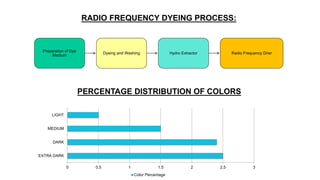
- 37. RADIO FREQUENCY DYEING PROCESS: Preparation of Dye Medium Dyeing and Washing Hydro Extractor Radio Frequency Drier 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 EXTRA DARK DARK MEDIUM LIGHT Color Percentage PERCENTAGE DISTRIBUTION OF COLORS
- 38. DYEING MACHINES PIECE DYEING YARN DYEING
- 39. RECOMBING Recombing means combine or cause to combine again or differently. Recombing is done when fine yarns of uniform shade and high quality are to be made. DEFELTER BLENDER GILLING 1 GILLING 2 GILLING 3 COMBER PRE FINISHER FINISHER PROCESS FLOW
- 41. RECOMBING PROCESS CONSIST OF
- 43. Process flow chart from wool scouring to ready-for- spinning
- 44. SPINNING Twisting together of drawn out strands of fibers to form yarn which is further used to create fabric.
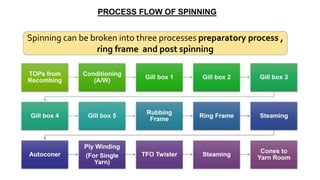
- 45. Spinning can be broken into three processes preparatory process , ring frame and post spinning PROCESS FLOW OF SPINNING
- 46. PREPRATORY PROCESS- CONDITIONING AND GILLING
- 47. ROVING AND RING FRAME
- 48. POST SPINNING - STEAMING AND AUTO-CORNER
- 49. TFO & PLY WINDING
- 50. YARN ROOM Three major purposes of yarn room are: •Storage •Identification •Issue
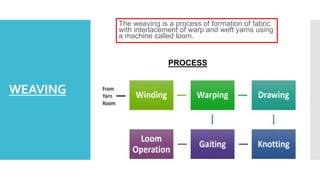
- 51. WEAVING The weaving is a process of formation of fabric with interlacement of warp and weft yarns using a machine called loom. PROCESS
- 52. WINDING Winding is the process of yarn transfer to obtain a larger package from several small spinner’s packages. . There is only one soft winding machine with 48 heads and 3 SSM winding machines with 55 heads at this unit.
- 53. Warping is a process by which long length of many yarns are winded on a flanged bobbin to produce a warp beam. Warping may be carried out directly (direct beaming) or indirectly, in sections (sectional warping) WARPING
- 54. DRAWING & DRAFTING The warp ends are passed through the drop wires and heddles of the harness frames and dents of the reeds by drawing process. This can be performed either manually or by automatic machines. MACHINE DRAWING MANUAL DRAWING
- 55. KNOTTING It refers to dressing of old warp sheets over new warp sheets by clamp knotting process. It is done only for same quality material. The dressing of the yarns is done to get the parallel yarns for knotting.
- 56. GATING In this process the drawn beam, which is prepared in warping, is directly mounted on a loom LOOM SPECIFICATION
- 57. AIR – JET LOOM RAPIER LOOM
- 58. FABRIC STRUCTURE
- 59. MENDING Fabric is checked on both the front and back sides i.e. 100% inspection. Minor defects such as protruding fiber are corrected on the spot manually; this Is known as general mending The major marked defects comes under extra work category. General Mending includes: Nods pulling and relaxing Nods and tails are trimmed Wrong end – correct end is inserted Broken pick – refilling by needle End missing – refilling by needle
- 60. 30,000-35,000 meter of fabric on average checked per day . In the mending department 90% of the workers are hired on contract basis MENDING AREA
- 61. FINISHING Textile finishing is a term used for a series of processes to which all bleached, mended, dyed and certain grey fabric are subjected before they are put into market. They are carried out to improve the natural properties of the fabric Various finishes applied on fabrics in Raymond are - soft finish, anti microbial, water repellent, wrinkle free.
- 62. DIFFERENT PROCESSES OF FINISHING
- 63. DIFFERENT PROCESSES OF FINISHING
- 64. DIFFERENT PROCESSES OF FINISHING
- 65. FINISHING PROCESS OF POLY - VISCOSE
- 66. FINISHING PROCESS OF POLY WOOL
- 67. FINISHING PROCESS OF ALL WOOL
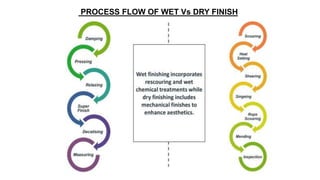
- 68. PROCESS FLOW OF WET Vs DRY FINISH
- 70. FOLDING . The folding of the fabric is carried out according to the requirements of the civil and exports market Inspection is done using the 4 point system Batch number, piece number, width, weight, quality and the quantity for each roll is mentioned on a flag attached to the package. Different qualities have different flags. Then selvedge stamping, hand rolling and top-end stamping is done. Minimum length of each package: 15m Minimum Tube roll length: 20m Maximum length: Depends on the customer
- 71. FOLDING AND DEFECT MARKING
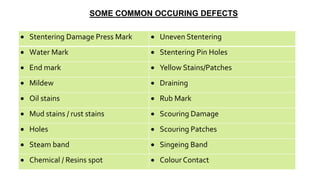
- 72. Stentering Damage Press Mark Uneven Stentering Water Mark Stentering Pin Holes End mark Yellow Stains/Patches Mildew Draining Oil stains Rub Mark Mud stains / rust stains Scouring Damage Holes Scouring Patches Steam band Singeing Band Chemical / Resins spot Colour Contact SOME COMMON OCCURING DEFECTS
- 73. PROCESS FLOW OF FOLDING Checking Perching Doffing Folding Wrapping Bar Code Packaging Warehouse
- 74. WAREHOUSE The warehouse is spread across an area of 1 lakh square feet with the capacity of up to 60 lakhmetres of fabric . This department is managed by Warehouse Management System (WMS) they are packed with HDPE (High Density Poly Ethylene) bags by the packing machine There are various Zones in the warehouse which enables efficient management of the large quantity of fabrics.
- 75. WAREHOUSE
- 76. DESIGNING It plays a vital role in determining the quality, pattern and color types of the fabrics to be produced for the civil as well as export market, every season. Design Sample Approval Final Order PROCESS FLOW
- 77. DESIGNING
- 78. WEAVES USED AT RAYMOND FOR SUITING
- 79. SAMPLING Once the design has been made, it goes for sample production. During this time, the master card containing all the necessary and vital information regarding the fabric construction, draft, peg plan, shade, warp & weft arrangement, yarn count, twist direction, TPI & tentative calculated fabric specifications.
- 80. PROCESS FLOW OF SAMPLING
- 81. SAMPLING
- 82. QUALITY CONTROL The purpose of quality control laboratory is to ensure the level of quality at the different stages of the production. The standards followed by the Quality Control laboratory at Raymond are: ASTM,AATCC, ISO and JISL. The machines have been purchased from various manufacturers across the globe
- 83. TEST SPECIMEN
- 84. FIBER STAGE
- 85. YARN STAGE
- 86. YARN STAGE
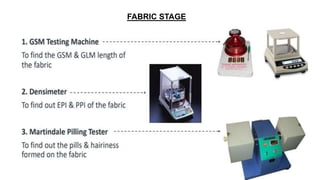
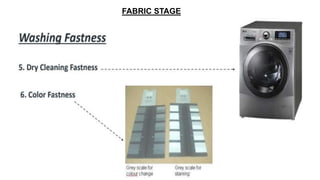
- 87. FABRIC STAGE
- 88. FABRIC STAGE
- 89. FABRIC STAGE
- 90. FABRIC STAGE
- 91. FABRIC STAGE
- 92. FABRIC STAGE
- 94. SUPPLYCHAIN MANAGEMENT Supply chain management means management of the material flow from customer to customer. It includes various attributes – • Production target • Sales • Marketing • Factory planning •Warehouse • Logistics At Raymond,Vapi supply chain management is mainly used for FACTORY PLANNING
- 95. EFFLUENT TREATMENT PLANT Waste water effluent that comes from dyeing, finishing, pre treatment of fabric is treated. PROCESS FLOW
- 98. WHATS NEW?
- 99. SOME NEW EVENTS AND PROJECTS OF RAYMONDS
- 100. THANKYOU