The AWS Shared Security Responsibility Model in Practice
- 1. ©2015, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved The AWS Shared Security Responsibility Model in Practice Dave Walker Specialist Solutions Architect, Security and Compliance 16/03/16
- 3. AWS Global Footprint US West (N.California) US West (Oregon) GovCloud US East (Virginia) EU West (Ireland) Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Asia Pacific (Singapore) Asia Pacific (Sydney) China (Beijing) São Paulo EU Central (Frankfurt) Asia Pacific (Seoul)
- 4. AWS Global Footprint US West (N.California) US West (Oregon) GovCloud US East (Virginia) EU West (Ireland) Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Asia Pacific (Singapore) Asia Pacific (Sydney) São Paulo EU Central (Frankfurt) Asia Pacific (Tokyo) China (Beijing) Asia Pacific (Seoul) Region An independent collection of AWS resources in a defined geography A solid foundation for meeting location- dependent privacy and compliance requirements
- 5. AWS Global Footprint US West (N.California) US West (Oregon) GovCloud US East (Virginia) EU West (Ireland) Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Asia Pacific (Singapore) Asia Pacific (Sydney) China (Beijing) São Paulo EU Central (Frankfurt) Asia Pacific (Seoul)
- 6. AWS Global Footprint US West (N.California) US West (Oregon) GovCloud US East (Virginia) EU West (Ireland) Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Asia Pacific (Singapore) Asia Pacific (Sydney) China (Beijing) São Paulo EU Central (Frankfurt) Asia Pacific (Seoul) Availability Zone Designed as independent failure zones Physically separated within a typical metropolitan region
- 8. AWS Global Footprint Edge Location collections of servers in geographically dispersed data centers deliver content to end users with lower latency
- 10. AWS Global Footprint 12 Regions 33 Availability Zones 54 Edge locations Over 1 million active customers Every day, AWS adds enough new server capacity to support Amazon.com when it was a $7 billion global enterprise.
- 11. Data Locality Customer chooses where to place data AWS regions are geographically isolated by design Data is not replicated to other AWS regions and doesn’t move unless you choose to move it
- 12. Shared Responsibility Who manages which parts?
- 13. AWS Foundation Services Compute Storage Database Networking AWS Global Infrastructure Regions Availability Zones Edge Locations Client-side Data Encryption Server-side Data Encryption Network Traffic Protection Platform, Applications, Identity & Access Management Operating System, Network & Firewall Configuration Customer content Customers AWS Shared Responsibility Model Customers are responsible for their security and compliance IN the Cloud AWS is responsible for the security OF the Cloud
- 14. AWS Shared Responsibility Model – Deep Dive Will one model work for all services? Infrastructure Services Container Services Abstract Services
- 15. AWS Foundation Services Compute Storage Database Networking AWS Global Infrastructure Regions Availability Zones Edge Locations Optional – Opaque data: 1’s and 0’s (in transit/at rest) Platform & Applications Management Customer content Customers AWS Shared Responsibility Model: for Infrastructure Services Managed by Managed by Client-Side Data encryption & Data Integrity Authentication Network Traffic Protection Encryption / Integrity / Identity AWSIAMCustomerIAM Operating System, Network & Firewall Configuration Server-Side Encryption Fire System and/or Data
- 16. Infrastructure Service Example – EC2 • Foundation Services — Networking, Compute, Storage • AWS Global Infrastructure • AWS IAM • AWS API Endpoints AWS • Customer Data • Customer Application • Operating System • Network & Firewall • Customer IAM • High Availability, Scaling • Instance Management • Data Protection (Transit, Rest, Backup) Customers RESPONSIBILITIES
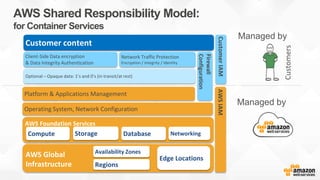
- 17. AWS Foundation Services Compute Storage Database Networking AWS Global Infrastructure Regions Availability Zones Edge Locations Optional – Opaque data: 1’s and 0’s (in transit/at rest) Firewall Configuration Platform & Applications Management Operating System, Network Configuration Customer content Customers AWS Shared Responsibility Model: for Container Services Managed by Managed by Client-Side Data encryption & Data Integrity Authentication Network Traffic Protection Encryption / Integrity / Identity AWSIAMCustomerIAM
- 18. Infrastructure Service Example – RDS • Foundational Services – Networking, Compute, Storage • AWS Global Infrastructure • AWS IAM • AWS API Endpoints • Operating System • Platform / Application AWS • Customer Data • Firewall (VPC) • Customer IAM (DB Users, Table Permissions) • High Availability • Data Protection (Transit, Rest, Backup) • Scaling Customers RESPONSIBILITIES
- 19. AWS Foundation Services Compute Storage Database Networking AWS Global Infrastructure Regions Availability Zones Edge Locations Platform & Applications Management Operating System, Network & Firewall Configuration Customer content Customers AWS Shared Responsibility Model: for Abstract Services Managed by Managed by Data Protection by the Platform Protection of Data at Rest Network Traffic Protection by the Platform Protection of Data at in Transit (optional) Opaque Data: 1’s and 0’s (in flight / at rest) Client-Side Data Encryption & Data Integrity Authentication AWSIAM
- 20. • Foundational Services • AWS Global Infrastructure • AWS IAM • AWS API Endpoints • Operating System • Platform / Application • Data Protection (Rest - SSE, Transit) • High Availability / Scaling AWS • Customer Data • Data Protection (Rest – CSE) Customers Infrastructure Service Example – S3
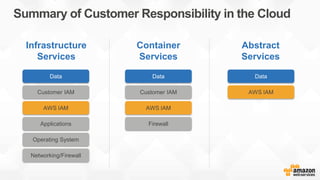
- 21. Summary of Customer Responsibility in the Cloud Customer IAM AWS IAM Firewall Data AWS IAM Data Applications Operating System Networking/Firewall Data Customer IAM AWS IAM Infrastructure Services Container Services Abstract Services
- 22. Shared Responsibility What about security OF the cloud?
- 23. Security Shared Responsibility Model AWS is responsible for the security OF the cloud AWS Foundation Services Compute Storage Database Networking AWS Global Infrastructure Regions Availability Zones Edge Locations
- 24. Auditing - Comparison on-prem vs on AWS Start with bare concrete Functionally optional – you can build a secure system without it Audits done by an in-house team Accountable to yourself Typically check once a year Workload-specific compliance checks Must keep pace and invest in security innovation on-prem Start on base of accredited services Functionally necessary – high watermark of requirements Audits done by third party experts Accountable to everyone Continuous monitoring Compliance approach based on all workload scenarios Security innovation drives broad compliance on AWS
- 25. What this means You benefit from an environment built for the most security sensitive organizations AWS manages 1,800+ security controls so you don’t have to You get to define the right security controls for your workload sensitivity You always have full ownership and control of your data
- 27. AWS Foundation Services Compute Storage Database Networking AWS Global Infrastructure Regions Availability Zones Edge Locations Meet your own security objectives Customer scope and effort is reduced Better results through focused efforts Built on AWS consistent baseline controls Your own external audits Customers Your own accreditation Your own certifications
- 28. Navigating Shared Responsibility Achieving accreditation or certification on AWS is possible but how can we help?
- 29. Shared Responsibility & Security By Design Phase 1. Outline your requirements • Outline your policies, controls you inherit from AWS • Document controls you own and operate on AWS Phase 2. Build a Golden Environment • Define your AWS resources and controls as Code Phase 3. Enforce with the use of Templates • Templates presented to users within Service Catalogue as Products within Portfolios Phase 4. Perform validation checks • Deploying your environment through Service Catalogue as Gold Templates you make your environment audit ready
- 30. GoldBase — Security Control Responsibility Matrix NIST SP 800-53 rev. 4 control security control matrix
- 31. GoldBase — Architecture Diagrams
- 32. GoldBase — CloudFormation Templates
- 33. GoldBase — Additional Resources
- 34. Getting help — AWS Compliance Workbooks – IT Grundschutz (TUV Trust IT) – CESG UK Security Principles – PCI Workbook – Anitian – Audit Checklists Whitepapers – EU Data Protection – Risk & Compliance – Overview of Security Processes – FERPA FAQs – PCI, HIPAA, EU Data Protection, ISO 27001, 9001 etc… Training – eLearning: Security Fundamentals, 3 hour free online course – Instructor Lead Training: 3day course for Security Professionals – Qwiklab: Security & Auditing Self Paced Lab Security Blog: http://blogs.aws.amazon.com/security/
- 35. Helpful Resources Compliance Enablers: https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/compliance-enablers/ Risk & Compliance Whitepaper: https://aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/overview-of-risk-and-compliance/ Compliance Center Website: https://aws.amazon.com/compliance Security Center: https://aws.amazon.com/security Security Blog: https://blogs.aws.amazon.com/security/ AWS Audit Training: awsaudittraining@amazon.com
- 37. ©2015, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved Dave Walker Specialist Solutions Architect Amazon Web Services Thank You
Editor's Notes
- #4: 12 regions as of today, 5 more on the way Ohio (USA), Montreal (Canada), UK, China, and India
- #5: geographically isolated and can help customers meet Data Locality requirements
- #6: 29 availability zones
- #7: AZs consist of 1 or more DCs clustered to make up an AZ Within a Region AZs are isolated on and highly available with multiple ISP/Power connections per AZ Typcially 2-3 AZs per region
- #9: 64 edge locations today
- #11: We define an “active customer” as non-Amazon customers who have account usage activity within the past month Scale and capacity matter. Every day, we add enough new server capacity to support Amazon.com when it was a $7B global enterprise.
- #12: AWS recognises that there are legal and regulatory directives around the location of data.
- #14: We look after the security OF the cloud, and you look after your security IN the cloud. Talk about: AWS Global Infrastructure – mention Environmental/Physical controls Foundational Services – logical controls Customers responsible for Operating System and Applications – however not every service provides the customer with visibility to the O.S or App Layer
- #15: We look after the security OF the cloud, and you look after your security IN the cloud.
- #16: Mention: O.S App development Protecting Data – Encryption Rest/Transit Customer IAM – local or corporate identity management system
- #18: Change in IAM RDS as an example Customer manages DB – DB Users etc AWS manages OS, Engine
- #20: Change in IAM S3 example Customers are responsible for controlling access to their data on S3 via AWS IAM Also responsible for creating/deleting the content
- #22: Talk about Customer Key Management
- #24: Quick re-cap on SRM
- #25: Refer to AWS part of Shared Responsibility Model On Prem: Audits usually done by an in-house team Typically done once a year Tend to be workload specific compliance checks Must keep pace and invest in security innovation On AWS: You start with a base of accredited services Audits are performed by 3rd party experts Accountable to everone Security Innovation drives broad compliance Leads into Audit rights discussion: ------------------------------------ (FINRA – example on-prem vs aws) Anonymize finra
- #28: Own your own accreditation Own your own certifications Own your own external audits Essentially – just because AWS is certified against PCI-DSS, customers still need to work with a QSA to ensure that from the 12 requirements of PCI – which the customer is still responsible for based on the shared responsibility models to assist the customer in becoming accredited in running PCI workloads on top of AWS
- #30: This leads into a program called GoldBase Talk about Launch Constraints – Leveraging an IAM Role to perform Launch for User Talk about Template Constraints – limiting VPCs, Instance Types etc
- #34: Talk about packages being developed