The Dangers of Cocaine
- 1. The Dangers of Cocaine on Society Frances Coronel Maria Marisigan Alex Cady Yasmina Abdous
- 2. Cocaine Assessment... • Why should we even care • What is cocaine • Relevance to Health -Usage in the U.S. -Effects on Body and Mind -Side Effects on Body -Side Effects on BodyVisual -Special BrainVideo -Statistics on Body and Mind -Effects & Statistics on Community -Statistics on World • Relevance to Chemistry • Brief Look On Government Involvement • THE Facts on Cocaine • Freud Paradox • Works Cited Surprise at End!
- 3. Why should we even care •Cocaine use is prevalent across all socioeconomic strata, including age, demographics, economic, social, political, religious, and livelihood •Over 6 million people are under the effects of cocaine •Symbolizes large scale danger to global health •Euphoria is only temporary, with euphoria soon becoming addiction, with addiction soon becoming vindication of life or death
- 4. What is cocaine •cocaine: drug (paste) extracted from leaves of South American coca plant that also serves as a strong stimulate that effects body's central nervous system •“crack” refers to crackling sound heard when mixture is smoked •processed with ammonia or sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and water, then heated to remove hydrochloride and produce powder •can be injected, smoked, sniffed, or snorted •labeled drug of 1980s and ‘90s because of extensive popularity and use
- 5. Relevance to Health • Usage -global problem that affects many -hospitalization high for those influenced by drugs • Effects on the Body/Mind -many short term/long term central effects -many awful side effects -causes dopamine transporter to stop in brain and when effect of cocaine is gone, you stop producing dopamine and only way to get it flowing again.. is by taking more cocaine...hence you get addicted... • Effects on the Community -#2 most popular recreational drug used in U.S. -most frequently reported illicit substance associated w/ drug abuse fatalities -leading cause of all drug-related deaths (40%)
- 6. Usage In the United States •WHAT? -one of oldest known drugs -cocaine hydrochloride, has been abused substance for more than 100 years -coca leaves, the source of cocaine, have been ingested for thousands of years -2nd most popular illegal recreational drug in the U.S. (behind marijuana) •WHO? -U.S. is world's largest consumer of cocaine -commonly used in middle to upper class communities -popular amongst college students, as party drug -users span over different ages, races, and professions -1970s and 80's, drug became particularly popular in disco culture
- 7. Usage In the United States •PRODUCTION, DISTRIBUTION, AND CONSUMPTION -produced as white chunky powder -sold most often in aluminum foil, plastic or paper packets, or small vials -chop, fix, snort/inject •WHY? -after smoked, user experiences a high in less than 10 seconds -this fast euphoric effect is primary reason that crack became enormously popular in mid 1980s -crack is also cheap, whether it is production or consumption
- 8. Effects on the Body/Mind •Short term physical effects: -restlessness, euphoria, alertness -these are felt within minutes of taking drug -continue for about 20 to 120 minutes -later on.... insomnia, vomiting, pupil dilation, nosebleeds, increased temperature and pulse rate, rapid breathing •Long term physical effects -death from overdose, lung or heart failure, or constant strokes (common) -increased blood pressure, low sex drive, insomnia, dizziness, and involuntary muscle twitching strokes -physical addiction to the drug -Hepatitis/AIDS transferrable through non-sterile needles Effects on body -vary depending on several factors -person’s history can affect body reaction -amount and way drug is taken also affects •Effects on Mind -change in way person handles interpersonal relationships -drug will become so central in the person’s thought that mind can only process information that would help the person get more access to cocaine -anxiety, hallucination and depression, low sex drive, severe sleeping, extreme paranoia, and eating disorder can also progress from continuous use
- 9. Side Effects on the Body Insomnia Loss of appetite Blurred vision Vomiting High anxiety Physical/Mental Dependence Sweating Violent behavior Twitching Hallucinations Rapid breathing Chest pain Rapid breathing Irritability Constricted blood vessels Dilated pupils Nasal infections Nose bleeds
- 10. Side Effects
- 12. Effects on Community These facts are based off 2009 U.S. (World Drug Report 2010) statistics... • Cocaine use represents a major health problem: -almost a fifth (18%) of people who used cocaine were found to be dependent on it, higher proportion than any drug, except heroin -results in tens of thousands of deaths each year worldwide -represents close to 40% of all drug related deaths • Cocaine use represents major danger to the community: -cocaine and crime have positive correlation; between 29-35% of male arrested in US were found to have used cocaine in previous month. -cocaine trafficking also positively correlated with corruption; such as with West Africa -produces major security threat in number of countries, such as with “FARC” in Colombia and Shining Path in Peru (both are revolutionary armed forces that take part in kidnappings, guerilla warfare, mass killings,drug trade, and exploitation)
- 13. • National Drug Control Policy: # chronic cocaine users: 3.6 million • 18 to 25 years of age: highest % of cocaine use • 90%: cocaine users smoked, drank, or used marijuana before trying cocaine • 1988: …300,000 infants were born addicted to cocaine • 1 /4 Americans between 26 and 34 have used cocaine in lifetime • 22 to 25 million people have tried cocaine at least once • 0.9% college students; 1.3% young adults reported past year crack use -2010 • 0.1% college students and 0.4% young adults reported using crack in past month -2010 Statistics on Community
- 14. Statistics on World Production •Demand has emerged in many developing countries, particularly among elites. Crack use was rare outside the US and UK, but this appears to be changing rapidly, especially in Latin America and parts of Africa. •Current estimates suggest that about 500 mt. of pure cocaine were available for consumption in 2008, of which around 480 mt. were actually consumed. Price •New Zealand has highest price with $714.30 per gram of cocaine. •Colombia has cheapest price with $2 per gram of cocaine, cheaper than a Big Mac.
- 15. Statistics on World Consumption • Following significant increase over period 2002-2005, global cocaine seizure totals have followed stable trend, amounting to 712 mt. in 2007 and 711 mt. in 2008. Seizures continued concentrated in Americas and Europe. However, transition from 2007 to 2008 brought about geographical shift in seizures towards the source countries for cocaine (Latin America/Africa). Seizures • UNODC estimates prevalence of cocaine use worldwide in 2008 ranged from .3% to .4% of adult population, or between 15 and 19 million people who had used cocaine at least once in previous years. Compared to 2007, range shifted to lower levels, suggesting decrease in global number of cocaine users.This change is due to decrease in number of cocaine users in North America.
- 16. World Drug Report 2010 United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (Source for Graphs/Statistical Data on Cocaine)
- 17. Represents “seizures” of cocaine ...seizure meaning the action of confiscating cocaine by warrant of legal right -Colombia has highest number with 257.2 metric tons being confiscated -US second highest with 97.8 metric tons being confiscated
- 18. • represents 2008 global cocaine consumption • 16% world users • 6.2% users in North America • represents 2008 overall value distribution in the global cocane market in US $ • $88 billion dollars worth globally • 480 metric tons consumed
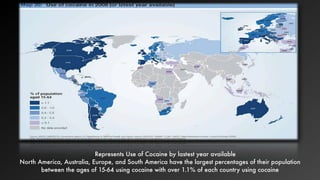
- 19. Represents Use of Cocaine by lastest year available North America, Australia, Europe, and South America have the largest percentages of their population between the ages of 15-64 using cocaine with over 1.1% of each country using cocaine
- 20. Relevance to Chemistry •Cocaine C₁₇H₂₁NO₄ molar mass: 303.35 grams/moles •Richard Willstätter- German Chemist: solved structure of cocaine •Coc-H+Cl– + NaHCO3 → Coc + H2O + CO2 + NaCl •cocaine hydrochloride+sodium bicarbonate (common backing soda)= cocaine+water+carbon dioxide+sodium chloride (common table salt) •freebase form of cocaine: practically insoluble in water whereas hydrochloride salt is water soluble •pure cocaine prepared by neutralizing its compounding salt with alkaline solution which will precipitate to non-polar basic cocaine •further refined through aqueous-solvent liquid-liquid extraction
- 21. Relevance to Chemistry •Dopamine C₈H₁₁NO₂ molar mass: 153.18 grams/moles •neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals in between neurons of brain •Dopamine also plays role in addiction •some drugs stimulate dopamine production leading to increased dopamine levels and corresponding high •when drug exits system, it leaves behind sense of depression and slowdown, which can only be remedied by increasing dopamine levels again •brain quickly learns to seek out drugs which will stimulate dopamine production, thereby creating addiction •altered levels of dopamine in brain can cause range of symptoms and problems, ranging from Parkinson's disease to Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)
- 22. Brief Look On Major U.S. Federal Drug Control Laws • 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act -regulates labeling of products containing -only certain drugs including cocaine and heroin • 1914 Harrison Narcotics Tax Act -regulates opium and cocaine • 1937 Marihuana Tax Act -required Taxation of marijuana • 1961 Convention on Narcotics -treaty to control marijuana • 1970 Controlled Substance Act -scheduling list for drugs (Schedule 1 drugs are most dangerous and have more consequences and so on...) -cocaine, because of its effects, is classified under Schedule 2 -this gave drug possession/ distribution/etc. several penalties
- 23. Based on Year 2008 THE Facts on Cocaine See Handouts Cocaine numbs any human tissue that it comes in contact with “Crack babies” can have brain damage, premature birth and can face spontaneous abortion Caught with cocaine: approx. 7 years in prison Caught with cocaine for purpose of trafficking: approx. life time in prison Typical withdrawal symptoms include depression, hunger and fatigue When using cocaine for first time ever, person feels extreme high, which they can never experience again Users try to experience same high again but almost impossible and only leads to overdose Chewing coca leaves (source of cocaine) produces very mild stimulation and is not at all addictive
- 24. Freud Paradox •as medical researcher, Freud was early user and advocate of cocaine as a stimulant •also a analgesic (someone who uses drugs frequently to relieve pain) •believed cocaine was cure for many mental and physical problems •in 1884 paper "On Coca" he extolled the virtues of cocaine •between 1883 and 1887 he wrote several articles recommending medical applications, including its use as an antidepressant •application as an anesthetic turned out as one of few safe uses of cocaine, and as reports of addiction and overdose rose globally, Freud's medical reputation became undermined •he then ceased to publicly recommend use of the drug, but continued to take it himself occasionally for depression, migraine and nasal inflammation during the early 1890s, before giving it up in 1896 •some critics have suggested that much of Freud's early psychoanalytical theory was a by-product of his cocaine use
- 25. Works/Pictures Sited 1. http://www.drug-rehabs.org/drug-statisticsc.htm 2. http://www.drug-rehabs.org/cocaine-c.htm 3.http://alcoholism.about.com/od/coke/a/cocaine.htm 4. http://news.change.org/stories/random-drug-test-finds-cocaine-in-racing-greyhounds 5. http://health.stateuniversity.com/pages/1476/Substance-Abuse-Dependence.html 6. http://druginfo.netfirms.com/cocaine.htm 7. http://www.primehealthchannel.com/how-long-does-cocaine-stay-in-your-system-urine-blood-hair-test-for-cocaine.html 8. http://www.newser.com/tag/43235/1/illegal-drugs.html 9.Byck, Robert. Cocaine Papers by Sigmund Freud. Edited with an Introduction by Robert Byck. New York, Stonehill, 1974. 10. Thornton, Elizabeth. Freud and Cocaine: The Freudian Fallacy. London: Blond and Briggs, 1983, pp. 45-46. 11.Jones, Ernest. Sigmund Freud: Life and Work, vol. 1. London: Hogarth Press, 1953, pp. 94-96. 12. http://www.unodc.org/pdf/research/wdr07/WDR_2007.pdf 13. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_64227_EN_EMCDDA_AR08_en.pdf 14. http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/WDR-2010.html 15. http://www.sethson.com/physical-and-psychological-effects-of-cocaine-addiction/ 16. http://topcultured.com/facts-about-cocaine/ 17.http://www.infobarrel.com/10_Facts_about_Cocaine 18. http://www.rxlist.com/cocaine-drug.htm 19. http://www.economist.com/node/9414607?story_id=9414607 20. http://www.economist.com/node/9414607?story_id=9414607 21. http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/mouse-man/200904/what-is-dopamine 22.http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-dopamine.htm 23.http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopamine
- 26. Time Hans Zimmer Hope you enjoyed the presentation.