TMK.edu Programmatic: September 2016
- 1. BE BRAVE BE INVENTIVE DEFY EXPECTATIONS
- 2. Programmatic Media 101 • Market Trends • What is Programmatic? • The Programmatic Evolution • Programmatic @ TMK • The Programmatic Buying Process • The Trade Desk • The Future
- 4. • Everything is becoming programmatic enabled, & that’s a good thing.
- 5. 5 Why This is Important • Direction of media planning and buying • Clients will ask • Your vendors use it • You will be in charge
- 6. 6 Programmatic has Flipped the Market eMarketer: “US Display Ad Spending Share, by Type” 2016 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 53% 63% 65% 73% 78% 82% 47% 37% 35% 27% 22% 18% Programmatic Non Programmatic
- 8. 8 Programmatic Media Buying Defined The use of software to automate the purchasing of digital advertising • Prioritizes the audience rather than the site • Simplifies point of access for inventory • Accesses robust data for smarter decisions • Provides real-time operational controls
- 9. 9 Programmatic Media Buying Defined Right Audience Right Medium Right Time Right Message • Who are we speaking to? • How are they related to the product/service? • How deep is the relationship? 1st Party data, 3rd party data, Demo, Behavioral, Attitudinal etc. • How can past behavior tailor creative? • How can real time location, site data inform better creative? Dynamic Creative using pub site, user location etc., site behavior • Is it Social? Native? Mobile? Video? • How can the user journey inform the choice of medium? Programmatic Native, Video, Rich media, banner & social channels • Can we reach the user when they’re most likely to buy? • How can time of day, location behaviors, seasonality leveraged? Programmatic location based data providers, time of day bidding etc.
- 15. 15 Programmatic Evolution Centralized to Trading Desks Decentralize to Planning Teams Early programmatic buying required fluency in cumbersome platforms and advanced quantitative skills. As buying technology evolved, the tools became much easier to use and media teams have become more analytical.
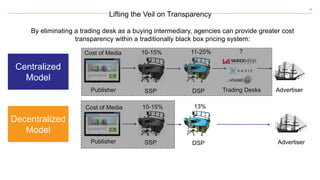
- 16. 16 Lifting the Veil on Transparency By eliminating a trading desk as a buying intermediary, agencies can provide greater cost transparency within a traditionally black box pricing system: Centralized Model Decentralized Model Publisher SSP DSP Publisher SSP DSP Cost of Media 10-15% 11-25% Trading Desks ? Advertiser Cost of Media 10-15% 13% Advertiser
- 18. 18 Starting with Our Search Team Search teams were technically the first programmatic buyers, experienced with • Bidding on auctions • Optimizing in real time • Managing with UIs • Integrating with planning teams • Providing transparency to complicated topic
- 19. 19 Evolve Into a Programmatic Agency • More strategic recommendations • Closer eye on performance • Providing transparency to complicated topic • Less middlemen
- 20. 20 Misconceptions about Programmatic Media • Too complicated • Due to opaque business model of trading desks • Only remnant inventory • Opening with top publishers like Forbes, Conde Nast, Hearst • Programmatic = retargeting • Only one type of programmatic buying • Lower CPMs than traditional buys • Not necessarily when targeting exact audience at right time • No publishers • Publisher relationships very important for private market places • Standard desktop banner ads only • Includes video, mobile, social native, rising star, skins
- 21. The Programmatic Buying Process
- 22. 22 The Publisher Waterfall Publisher ad servers show ads based on a priority listing known as “the waterfall” Publisher Direct and Automated Guaranteed PMP Open Exchange Advertisers need to consider the implications for media buys Priority ScaleandEfficiency
- 23. 23 Types of Programmatic Buys Open Exchange (RTB) Private Marketplaces (PMP) Automated Guarantee/Direct Definition Purchase of ads through real-time auction Restricted auction to select buyers via DealIDs Software enabled direct buys to help with RFP and IO process Publisher/Advertiser Many to Many Some to Some One to One Pros Higher scale with typically cheaper pricing More premium inventory and transparency Streamline traditional planning process Cons Typically less premium inventory Requires time for negotiation and set-up Tech in early stages and cumbersome
- 24. 24 Programmatic Process Publisher Publisher Ad Server SSP DSP Advertiser Advertiser Ad Server 1: Set Max Bid2. Find Winning Bid 3. Place Ad Note: Process happens within milliseconds
- 25. 25 Programmatic Process: Set Max Bid DSP Advertiser 1. Advertiser places max CPM bid in DSP
- 26. 26 Programmatic Process: Find Winning Bid Publisher Publisher Ad Server 2a. When ad is needed on a webpage, publisher requests ad from its ad server DSP Advertiser
- 27. 27 Programmatic Process: Find Winning Bid SSP 2b. If programmatic has priority on waterfall, ad server reaches out to SSP for ad Publisher Publisher Ad Server DSP Advertiser
- 28. 28 Programmatic Process: Find Winning Bid 2c. SSP requests bids from DSPs of different advertisers and chooses highest bidder SSPPublisher Publisher Ad Server DSP Advertiser
- 29. 29 Programmatic Process: Place Ad 3. Winning advertiser’s ad server provides advertiser to publisher SSPPublisher Publisher Ad Server DSP Advertiser Advertiser Ad Server
- 30. 30 Programmatic Process Publisher Publisher Ad Server SSP DSP Advertiser Advertiser Ad Server 1: Set Max Bid2. Find Winning Bid 3. Place Ad Note: Process happens within milliseconds
- 31. 31 Programmatic Players Demand-Side Platform (DSP): software used to buy advertising in an automated fashion Supply-Side Platform (SSP): software used to sell advertising in an automated fashion Data Management Platform (DMP): data warehouse used to analyze and target audiences
- 32. The Trade Desk
- 33. 33 Our DSP: The Trade Desk Problem with typical DSPs • Line-item system: Campaigns are set-up in a line-item system. When optimizations are needed, separate campaigns need to be made, which creates major operational efficiencies • Example: To bid more on “News” sites, a new campaign would be created and managed. • Black box optimizations: Most DSPs use automated algorithms for optimizations. Unfortunately, this typically don’t provide transparent insights into what worked and what didn’t. The Trade Desk’s Solution: Bid Factors • Multiple bids can be made within a single campaign, removing the need for separate line items • Example: Bidding more on “News” sites can be done within the same campaign. • Bid factors empower advertisers with full control, and thus transparency, over optimizations
- 34. 34 DSP Levers Targeting Control Audience • Demographic • Interests • Behaviors • Geography Site • Whitelist • Blacklist • Category • Content • Budget • Bids • Time of Day • Day of Week • Frequency • Recency • Brand Protection
- 35. Audience composition of 3rd party data Example: look-a-like modeling Online actions on proprietary assets Example: site retargeting 35 Targeting with Data Data 1st Party Retargeting 2nd Party Publisher 3rd party DMP Predictive Audience 1st Party Onboarding Online cookies matched with hashed PII Example: emails onboarded by LiveRamp Publisher proprietary data used via PMP Example: C-Level Execs who read NYT Segments built by DMPs like BlueKai Example: Dog lovers, in-market for BMW
- 36. 36 Things to Consider • Agency Fee • DSP Fee • Lack of Make Goods – Viewability and Ad Fraud • Team Support • Not Required by Highly Recommended
- 37. The Future
- 38. 38 Things on the Horizon • Walled Gardens • Tactical DSPs • Evolving deal types • Header Bidding
Editor's Notes
- who am i? how am i related to prog? how is this beneficial to you?