Tools and techniques for developing learning communities lsg june 2011
- 1. Nic Laycock Amos Laycock Consulting
- 2. What we will do this morning What is a learning community? How do successful communities work? The place of Learning Communities in L&D Tools for Learning Communities Roles in initiating and supporting LC’s Beyond LC’s – Communities of Practice New kinds of Community
- 3. What is a Learning Community? Framework for “talking” about things connected with learning that is in common Learning Communities are about the way people talk to one another Embed good practice About people not technology Different kinds of community Overlaps of communities, networks and people
- 4. Information Overload Many communities and networks – too much information! What do you need? Follow people who will do the work for you! Tag, filter, prioritise Bookmark, index – but update the index! Use platforms that help you – disengage and unsubscribe Be selfish in expressing needs clearly – learn to use 140 characters (Twitter) Remember communities are made up of people Human rules apply! Respect, Listening, Offering, Being part of the community
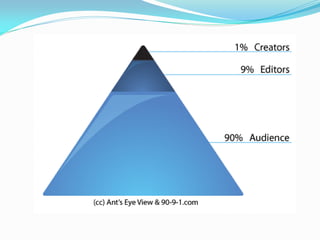
- 5. How Successful Communities Work Self- sustaining – develop their own life 90:9:1 model 90% lurk (do not contribute) 9% contribute 1% energise and lead Need for critical mass! 90 lurking is OK so long as can check people are learning Facilitation - aimed at creation of internal energy – the internal champion People only stay in successful communities – spend time where there is benefit Need to continuously stimulate, evaluate – self appraisal
- 7. Facilitating Successful Learning Communities Facilitation of LC’s aims at the creation of internal energy – the internal champion SME – willingly sharing Enthusiast – involved! Socialite – welcoming, empathising, praising Change agent – strategist – shaping the community’s direction Service role – efficient and effective not a part time role for big communities or major interventions
- 8. The Place of Learning Communities in L&D Socialisation medium – virtual interventions Supporting formal learning - especially long timescale interventions, geographic separation Working space – physical and virtual – Yammer, Socialcast, Moodle etc Sharing space – physical and virtual – LSG, LinkedIn, SlideShare, Share and Learn Repository – mostly virtual – Blogs. Wikis, etc Point of cohesion in learning process – groups within platforms – FB groups, #groups in Twitter, Yammer threads, Source of expertise – mutual assist – Twitter, OER movement, SoMe networks Networking hub – I know someone/place who/where…..
- 9. What tools do we use? Have to work with approved platforms/media Some key principles Have to resonate with the potential community members Especially important with SME’s Our personal comfort zone – but not hiding! Have to be consistent with the learning proposition
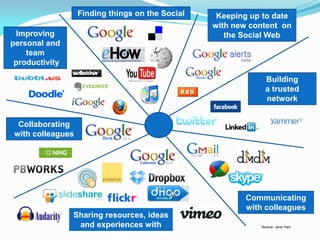
- 10. Finding things on the Social Keeping up to date Web with new content on Improving the Social Web personal and team productivity Building a trusted network of colleagues Collaborating with colleagues Communicating with colleagues Sharing resources, ideas and experiences with Source: Jane Hart colleagues
- 11. Principles explained (1) Have to resonate with the potential community members Especially important with SME’s Place of comfort Technology they are familiar with Supportive facilitation Sense of community Familiar people Recognisable formats Spirit of interchange
- 12. Principles explained (2) Personal comfort zone – but not hiding! Not comfortable with a tool - don’t use it! Don’t like where a community meets – don’t go! Don’t like the people – disengage! Value of virtual communities – don’t have to like or dislike – just use ! Not getting value – try to improve it – but ultimately leave!
- 13. Principles explained (3) Have to be consistent with the learning proposition Eg Twittter inappropriate for engineering content? Unless ……. Use of hyperlinks – be inventive Linkages to other resources and platforms
- 14. L&D role in supporting Learning Communities Seed, feed, weed Identify personal and mutual need Energise, facilitate, enable, ……. What’s the right term? What’s the intent? Doing what the community needs Technical assistance Collation Stimulation “Warming” – the human touch Subject expertise – Ukabhabha Servant leadership!
- 15. Evolving Learning Communities into Communities of Practice LC – an end in itself or pathway to a business hotspot? Transition from LC to CoP COP’s are not the same as LC’s Need to have WIFM Gaining as well as giving Authenticity and integrity Improved results Faster – Better - Novel Focus on content not process Facilitated interaction Facilitated data and information mining
- 16. LC’s in the shift to Social Learning Learning is ubiquitous – a characteristic of being human Need to awaken and heighten learning skills 70:20:10 – model 90% of learning happens away from the classroom Communities facilitate sharing and learning Need to design L&D strategy and practice around the model – communities facilitate the change Turn learning into a business driver
- 18. New kinds of Community LSG – Conference, website, webinars, physical meetings Communities that evolve from other events – webinar alumni Backchannels with lives beyond events/interventions – Social Learning Community Noddlepod Share and Learn 1st platform I’ve seen predicated on 70;20:10 Others will emerge as we recognise and enable Social Learning move away from Kirkpatrick levels and LMS’s into collaborative SoMe enabled wierarchies Story for another day…………
- 19. As a result of being here ….. What have I learned from this workshop? List one thing I will do/do differently as a result of the session Share your learning and your plan in one of your networks