Toxoplasma+trichomonas
- 1. Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Dr Kamran Afzal Classified Microbiologist
- 3. What is Toxoplasma gondii ? Class Sporozoa Protozoan parasite capable of infecting all vertebrates Remains alive in soil for up to a year, consumed by cats and other hosts Toxoplasma in meat can be killed by cooking at 152ºF (66ºC) or higher or freezing for a day in a household freezer
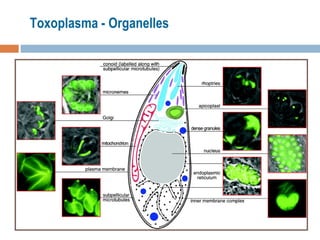
- 4. Morphology
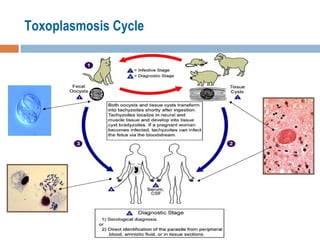
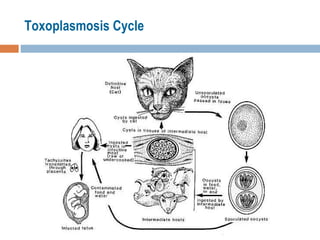
- 6. Transmission Felines are primary (definitive) hosts: only sexually reproductive in feline gut epithelium, disperses through oocysts in feces Vertebrates are the intermediate host Amphibians, fish, reptiles and all warm-blooded animals including man There are 3 principal ways Toxoplasmosis is transmitted: Ingestion of food or water or inhalation of dust contaminated with a very resistant form of Toxoplasma called the ‘oocyst’ Consumption and handling of undercooked or raw meat from infected animals Directly from pregnant mother to unborn child Transplacental Transmission - Tachyzoites multiply within the placenta and spread to the fetus
- 10. The Toxoplasma life cycle
- 11. Factors determining infection prevalence Climate Dwelling among cats Working with soil/poor hygiene Cuisine including rare or undercooked meats
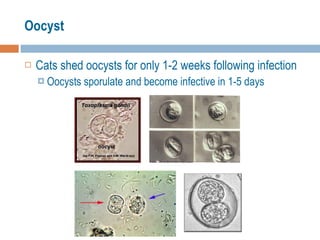
- 12. Oocyst Cats shed oocysts for only 1-2 weeks following infection Oocysts sporulate and become infective in 1-5 days
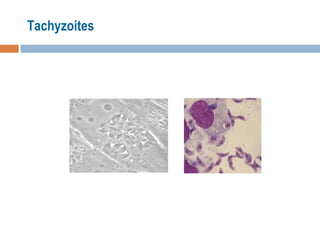
- 13. Tachyzoites
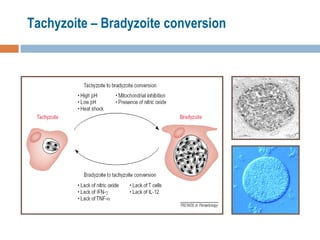
- 14. Latent Bradyzoite cysts confer life-long infection Bradyzoites are resistant to all currently available drugs Bradyzoites (not tachyzoites) are resistant to low pH and digestive enzymes during stomach passage Cysts form in brain and skeletal muscle Bradyzoite cyst persist in the immune host Protective cyst wall is finally dissolved and bradyzoites infect tissue and transform into tachyzoites Bradyzoite cysts are highly infective if ingested
- 15. Tachyzoite – Bradyzoite conversion
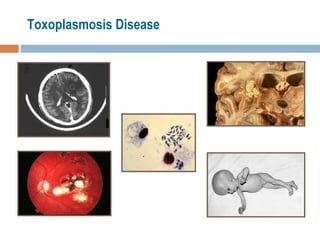
- 16. Symptoms Majority of cases are asymptomatic There are two populations at high risk for infection with Toxoplasma; pregnant women and immunosuppressed individuals Congenital infections occur in about 1/1000 pregnancies of which 5-10% result in miscarriage 8-15% result in serious brain and eye damage to the fetus Blindness, retino-chorditis, hydrocephalus, loss of hearing, seizures and mental retardation are common symptoms of toxoplasmosis in congenitally infected children Death in severe cases
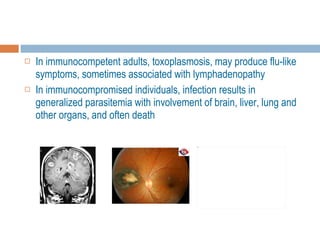
- 17. In immunocompetent adults, toxoplasmosis, may produce flu-like symptoms, sometimes associated with lymphadenopathy In immunocompromised individuals, infection results in generalized parasitemia with involvement of brain, liver, lung and other organs, and often death
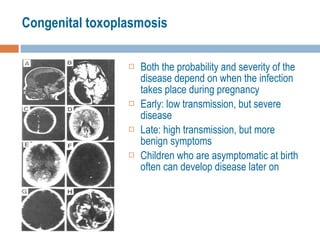
- 18. Congenital toxoplasmosis Both the probability and severity of the disease depend on when the infection takes place during pregnancy Early: low transmission, but severe disease Late: high transmission, but more benign symptoms Children who are asymptomatic at birth often can develop disease later on
- 20. Does T. gondii affect people? YES, it modifies the behavior of the host Mild flu-like symptoms initially, then the parasite becomes dormant in the brain (or other tissues) Psychomotor disturbances and intracerebral calcification Long-term personality changes Mechanism in brain = unknown; speculated to be elevated dopamine levels caused by altered cytokine levels (brain’s local immune response against T. gondii )
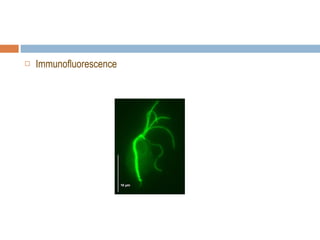
- 21. Laboratory Diagnosis Serological Testing—ELISA tests IgG and IgM Titers of IgG can last for years Titers of IgM usually persist for only 12 weeks Toxoplasmosis IHA Test Biopsy and histopathology Immunofluorescence PCR
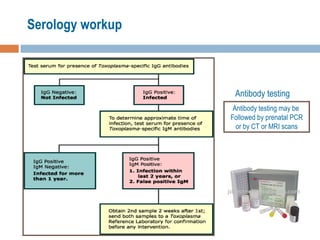
- 22. Serology workup Antibody testing Antibody testing may be Followed by prenatal PCR or by CT or MRI scans
- 23. Treatment Antibiotics Potentiated Sulfa Drugs Acute infections benefit from pyrimethamine or sulphadiazine Clindamycin and Spiramycin are successful alternatives
- 24. Prevention and Control Cook all meat and fish thoroughly Freezing at -14 o C for several hours kills tissue cysts Wash hands thoroughly after preparing raw meats and fishes Pork is reported to be the most common meat infected Pregnant women are advised to avoid cat litter or gardening , handle uncooked and undercooked meat carefully Have another person clean the litter box Immunocompromised individuals should use the same caution with cat litter and cooking of meats
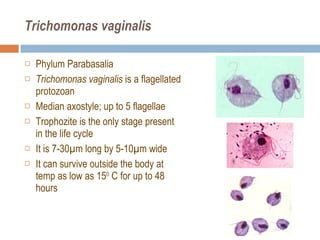
- 26. Trichomonas vaginalis Phylum Parabasalia Trichomonas vaginalis is a flagellated protozoan Median axostyle; up to 5 flagellae Trophozite is the only stage present in the life cycle It is 7-30 µm long by 5-10µm wide It can survive outside the body at temp as low as 15 0 C for up to 48 hours
- 27. Morphology
- 28. Prevalence Most common cause of vaginitis world wide It is cosmopolitan in distribution, however prevalence is not uniform because of sanitary and hygiene habits 20-40% in Women 10% in Men
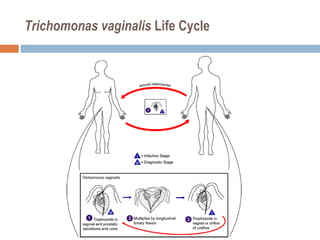
- 29. Transmission It lives in the reproductive and urinary systems of humans Human is the only host More specifically it is found in the vagina and urethra of women, and in the prostate, seminal vesicles, and urethra of men It is more common in women, and hard to find in men because most are asymptomatic By sexual contact Transfer to neonates from infected mothers T. vaginalis can live in moist clothing for 1-2 days In very rare instances it has passed through sharing wet towels, washing of clothes together or sharing bathing suits
- 30. Trichomonas vaginalis Life Cycle
- 31. Why is it Pathogenic in Females? Natural flora (bacteria) keep the pH of the vagina at 4-4.5 and ordinarily this discourages infections T. vaginalis can survive at a low pH Once established it causes a shift towards alkalinity (pH 5-6) which further encourages its growth
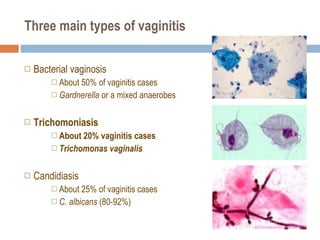
- 32. Three main types of vaginitis Bacterial vaginosis About 50% of vaginitis cases Gardnerella or a mixed anaerobes Trichomoniasis About 20% vaginitis cases Trichomonas vaginalis Candidiasis About 25% of vaginitis cases C. albicans (80-92%)
- 34. Vaginitis Differentiation Normal Trichomoniasis Candidiasis Bacterial Vaginosis Symptom presentation Itch, discharge, 50% asymptomatic Itch, discomfort, dysuria, thick discharge Odor, discharge, itch Vaginal discharge Clear to white Frothy, gray or yellow-green; malodorous Thick, clumpy, white “cottage cheese” Homogenous, adherent, thin, milky white; malodorous “foul fishy” Clinical findings Cervical petechiae “strawberry cervix” Inflammation and erythema Vaginal pH 3.8 - 4.2 > 4.5 Usually < 4.5 > 4.5 KOH “whiff” test Negative Often positive Negative Positive NaCl wet mount Lacto-bacilli Motile flagellated protozoa, many WBCs Few WBCs Clue cells ( > 20%), no/few WBCs KOH wet mount Pseudohyphae or spores if non- albicans species
- 36. What is Trichomoniasis? SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS Tirchomoniasis also known as “Trich”, that causes itchy, burning, and inflammatory symptoms in women Symptoms usually occur within 4 to 20 days of exposure Vulva may be hyperemic, pruritic and edematous The vaginal and cervical mucosa is erythematous, and punctate to petechial lesions are seen When these are seen on the cervix – Strawberry cervix Eventually there is disintegration of vaginal epithelial lining Some patients exhibit dysuria and dyspareunia with a profuse vaginal discharge The discharge is yellowish gray or green in color and foul smelling
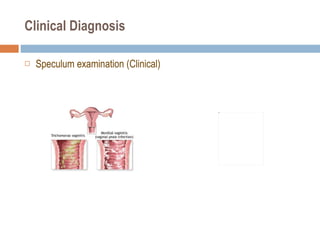
- 37. Clinical Diagnosis Speculum examination (Clinical)
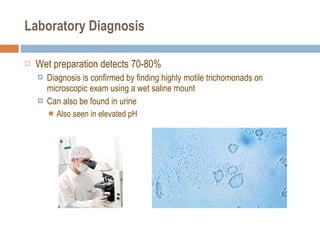
- 38. Laboratory Diagnosis Wet preparation detects 70-80% Diagnosis is confirmed by finding highly motile trichomonads on microscopic exam using a wet saline mount Can also be found in urine Also seen in elevated pH
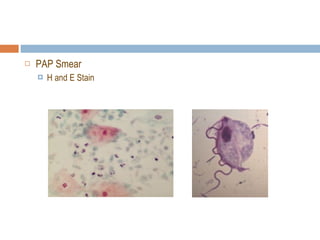
- 40. PAP Smear H and E Stain
- 41. Rapid diagnostic strips ICT
- 42. Gold standard is Trichomonas culture Culture is most sensitive Diamonds media PCR
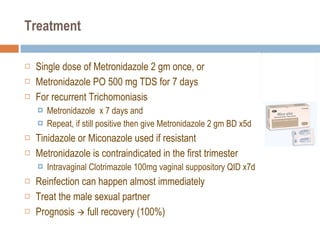
- 43. Treatment Single dose of Metronidazole 2 gm once, or Metronidazole PO 500 mg TDS for 7 days For recurrent Trichomoniasis Metronidazole x 7 days and Repeat, if still positive then give Metronidazole 2 gm BD x5d Tinidazole or Miconazole used if resistant Metronidazole is contraindicated in the first trimester Intravaginal Clotrimazole 100mg vaginal suppository QID x7d Reinfection can happen almost immediately Treat the male sexual partner Prognosis full recovery (100%)
- 44. Prevention Trichomoniasis may occur solely or in conjunction with other STDs, such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis and HIV Personal hygiene Barrier precautions