Training
- 2. Training is the act of increasing the knowledge and skills of an employee for doing particular job. Its purpose is to achieve a change in the behavior of those trained and to enable them to do jobs better. Training is a continuous process.
- 3. Introduction Organizational Training Structure Of Training Departments. Employee Training Methods Executive Training Methods Training @ infosys ADD PRINCIPLES OF LEARNING
- 4. On the basis of purpose several types of training programmes are offered to employees. Induction or Orientation Training Job Training Apprenticeship Training Internship Training Refresher Training or Retraining Training for Promotion
- 5. The term training refers to the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and competencies as a result of practical skills and knowledge that relate to specific useful competencies.
- 6. The purpose of Organizational Training (OT) is to develop the skills and knowledge of people so they can perform their roles effectively and efficiently.
- 7. An organizational training program involves the following: Identifying the training needed by the organization . Obtaining and providing training to address those needs . Establishing and maintaining training capability Establishing and maintaining training records. Assessing training effectiveness.
- 8. In deciding what structure is appropriate, it is helpful to revisit what has to be done when delivering a training service. A training service normally has the following roles: Training manager: Leads, manages, and integrates with organization's strategy. Trainer/facilitator: Delivers, presents and facilitates the learning. Instructional designer: Designs the documents the training program. Administrator : Organises venue, printing, logistics, training records etc. Internal consultant : Diagnoses, facilitates change and meetings, liases with consultants. Training broker : (Both internal and external role) Finds external providers.
- 9. Exclusive Internal Structure. Exclusive External Structure. The Eclectic Structure.
- 10. Economics. Ideology. Head count reduction. Quality. Preparedness.
- 12. Merits More direct. Large no. of people can be instructed at a same time. Time factor Controlled by the instructor Demerits: Minimum active involvement Less motivation Ability of learners Lectures cannot be remembered
- 13. Merits: improvement over lecture great value in modifying attitude members can defend their views Demerits: size should be small individuals may not appreciate will give rise to heated arguments
- 14. Merits Criticism from peers Participation Loyalty Demerits Tension and enmity May hurt a member
- 15. Merits Amusing and Practical approach. Demerit Lot of merriment hence seriousness may be lost. Observer may not be convinced of his bad communication.
- 16. Merits Opportunity to develop insight. Imp of feelings and emotions Observation Feedback Demerits Time consuming Boring
- 17. Merits Active involvement Practise decision making Exchange ideas Instant feedback Demerits Cost is more Intense emotions Artificial Not universally applicable
- 18. Executive people are those who have authority over others in the operations of the enterprise. The caliber and performance of managers will largely determine the success of any business.
- 19. Knowledge management. Behavior change Attitude change Performance change
- 20. Improvement in technical performance Improvement in conceptual performamce Improvement in human skills Stimulate juniors
- 21. To develop all those who are under him. Providing for future and present needs of the firm. Provide opportunity for every manager to take an active part in his own development.
- 22. ON JOB TECHNIQUE OFF JOB TECHNIQUE
- 23. COACHING METHOD SYNDICATE METHOD
- 24. CASE STUDY INCIDENT METHOD ROLE PLAYING IN BASKET MANAGEMENT GAMES SIMULATION T-GROUP
- 25. Advantages: Superior can guide the employee even though there is no management programs. Evaluation and feedback. Disadvantages: Superior may be authoratian. Coaches ability . Superior should not be dominant.
- 26. Advantages: Discussions, recommendations, criticism, comments. Disadvantages: Waste of time. Frustration if participants don’t understand this method.
- 27. Merits: Provides stimulating discussion. Employee can defend his analytical and judgemental views. Systematic way of thinking. Demerits: Time consuming. Rushing towards a solution.
- 28. Group members address questions such as what ,when,where ,how of situation in which an which an incident developed.Clues are trackled down if they seem to offer reliable insight into why of the situation.And then decision is taken accordingly.
- 29. Merits Decisions are rapid. Feedback is objective. Promising managers get a prospective of the company as a whole. Inexpensive Can be easily organized.
- 30. Demerits: Discourages originality. Logical solutions suggested tends to be abstracted from compulsions .
- 31. Merits: Less cost. Demerits: Difficult to duplicate the pressures and realities of actual decision making on the jobs Individuals act differently in real life situations.
- 32. Merits: Emplyee can learn more about their own weakness and strengths develop insight into how they react to others and vice versa. Demerits: Trainers often create stressful situations.
- 33. ®
- 34. Training at Infosys is an ongoing process. New recruits from colleges are trained through fresher training courses. They were trained then on new processes and technologies. As they reached the higher levels, they were trained on project management management development programs, followed by leadership development programs...
- 35. Infosys conducts a 14.5 week technical training program for all new entrants. The company spent around Rs 200,000 per year on training each new entrant. The new recruits are trained at the Global Education Center (GEC) in Mysore, which had world class training facilities and the capacity to train more than 4500 employees at a time.
- 36. Infosys also conducts training programs for experienced employees. The company had a competency system in place which took into account individual performance, organizational priorities, and feedback from the clients...
- 37. The Infosys Leadership Institute (ILI) was set up in 2001. At the Institute, the executives were groomed to handle the changes in the external and internal environment... Internal Synergy Model
- 38. BY: KASTURI DIMPLE (PGM07060532)
- 39. What is Training? Distinction between Training and Development Why Training is necessary? What can Training do for Employees? Types of Training Methods of Training Difficulties in various Training Programs Why Training Fails? How to make Training Effective?
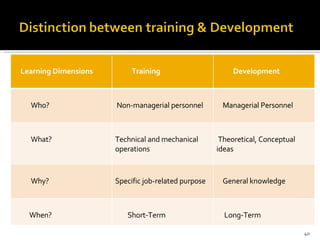
- 40. Learning Dimensions Training Development Who? Non-managerial personnel Managerial Personnel What? Technical and mechanical operations Theoretical, Conceptual ideas Why? Specific job-related purpose General knowledge When? Short-Term Long-Term
- 41. Increase Productivity Quick Learning Higher Productivity Standardization of Procedures Less Supervision Economical Operations Higher Morale Preparation of Future Managers
- 42. Training helps the employees or work-force in the following ways: Confidence New Skills Promotion Higher Earnings Adaptability Increased Safety
- 43. On the Job Training Instruction is highly disorganized and haphazard and not properly supervised. Lack of motivation. Low productivity when he is unable to fully develop. Skilled trainer Learners are often subjected to distractions of a noisy shop floor or office. Mostly used for unskilled and semiskilled jobs.
- 44. Vestibule Training The splitting of responsibilities leads to organizational problems. Additional investment in equipment is necessary This method is of limited value for the jobs which utilize equipment which can be duplicated. The number of trainees are large. Mostly used for semiskilled jobs.
- 45. Off the Job Training Minimum active involvement of trainees. One-way Communication. Can raise arguments. Some individuals may tend to dominate. Time consuming to arrive at an any decision . Effectiveness depends on the skill of leader. Mostly used for development of higher level employees and executives.
- 46. Benefits of training are not clear to top management. The top management hardly rewards supervisors for carrying out effective training. The top management rarely plans and budgets systematically for training. Trainers provide limited counseling and consulting services to rest of the organization.
- 47. The middle management without proper incentives from top management ,does not account for training in production scheduling. Without proper scheduling from above, first line supervisors have difficulty production norms if employees are attending training programmes. Training external to the employees unit sometimes teaches techniques on methods contrary to the practices of the participants organization.
- 48. Contents of training program be chalked out after identifying the training needs or goals. Training should be job relevant. Should be conducted by well qualified and experienced trainers. Should recognized that all the trainees do not progress at the same rate.
- 49. Regular constructive feedback concerning his progress in training and implementation of the newly acquired abilities.
- 50. Presented By :- Anita A. Ramteke PGM07060530
- 51. About executive training Who are the executives in organizations Their functions of executives in organization Purpose and objective of executive training Importance of executive training
- 52. Methods of executive training ON-THE-JOB TECHNIQUES OFF-THE-JOB TECHNIQUES
- 53. ON-THE-JOB TECHNIQUE The Coaching or guided Method. Job Rotation or Channel Method of Development. Participation in deliberation of the Boards and Committees.
- 54. The Coaching Method thinking processes and operative skills. guide and instructor. follow up suggestions and corrects errors. objective of coaching.
- 55. Advantages least centralized staff co-ordination. feedback and evaluation Disadvantages authoritarian. relies on coaches’ ability no training atmosphere . Effectiveness of the method
- 56. Job rotation or channel method of development movement of executives for beginning level managers from 6 months to 24 months great deal of job experience overall knowledge and familiarity horizontal or lateral on a planned basis on a situational basis
- 57. Advantages Develops inter-departmental co-operation Boredom and monotony are reduced Chance to step into a higher position Equal chance for advancement Best utilization Disadvantages Upsets family and home life Difficult to adjust Demotivate intelligent and aggressive trainees A highly competitive game Established operations are disturbed
- 58. Participation in Deliberation of the Junior Board and Committees or the Multiple Management technique For middle and senior level managers Real life actual problems Opportunity for managers to share Make a recommendation Exposure to other members
- 59. Advantages Opportunity to gain knowledge Identify those who have executive talent Practical experience of group decision making Inexpensive Better human relations climate Disadvantages Only for middle and senior level managers Does not permit any specific attention Tend to be discursive lacking authority
- 60. OFF-THE-JOB TECHNIQUE The Case Study Incident Method Role Playing In Basket Method Business games Sensitivity Training Simulation Grading Training u can read description from above slides
- 61. OFF-THE-JOB TECHNIQUES The Case Study Actual business situation Appraise and analyze Suggest solutions Actual decision known to the executives only Compared with the various solutions Stimulating discussion Improving decision making abilities
- 62. Incident Method Stimulate self-development Intellectual ability Practical judgement Social awareness Studies a written incident Short term decisions Find out what, when, where, how of the situation
- 63. Grid Training Several possible leadership styles Two basic orientation Concern for people and concern for production Lasts for 3 to 5 years Weekend conference Discussion, analysis and solution
- 64. By Radhika Mor MBA-IT
- 65. What is training evaluation? Methods to evaluate training. Purpose of evaluation Why training evaluation? Benefits of evaluation. Evaluation process. Evaluation Methods 1.Expert and Peer Review 2.Quality Review 3.One-to-one observation test 4.Pilot Test
- 66. Evaluation Conclusion Example and final Review.
- 67. Assessing the effectiveness of the training program in terms of the benefits to the trainees and the company. It is a process of collecting outcomes to determine if the training program was effective from whom, what, when, and how information should be collected
- 68. It is a process of establishing a worth of something. The ‘worth’, which means the value, merit or excellence of the thing
- 69. State of mind, rather than a set of techniques
- 71. Formative evaluation – evaluation conducted to improve the training process. Summative evaluation – evaluation conducted to determine the extent to which trainees have changed as a result of participating in the training program.
- 72. Feedback - on the effectiveness of the training activities. Control - over the provision of training. Intervention - into the organizational processes that affect training
- 73. Companies are investing millions of dollars in training programs to help gain a competitive advantage. Training investment is increasing because learning creates knowledge which differentiates between those companies and employees who are successful and those who are not .
- 74. Because companies have made large dollar investments in training and education and view training as a strategy to be successful, they expect the outcomes or benefits related to training to be measurable.
- 75. Improved quality of training activities Improved ability of the trainers to relate inputs to outputs Better discrimination of training activities between those that are worthy of support and those that should be dropped Better integration of training offered and on-the job development Better co-operation between trainers and line-managers in the development of staff Evidence of the contribution that training and development are making to the organization
- 77. Cognitive Learning Skills Learning Affect ‘ Objective’ results
- 78. quantitative, experimental objective broad numerical measurements questionnaires on large groups data collection, logging checklists qualitative, rich subjective in-depth qualitative interviews personal views descriptive naturalistic
- 79. Review by peers and experts on content, pedagogy and interface Editorial review of the whole course for inaccuracies, omissions, inconsistencies Provide simple methods for busy experts: give the background, analysis, and a checklist and leave them to do it Or talk-through with the evaluator using the material as if he/she were a novice - a cooperative evaluation
- 80. systematic exercise on a complete draft before pilot use, using checklists (also for ready made packages, for selection) ready made checklists exist e.g. Alessi & Trollip, MEDA modify these to create an appropriate evaluation tool score package against list, y/n or numbers (see SB’s web site documents for checklists)
- 81. developer observes learners using it record learner’s activity on paper, user log, video... students ‘think aloud’ their activities, which can also be recorded and then compared to expectation evaluator is a learner who has taken a similar course already time-consuming but valuable once substantial material is available
- 82. a small group of experienced students, in the environment of use complete the course to identify omissions, inappropriate examples, poor questions, weak text comment on content and usability done in student pairs or singly collect data by interview, questionnaires, software logs, learning assessment, manual record sheets, video
- 83. use by a representative sample of target group, including a range of ability, whose role is user rather than evaluator instruments should be non-intrusive observations, recording, automatic logs diaries, record sheet of progress. interviews, questionnaires afterwards for user views and assess learning achieved. similar to pilot tests but with real learners so only a short explanation of the evaluation being done and less data collected per user.
- 84. Uirle-Patrick Approach. Bells Systems Approach. CIRO Approach. Sorologa Institute Approach. IBM Approach. Xerox Corporation Approach. CIPP Model.
- 85. KIRKE PATRICK MODEL FOR EVALUATION
- 86. LEVEL QUESTIONS REACTION Were the participants pleased with the program? LEARNING What did the participants learn in the program? BEHAVIOR Did the participants change their behavior based on what was learnt? RESULTS Did the change in plan positively effect the organization?
- 87. REACTION OUTCOMES: Contents, materials, method, activity. CAPABILITY OUTCOMES: Outcomes against participant’s expectation. APPLICATION OUTCOME: Application of training in work setting. WORTH OUTCOME: Organizations’ benefits in terms of money, efforts, time and resources.
- 88. Developed by Warr, Bird and Rachal. It gives Evaluation in terms of CONTEXT, INPUT, REACTION, OUTCOME.
- 89. IMMEDIATE OBJECTIVE: New knowledge, skills and attitudes required to reach intermediate objective. INTERMEDIATE OBJECTIVE: Change in employees work balance necessary for ultimate objective. ULTIMATE OBJECTIVE: Particular deficiency in the organization that will be eliminated.
- 90. Following relevant questions are considered: What are the relative merits of the different HRD methods? Is it feasible for an outside organization to be more efficient at conducting the programme? Should it be developed with the internal resources? Should the line managers be involved? How much time is available for HRD? What results were achieved when a similar programme was conducted in the past?
- 91. Includes subjective reports of the participants about the whole pogramme.
- 92. STEPS: Defining trained objectives. Selecting and constructing some measures of those objectives. Making the measurements in the appropriate time. Assessing the results and using them to improve future programme.
- 93. This approach highlights that the evaluation of the programme should judge: The Satisfaction, Learning Change, Change in behavior, organizational change.
- 94. REACTION: A satisfaction rating that asks the trainees how valuable they found the program? TESTING: Pre- and Post-programme measurements in terms of knowledge and skills improvement. APPLICATION: Extent to which skills applied on the job and the results achieved. BUSINESS RESULTS: What IBM expected from the programme in the form of a return that?
- 95. ENTRY CAPABILITY: Prerequisites for the program evaluated. END OF COURSE PERFORMANCE: Whether trainees achieved the desired outcomes? MASELEY JOB PERFORMANCE: Whether trainees exhibit mastery performance under normal job condition? ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE: Which programme participants meet or exceed the organizational targets?
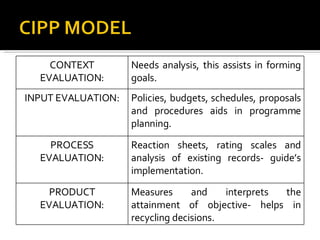
- 96. CONTEXT EVALUATION: Needs analysis, this assists in forming goals. INPUT EVALUATION: Policies, budgets, schedules, proposals and procedures aids in programme planning. PROCESS EVALUATION: Reaction sheets, rating scales and analysis of existing records- guide’s implementation. PRODUCT EVALUATION: Measures and interprets the attainment of objective- helps in recycling decisions.
- 97. Brainstorming is a group creativity technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. Although brainstorming has become a popular group technique, researchers have generally failed to find evidence of its effectiveness for enhancing either quantity or quality of ideas generated. brainstorming groups are little more effective than other types of groups, and they are actually less effective than individuals working independently.
- 98. Advantages ➔ Listening exercise that allows creative thinking for new ideas. ➔ Encourages full participation because all ideas are equally recorded. ➔ Draws on group's knowledge and experience. ➔ Spirit of cooperation is created. ➔ One idea can spark off other ideas.
- 99. Disadvantages ➔ Can be unfocused. ➔ Needs to be limited to 5-7 minutes. ➔ Students may have difficulty getting away from known reality. ➔ If not managed well, criticism and negative evaluation may occur. ➔ Value to students depends in part on their maturity level.