Unicasting , Broadcasting And Multicasting New
- 1. Unicasting , broadcasting and multicasting
- 2. UnicastingUnicast transmission: Sending of messages to a single network destination host on a packet switching network.packet switching: Groups all transmitted data irrespective of content, type, or structure – into suitably-sized blocks, called packets. One-to one connection between the client and the server.
- 3. How it works????? Use IP delivery methods (session-based protocols)such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP)Each unicast client that connects to the server takes up additional bandwidth.Client has a direct relationship to the server
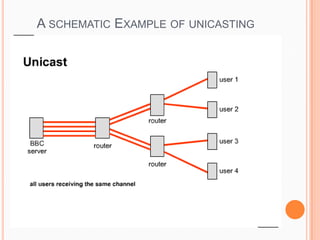
- 4. A schematic Example of unicasting
- 5. AdvantagesUsed for all network processes in which a private or unique resource is requested.Disadvantageapplications which are mass-distributed are too costly to be conductedeach network connection consumes computing resources on the sending host and requires its own separate network bandwidth for transmission.
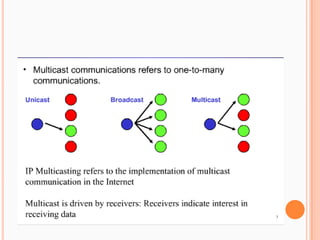
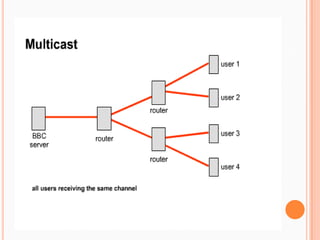
- 6. multicastA multicasting is associated with a group of interested receivers.No direct relationship between the clients and server.Clients that are connected to the multicast adds no additional overhead on the server. In fact, the server sends out only one stream per multicast station. The same load is experienced on the server whether only one client or 1,000 clients are listening
- 8. How it works???Step1: The sender sends a single datagram to the multicast address Step 2:The intermediary routers take care of making copies and sending them to all receivers that have registered their interest in data from that sender.
- 10. ADVANTAGES Datagarm received only by the interfaces that want it Group addressesMessages are UDP so there is no connection setup Can be used across a WANDisadvantage Not good for bulk data transfer Multicast on the Internet is generally not practically used on large scale
- 11. BroadcastingBROADCAST - A method of sending information over a network. Data comes from one source and goes to all other connected sources.This has the side effect of congesting a medium or large network segment very quickly.
- 12. 9 - 12Uses and its applicationsNetworkSpotSyndicatedGroup of local affiliates connected to one or more national networksViable national medium for food and beverages, cars, and over-the-counter drugsGrowth has contributed to increase in syndicated radio
- 13. 9 - 13Uses and its applicationsNetworkSpotSyndicatedWhen an advertiser places an ad with an individual station rather than a networkMakes up nearly 80% of all radio advertisingMessages can be tailored for particular audiences
- 14. 9 - 14Uses and its applicationsNetworkSpotSyndicatedOffers advertisers a variety of high-quality, specialized, and usually original programsAdvertisers value syndicated programming because of the high level of audience loyalty
- 15. thanks