Union budget 2015
- 2. ARUN JAITLEY
- 4. THREE KEY ACHIEVEMENTS Financial Inclusion - 12.5 crores families financially mainstreamed in 100 days. Transparent Coal Block auctions to augment resources of the state Swachh Bharat is not only a programme to improve hygiene and cleanliness but has become a movement to regenerate India.
- 6. Inflation declined CPI inflation projected at 5% by the end of the year, consequently, easing of monetary policy. Monetary Policy Framework Agreement with RBI, to keep inflation below 6%. GDP growth in 2015-16, projected to be between 8 to 8.5%
- 7. Housing for all - 2 crore houses in Urban areas and 4 crore houses in Rural areas Basic facility of 24x7 power, clean drinking water, a toilets, and road connectivity. Ensure SS school within 5 km reach of every child. Ensure communication connectivity to all villages To make India manufacturing HUB. Growing the spirit of Entrepreneurship. Turning the youth into Job creator.
- 9. The fiscal deficit targets are 3.9%, 3.5% and 3.0% in FY 2015-16, 2016-17 & 2017-18 respectively.
- 11. Target of `8.5 lakh crore of agricultural credit during the year 2015-16. Focus on improving the quality and effectiveness of activities under MGNREGA. Need to create a National Agriculture Market for the benefit farmers
- 12. In lending, priority will be given to SC/ST enterprises. NBFCs registered with RBI and having asset size of `500 crore and above may be considered for notifications as ‘Financial Institution’ in terms of the SARFAESI Act, 2002.
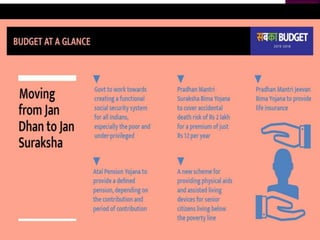
- 13. Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojna to cover accidental death risk of `2 Lakh for a premium of just `12 per year. Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana to cover both natural and accidental death risk of `2 lakh at premium of `330 per year for the age group of 18-50. A new scheme for providing Physical Aids and Assisted Living Devices for senior citizens, living below the poverty line.
- 15. Sharp increase in outlays of roads and railways. Capital expenditure of public sector units to also go up. National Investment and Infrastructure Fund (NIIF), to be established with an annual flow of `20,000 crores to it. Tax free infrastructure bonds for the projects in the rail, road and irrigation sectors. 5 new Ultra Mega Power Projects, each of 4000 MW, in the Plug-and-Play mode.
- 16. `1000 crores to the Nirbhaya Fund.
- 17. Resources to be provided to start work along landscape restoration, signage and interpretation centres, parking, access for the differently able , visitors’ amenities, including securities and toilets ,around various heritage sites. Visas on arrival to be increased to 150 countries in stages.
- 18. Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gramin Kaushal Yojana to enhance the employability of rural youth. A Committee for 100th birth celebration of Shri Deen Dayalji Upadhyay to be announced soon. An IIT to be set up in Karnataka and Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad to be upgraded in to a full-fledged IIT. New All India Institute of Medical Science (AIIMS) to be set up in J&K, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Himachal Pradesh and Assam. Another AIIMS like institutions to be set up in Bihar. A post graduate institute of Horticulture Research & Education is to be set up in Amritsar. The first phase of GIFT to become a reality very soon.
- 19. Fight against the scourge of black money to be taken forward. Efforts on various fronts to implement GST from next year. No change in rate of personal income tax. Proposal to reduce corporate tax from 30% to 25% over the next four years, starting from next financial year. PAN being made mandatory for any purchase or sale exceeding Rupees 1 lakh.
- 20. Metallurgical coke from 2.5 % to 5%. Tariff rate on iron and steel and articles of iron and steel increased from 10% to 15%. Tariff rate on commercial vehicle increased from 10 % to 40%. the new pension scheme increased from ` 1 lakh to `1.5 lakh. (Limit on deduction on account of contribution to a pension fund Service-tax plus education cesses increased from 12.36% to 14% to facilitate transition to GST. General Anti Avoidance Rule (GAAR) to be deferred by two years.