Unit 1 product-design&development
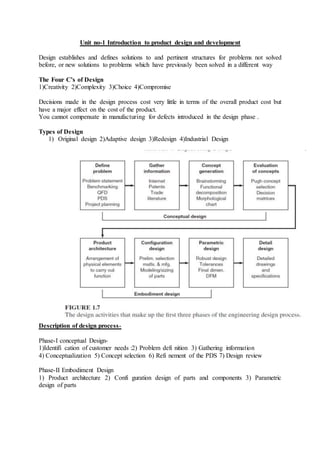
- 1. Unit no-1 Introduction to product design and development Design establishes and defines solutions to and pertinent structures for problems not solved before, or new solutions to problems which have previously been solved in a different way The Four C’s of Design 1)Creativity 2)Complexity 3)Choice 4)Compromise Decisions made in the design process cost very little in terms of the overall product cost but have a major effect on the cost of the product. You cannot compensate in manufacturing for defects introduced in the design phase . Types of Design 1) Original design 2)Adaptive design 3)Redesign 4)Industrial Design Description of design process- Phase-I conceptual Design- 1)Identifi cation of customer needs :2) Problem defi nition 3) Gathering information 4) Conceptualization 5) Concept selection 6) Refi nement of the PDS 7) Design review Phase-II Embodiment Design 1) Product architecture 2) Confi guration design of parts and components 3) Parametric design of parts
- 2. Phase-III Detail Design 1) Detailed engineering drawings suitable for manufacturing 2) Verifi cation testing of prototypes 3) Assembly drawings and assembly instructions 4) A detailed product specifi cation 5) detailed cost estimate 6) design review Phase-IV Planning for manufacture 1)Designing specialized tools and fixtures 2)Specifying the production plant that will be used (or designing a new plant) 3)laying out the production lines 4)Planning the work schedules and inventory controls (production control) 5)Planning the quality assurance system 6)Establishing the standard time and labor costs for each operation 7)Establishing the system of information flow necessary to control the manufacturing Phase-V Planning & Distribution Provide for the effective distribution to the consumer of the products that have been produced Phase-VI Planning for use The following specific topics can be identified as being important user-oriented concerns in the design process: ease of maintenance, durability, reliability, product safety, convenience in use (human factors engineering), aesthetic appeal, and economy of operation Product Development Process Product development process is the entire set of activities required to bring new concept to a state of market readiness. This set includes everything from the initial inspiring new product vision to business case analysis activities, marketing efforts, technical engineering design activities development of manufacturing plans and validation of product design to confirm these plans. It also includes development of distribution channels for strategically marketing and introducing new product. Product development and design is closely linked with industrial activity and production. When a new product is planned the designer has to bear in mind the available resources of plant and the possible impact of firm having to acquire, modify or substitute existing machines and equipment or buy various components from other supplier. The detail process of product development is explained in six phases as per below diagram
- 3. Phase 0: Product planning is usually done in two steps. The first step is a quick investigation and scoping of the project to determine the possible markets and whether the product is in alignment with the corporate strategic plan. It also involves a preliminary engineering assessment to determine technical and manufacturing feasibility. If things look promising after this quick examination, the planning operation goes into a detailed investigation to build the business case for the project Phase-1 Concept Development product design specifi cation (PDS) are developed in this phase by understanding customer needs by customer survey and by using tools like quality function deployment (QFD). Phase 2 , System-Level Design (embodiment design) Functions of the product are examined, leading to the division of the product into various subsystems. In addition, alternative ways of arranging the subsystems into a product architecture are studied Phase 3 , Detail Design It is the phase where the design is brought to the state of a complete engineering description of a tested and producible product At the end of Phase 3, a major review is held to determine whether it is appropriate to let contracts for building the production tooling. Phase 4 , Testing and Refinement, It’s concerned with making and testing many preproduction versions of the product. The first prototypes are usually made with production-intent parts. These are working models of the product made from parts with the same dimensions and using the same materials as the production version of the product but not necessarily made with the actual processes and tooling that will beused with the production version Phase 5 , Production Ramp-Up, At this stage manufacturing operation begins to make and assemble the product using the intended production system For certain products the manufacturing process places strict constraints on the properties of the product, so product design cannot be separated from the design of the production process. Examples of process-intensive products are automotive sheet steel, food products, semiconductors, chemicals, and paper
- 4. Major Activities of Modern product development process are 1)Identify opportunity- i)Develop a vision ii)Market opportunity Analysis iii)Customer need Analysis iv)Competitive analysis 2)Development of Concept: i)Portfolio planning ii)Functional modeling iii)Product architecture development iv)concept engineering 3)Implementation of concept- i)Embodiment Engineering ii)Physical and analytical modeling iii)Design for X iv)Robust design Standardization ,simplification and specialization in product design . Advantages of standardization- i)Reduction of material waste and obsolescence ii)Reduction in inventories iii)Concentration of manufacturing efforts iv)Reduction in book keeping v)Lowering the grades of skill required vi)Reduction in price vii)Reduction in repair and maintenance cost Advantages of simplicity- i)Reduction in inaccuracy ii)Reduction in equipment iii)Save of storage space iv)simplify inspection and control v)shorten or eliminate order ques Advantages of variety- i)Satisfy wide range of demand ii)Enable better contact with market to study its taste and requirement iii)create demand structure of Product Development team: A team may be defined as two or more persons engaged in a common goal who are dependent on one another for results and who have joint accountability for the outcomes. Various team roles includes 1)Administrator 2)Troubleshooter 3)Producer/test pilot 4)Manager/coordinator 5)Councilor or critic 6)Investigator 7)Performer 8)visionary 9)strategist 10)Need Identifier 11)Entrepreneur 12)Diplomat 13)Simulator
- 5. Product Development versus Product Design Sr no Product Development Product design 1 It is a process which contains entire set of activities required to bring new concept to a state of market readiness It is a process which contains technical activities within product development process that works to meet market and business requirements. 2 This set includes everything from initial inspiring new product vision to business case analysis ,commercialization activities It includes refinement of product vision in to technical specifications 3 Includes marketing efforts and technical engineering design activities It only includes technical activities 4 Includes financial activities Do not include 5 Includes design for manufacture(DFM),Design for assembly(DFA) Do not include 6 Independent process It’s a part of Product development Product Verification and product validation: Sr no Product verification Product validation 1 It is the evaluation process of determining whether or not a product ,services or system satisfies the requirements, regulations and complies with specifications or not those are imposed or for which it has made It is assurance of product ,services or system which requires and satisfies different customer needs. Customer needs are validated or not it often involves acceptance 2 It is a process to check product services or system need a set of initial design specifications or not validation is a technique to check that development and verification procedure for service. or system result in initial specifications or not 3 It involves performing special test on model. This performance is reviewed or analysis of modeling result is done It involves modeling the entire flow and its verification using simulation to product.If any gap is generated during the process it may lead to incomplete verification or development of product 4 It is internal process of verification It is external process of validation
- 6. Product testing: Product testing, also called consumer testing or comparative testing, is a process of measuring the properties or performance of products. The theory is that since the advent of mass production manufacturers produce branded products which they assert and advertise to be identical within some technical standard. Product testing seeks to ensure that consumers can understand what products will do for them and which products are the best value. Product testing is a strategy to increase consumer protection by checking the claims made during marketing strategies such as advertising, which by their nature are in the interest of the entity distributing the service and not necessarily in the interest of the consumer. The advent of product testing was the beginning of the modern consumer movement. Product testing might be accomplished by a manufacturer, an independent laboratory, a government agency, etc. Often an existing formal test method is used as a basis for testing. Other times engineers develop methods of test which are suited to the specific purpose. Comparative testing subjects several replicate samples of similar products to identical test conditions. In India bodies like ARAI (Automotive Research Association Of India) performs crash test which is a form of destructive testing .It is performed in order to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness and crash compatibility for various modes of transportation (see automobile safety) or related systems and components like safety belts and Helmets.