VMworld 2013: vSphere Flash Read Cache Technical Overview
- 1. vSphere Flash Read Cache Technical Overview Kiran Madnani, VMware Rawlinson Rivera, VMware STO5588 #STO5588
- 2. 2 Agenda VMware and SDS The importance of Flash vSphere Platform – Flash Functions and Considerations What is vSphere Flash Read Cache vSphere Flash Read Cache Configuration Options vSphere Flash Read Cache vSphere Features Interoperability Performance and Monitoring Packaging Summary
- 3. 3 Software-Defined Data Center Software-Defined Storage SDDC | SDS All infrastructure is virtualized and delivered as a service, and the control of this data center is entirely automated by software. Heterogeneous storage resources are abstracted into logical pools, consumed and managed through app-centric policy-based automation
- 4. 5 VMware Approach To Software-Defined Storage vSphere App-centric Data Services Policy-Driven Control Plane Virtual Data Plane External storage Pool Converged Infrastructure Pool Backup VM Storage Policy Capacity Performance Availability … BLOB
- 5. 6 The Importance of Flash
- 6. 7 The Importance of Flash Based Devices Moore’s Law will continue to improve CPU performance Disk drive performance remains flat.Time Performance FLASH
- 7. 8 vSphere Platform – Flash Functions and Considerations
- 8. 9 Leveraging Flash Based Devices in vSphere Key Feature vSphere Functionality Considerations • Must be simple to configure, and manage • Work with any flash based device – SAS, SATA, or PCIe • Support all types of vSphere datastore – VMFS and NFS • Must be agentless and transparent to the guess OS/App • Support granular allocation – not all disks are the same! • Significantly improve application performance • Seamlessly work with other vSphere features: • vMotion • DRS, • HA
- 9. 10 vSphere Flash Read Cache: Accelerate VM Performance • Pools multiple flash devices as a resource • Hypervisor-based caching solution • Per-VMDK granular allocation • Compatible with vMotion, DRS & HA • VMFS and NFS data stores supported • Supports PCIe, SAS, SATA interfaces • Accelerates performance for business critical applications • Enables efficient use of server flash in virtual environments • Fully transparent read-caching – no host agents or application changes Overview Benefits vSphere SAN/NAS CPU Pool Memory PoolFlash Pool New Accelerate performance
- 10. 11 Components of the solution Virtual Flash Resource vSphere Flash Read Cache Pools multiple flash devices to present a single resource; seamlessly integrates with vSphere capabilities Provides per-VMDK caching vSphere
- 11. 12 vSphere Flash Read Cache Configuration Options
- 12. 13 Configure Virtual Flash Resource • vSphere Admin configures Virtual Flash Resource by combining local flash devices on a single or across multiple hosts
- 13. 14 Configure vSphere Flash Read Cache for VMDKs • vSphere Admin configures virtual machines to use vSphere Flash Read Cache for VMDKs.
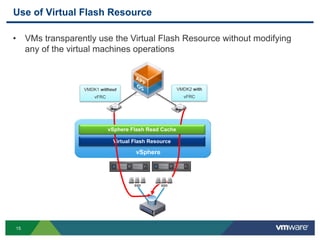
- 14. 15 Use of Virtual Flash Resource Virtual Flash Resource VMDK1 without vFRC VMDK2 with vFRC vSphere Flash Read Cache SSD vSphere SSD • VMs transparently use the Virtual Flash Resource without modifying any of the virtual machines operations
- 15. 16 vSphere Flash Read Cache in Action – vMotion, DRS, HA Virtual Flash Resource vSphere Flash Read Cache vSphere Flash Read Cache vSphere Flash Read Cache Flash Resource Caching Module
- 16. 17 vSphere Flash Read Cache and vSphere Features Interoperability
- 17. 18 vSphere Flash Read Cache – vMotion Options vMotion workflows have been modified to include a new set of checkpoints applicable to the validation of cache contents. Advanced setting allow the selection of cache migration setting for individual VMDKs
- 18. 19 vSphere Flash Read Cache – vMotion Options vMotion vFRC vFRC XvMotion vMotion Migration if migrateCache is true, in order to effectively transfer the Cache content from source to the destination host, vMotion migration process is converted into XvMotion. VC compatibility check Sufficient Virtual Flash Resource on destination host
- 19. 20 vSphere Flash Read Cache – vMotion Options Migrate Rebuild Always migrate the cache contents Do not migrate the cache contents Migration Setting Virtual Flash Cache State
- 20. 21 vSphere Flash Read Cache – SvMotion vSphere Flash Read Cache migrations impose zero impact to the SvMotion Workflow
- 21. 22 vSphere Flash Read Cache – XvMotion In case of manual XvMotion migrations, the flash cache contents options are the same as vMotion migrations
- 22. 23 vSphere Flash Read Cache - High Availability (HA) vFlash Cache vFlash Cache Restart vFRC vFRC Failed Virtual Flash Cache state is not persistent across Guest OS and host lifecycle. In the event a VM crashes, since HA will restart the VM on the same host the cache will be rebuilt. For host crashes, the VM is restarted on a different host: Admission control will apply.
- 23. 24 vSphere Flash Read Cache - Distributed Resource Scheduler XvMotion vFRC vFRC Currently virtual flash resources are managed on host level only. No automatic host migration for resource optimization. DRS will perform placement constraints for vMotion and HA.
- 24. 25 vSphere Flash Read Cache - Resource Management • Virtual Flash Resources • provisioned dynamically across all the running VMs • Virtual Machine Failure • fails to power on if host runs out of Virtual Flash resource • Resource Attributes • Reservations = Limit (no expandable reservations) • Shares not supported • No oversubscription (No thin provisioning) • Resource Consumption • Created only when VM is powered on • Reclaimed when VM is powered off • Resized when necessary • Migrated when VM moves to a different host
- 25. 26 vSphere Flash Read Cache – Cache Contents is/is Not Preserved Across disk close/reopen Fast Suspend/Resume (FSR) Snapshot Clone svMotion, XvMotion When VM is migrated (vMotion) using following option: Always migrate vFlash Cache Preserved Suspend During vFlash Cache hot reconfigure VM and Host reboot Restore Snapshot When VM is migrated using following option: Do not migrate vFlash Cache Not Preserved
- 27. 28 vFRC Performance What workloads can benefit from vFRC ? • Read-dominated I/O pattern • High repeated access of data (E.g. 20% of working set accessed 80% of time) • Sufficient flash capacity to hold data that is accessed repeatedly
- 28. 29 vSphere Flash Read Cache Sizing Guidelines Define virtual cache working set based on: • % of VMDK or workload size (for e.g. 20% of database size) Once workload is stable, monitor vFRC stats for the following: • numBlocksCurrentlyCached • numBlocks Define Cache Block Size • Use vscsiStats to gather workload statistics • Use the ioLength histogram to identify suitable block size based on the largest number of I/O operations rawlinson
- 29. 30 vSphere Flash Read Cache Monitoring Performance Statistics Counters A new set of performance statistics counters for Virtual Flash Read Cache are available in vCenter Server performance manager.
- 30. 31 vSphere Flash Read Cache – Performance Statistics Counters v Flas hCac heIops Monitors the average number of I/O requests per second to the virtual disk cache. Unit – Number v Flas hCac heL atenc y Monitors the average number of microseconds to complete I/O to the virtual disk cache. Unit – Microsecond v Flas hCac he T hroug hput Monitors the average of caches currently controlled by the module. Unit – Number
- 31. 32 vSphere Flash Read Cache – Cache Statistics in ESXCLI esxcli storage vflash cache stats get –m <module > - c <cache file> vFRC Statistics: esxcli storage vflash cache stats reset –m <module> -c <cache file> Virtual Flash Read Cache performance statistics can be retrieved in greater details utilizing ESXCLI framework
- 32. 33 Data Warehousing Application Benchmark : Swingbench 2.4 using ‘Sales History’ Schema on Oracle 11g R2 database vFRC Configuration: 8GB Cache Size and 8KB Cache block size Up to 2X improvement in transactions/min, with a 2X reduction in latency 61.7 112.9 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Baseline VFRC TPM Transac ons Per Minute 20.389 10.859 0 5 10 15 20 25 Baseline VFRC ResponseTIme(s) Average Response Time
- 33. 34 Database Transaction Application Benchmark Used : DVDStore Simulates online e-commerce site operations Database : MS SQL Server 2008 Database Size : 15 GB Workload Characteristics • 60% reads • Mostly random I/Os • Predominant I/O size : 8KB 8802 8937 12319 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 Baseline vFRC - 10GB vFRC - 15GB Orders Per Minute Up to 39% improvement in application throughput
- 35. 36 Licensing
- 36. 37 Summary
- 37. 38 Summary Simple to use Works with any Flash device type Flexible deployment - Flash not required in every server Support for VMFS and NFS No agents - Transparent to the guest OS/App Supports VMDK granular allocation Seamlessly work with other vSphere features Significantly improve application performance Virtual Flash Resource vSphere Flash Read Cache vSphere
- 38. 39 Other VMware Activities Related to This Session HOL: HOL-SDC-1308 Virtual Storage Solutions Group Discussions: STO1004-GD vSphere Flash Read Cache, VSAN, VMware Virsto, Software Defined Storage Architecture with Rawlinson Rivera and Vmware R&D Engineers
- 39. THANK YOU
- 41. vSphere Flash Read Cache Technical Overview Kiran Madnani, VMware @kmadnani Rawlinson Rivera, VMware @punchingclouds STO5588 #STO5588