Waste free indore
- 1. A STUDY OF SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE By : Dhawal Kataria School of Planning and Architecture Vijayawada Project Guide : Er. Narendra Surana CEPRD , Indore
- 2. Acknowledgement I would like to thank my project guide Er. Narendra Surana for guiding and supporting me . I would also like to thank the staff members at CEPRD for their support . It is my great honour to thank Chief Health Officer, Dr Garg and Asst. Health officer Mr. Umesh Chache of IMC, Indore to provide me with the necessary information . Finally, I would also like to mention the efforts my family made to encourage me . By Dhawal Kataria Intern, CEPRD SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 2
- 3. CONTENTS • Vision , Objective and Methodology • Introduction to Indore • Municipal Solid waste Management Act • Present situation of SWM in Indore • Integrated Solid Waste Management Programme (ISWMP) • Comparison with SLB provided by MoUD • Issues Identification • Waste generation in Indore by 2021 • Case study of Surat • Recommendations SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 3
- 4. Vision :To address the emerging problem of increasing Solid Waste in Indore OBJECTIVES: • To understand the current scenario of waste generation and its handling in Indore. • To find the issues with the current SWM system. • To forecast the waste generated in 2031 and suggestions for addressing it . SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 4
- 5. Methodology Data collection from existing reports and IMC 1.Data analysis and Comparison with SLB by MoUD. 2.Waste forecasting and calculating demand for further infrastructure. Issues identification Recommendations SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 5 Meeting with Chief Health officer, Dr Garg at Indore Municipal Corporation.
- 6. Municipal Solid Waste Management Act 2000 The Municipal Solid Waste (Management & Handling) Rules, 2000 has specific directives to the Local Bodies, District Administrations and the Urban Development Departments of the State Governments for proper and scientific management of municipal solid waste. Under these rules, it is mandatory for all the urban local bodies to provide facilities for collection, transportation, treatment & disposal of municipal solid waste in a scientific and hygienic manner. SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 6
- 7. INDORE • The most prominent city of Madhya Pradesh, situated on the western part of the Malwa on the banks of the two rivers, the Khan and the Saraswati. • Indore is a dominant commercial center and host multi-level market for maximum goods and services. • It is well connected to other part of the country with Rail , Road and Air mode of transportation. • Most of the regions surrounding the city are administered by the Indore Development Authority (IDA). Indore City has been a metropolitan municipality with a mayor-council form of government. Indore Municipal Corporation (IMC) was established in 1956 under the Madhya Pradesh Nagar Palika Nigam Adhiniyam. It consist of 15 zones and 69 wards. • Population 2011 =1,960,631.(Decadal growth rate = 24.77%) • Area = 130.17 sq.km. • Population Density = 15062 • Literacy Rate = 87.38% • Sex ratio = 921 • Total no. of Households =435018 • Household Density = 4.5 Location Map of Indore SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 7
- 8. Existing situation of SWM in Indore Quantity of Solid Waste • Amount of waste generated -1000Tons/day • Amount of waste collected -900 tons/day • Amount of waste processed-400tons/day • Amount of waste disposed (by land filling)- 50tons/day Waste Collection – A2Z Infrastructure Pvt. Ltd. Is responsible for waste Handling and Disposal. • Area covered – 130 sq.km. • Total no. of Households covered – 4 Lakhs (approx.) • Total no. of commercial establishments covered – 50,000 • Total no. of institution, offices and other institutes covered – 50,000 • Door-to-Door collection – Tender calling in process Waste Storage Facilities • No. of Bins = Existing – 1500 , Proposed – 3000 • Containers = Existing - 1000 , Proposed – 2000 • Dumper Location , Placers= Existing – 500 , Proposed – 1000 • No facility of RCC Bins and Trolleys . • No segregated storage facility, but segregated manually and transported to treatment plant. Lack of availability of Bins Segregation of waste by Rag pickers SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 8
- 9. Waste transportation • Mini Truck – 39 nos. • Dumper Placers – 14 nos. • Tricycles – 450 nos. • Animal Cart – 2 nos. • Sweeping Machine – 2 nos. • Wheel Barros – 500 nos. Waste Treatment Technology • Composting – 50 tons/day • Refuse derived Fuel – 80 tons/day • Waste incineration – 2 tons/day Landfill sites • No. of landfill sites – 1 (Devguradia trenching Ground) • Area used – 242x112 m. • Fencing under process. • Lighting facility on site -Yes • Weigh Bridge facility available - Yes • Equipment used (specify) - Bulldozer, Loaders, Dumpers • Manpower available on site-Yes • Covering is done on daily basis - Yes • Adequate covering material is available -Yes • Provisions for gas venting provided - Yes • Provision for leachate collection - Yes Landfill Site at Dev Guradia Transportation of waste , no provision of safety measures SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE Source: Indore Municipal report SWM - 2013 9 Street Sweepers (Dalel system)
- 10. Media Reactions SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 10
- 11. Integrated Solid Waste Management Programme (ISWMP) • ISWMP is a technique which covers all the steps of SWM. SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 11 Door-to-Door Collection Primary transportation of waste to sub stations Transfer of waste into Long haulage Vehicles Secondary Transportation of waste from transfer station to project sites. Power generation from RDF Disposal of remnants in SLF Recover of resources like Compost, Fuel, Plastic Derivatives, Metal, Glass, Eco-brick, etc.. Segregating Machine at Waste Treatment Plant Source : A2Z Infrastructure Ltd.
- 12. Comparison with SLB provided by MoUD Indicator Benchmark levels Indore Household level Coverage of SWM service 100% 100% 88.9% Efficiency of Collection of MSW 100% 90% Extent of segregation of MSW 100% 45% Extent of MSW recovered / recycled 80% 40% Extent of scientific disposal of MSW 100% 8.34% Extent of cost recovery in SWM service 100% NA Efficiency of redressal of Customer Complaints 80% NA Efficiency in collection of user charges 90% NA SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 12 Source :SLBs issued by MoUD , 2012
- 13. Issues Identification The following issues have been identified : SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 13 Animals exposed to harmful waste. Therefore the waste storage should be covered and must be thrown into the storage facility. No segregated transport facility , No health gear provided to safai karamcharis and waste being out flown from vehicles. No health gears provided to workers and exploitation by Kabariwalas Waste thrown into natural drainage resulting in blockage of natural drainage.
- 14. SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 14 Waste transporting vehicle are old and insufficient. Poor will of people in throwing waste into the Bins provided by IMC. Bins are not maintained properly. Mixing up of different type of waste such as Construction waste , household waste , Bio-Medical waste etc.. Other issues which have been identified are : • Poor political will by the respective authorities towards the issues. • Negligence of people towards the issue . Segregation at household levels not at all done which is a serious issue. • Location and design of bins to be improvised .It is found that most of the bins are located on the street leading to reduction in ROW of the street. • Areas surrounding trenching ground remains undeveloped, Smoke and foul odour pollutes neighbourhood.
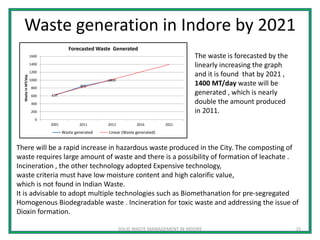
- 15. Waste generation in Indore by 2021 SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 15 The waste is forecasted by the linearly increasing the graph and it is found that by 2021 , 1400 MT/day waste will be generated , which is nearly double the amount produced in 2011. There will be a rapid increase in hazardous waste produced in the City. The composting of waste requires large amount of waste and there is a possibility of formation of leachate . Incineration , the other technology adopted Expensive technology, waste criteria must have low moisture content and high calorific value, which is not found in Indian Waste. It is advisable to adopt multiple technologies such as Biomethanation for pre-segregated Homogenous Biodegradable waste . Incineration for toxic waste and addressing the issue of Dioxin formation. 617 850 1000 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 2001 2011 2013 2016 2021 WasteinMT/day Forecasted Waste Generated Waste generated Linear (Waste generated)
- 16. Case study of Surat SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 16 • In 1994, Surat was struck by an outbreak of a virulent disease somewhat like the plague. • Within a span of 18 months the city made a complete reversal from a dirty, garbage-strewn city to become one of the cleanest cities in the country. • This transformation was possible thanks largely to the Surat Municipal Corporation and the efforts of the community. • The city was divided into six zones to decentralize the responsibilities for all civic functions. • A commissioner was appointed for each zone with additional powers. The officials responsible for solid waste management were made accountable for their work; and field visits were made mandatory for them each day. • Grievance redressal cards were issued to people so that complaints could be registered. • In addition to the administrative changes, the changed laws had an important role to play in improving the conditions by also making the citizens aware of and responsible for certain preventive actions. • The government realized that it was important to impose such a penalty in order to make people aware of their responsibility in maintaining their city’s cleanliness. Thereafter, a fine of Rs 50 was imposed for every offence of littering and it was doubled for every subsequent offence. •Private contractors are also actively involved in the transport, collection, and disposal of solid waste.
- 17. Recommendations • For Solid Waste Management in Indore , It is important that both Municipal Authority as well as citizens actively participate in waste management . • Community/Citizens role : 1. To segregate the Dry waste and wet waste. 2. To Reduce, Reuse and Recycle the waste . 3. To stop throwing waste into drainage lines as it not designed for solid waste. • Municipal Corporations Role : 1. To provide and maintain necessary infrastructure for waste management , if required through PPP projects. 2. To design innovative Waste management system which is sustainable and economically beneficial. 3. Provision of health gears to safai karamcharis. 4. Regular monitoring and field visits of the officers . • NGO / CBO’s role : 1. Public awareness of the situation of waste management . 2. Ensure and monitor the situation in the city. SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 17
- 18. Don’t Waste your Waste SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 18
- 19. THANK YOU SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN INDORE 19 For suggestions ; Contact : 07207899538 DHAWAL KATARIA