WCC COMM 101 CHAPTER #2
- 1. ©McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. Authorized only for instructor use in the classroom. No reproduction or further distribution permitted without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter 2: Convergence and the Reshaping of Mass Communication
- 2. Media Piracy •While traditional media consumption is down (and, along with it, traditional media profits) consumption via non-traditional channels is up; in fact, Americans are watching more videos, listening to more music, reading more often, playing more video games, consuming more news, and accessing the Internet more than ever before – we are consuming more media than ever but we’re simply doing it in new ways…and also not paying for it like we used to…
- 3. • Due to Media Convergence and the Digital Revolution and through a variety of technologies, it has gotten much easier and almost routine for people to get commercial mass media without paying for it. With that in mind, answer the following: • Part A.) What do you think about people “sharing” digital media? Have you ever illegally downloaded a song, movie, or some other form of digital media? If so, how do you justify that decision? • Part B.) If you were selling commercial mass media, how would you combat the problem of digital piracy? IN-CLASS STUDY FOCUS QUESTIONS
- 4. Good News for Media Industries • The “Rules” of media consumption have changed because of MEDIA CONVERGENCE; the erosion of traditional distinctions among types of media – consumers are now getting their media through the same channel/device instead of distinct ones •This “new” audience is described as being “platform-agnostic” • PLATFORM = MEDIA CHANNEL • AGNOSTIC = UNCOMMITTED TO ONE (often applied to religion)
- 5. Good News for Media Industries •Globally, media consumers average nearly 44 hours a week with mass media – a figure that grew by six hours a week between 2012 and 2014 alone •The average American child (between 8 and 18) spends more than seven hours a day engaged simultaneously with many different screens •They are adept at media multitasking; simultaneous consumption of many different kinds of media
- 6. Changes in Mass Media Business •Concentration of ownership: • Today six companies own about 90% of ALL corporate media content consumed by Americans •Conglomeration: • The ownership of media outlets by larger, NONMEDIA companies who are typically not interested at all in the process of communication, only the profits •Oligopoly: • A concentration of media interests in an even smaller number of companies • This runs the risk of the continuation of changing the goal from possible “shared meaning” to one of financial gain; being responsible to shareholders rather than an “audience” pushes communication into simply being a product instead of a process
- 7. Changes in Mass Media Business •Why do we have this Mass Media Corporation domination? •The Telecommunications Act of 1996 •FREE SPEECH FOR SALE
- 8. Mass Communication Trend: CONCENTRATION (SYNERGY) •SYNERGY = SYNCHED + ENERGY •CONCENTRATION (SYNERGY) = Synergy can be when a conglomerate’s subsidiaries promote a product owned by the company themselves.
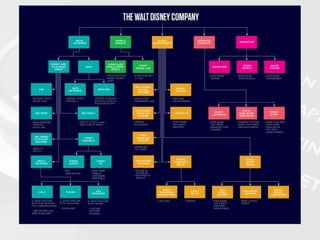
- 9. Mass Communication Trend: CONCENTRATION (SYNERGY) • DISNEY ASSETS • Use their TV and Radio networks to promote their movies, toys and theme parks by incorporating coverage into the programming itself. For example: • GOOD MORNING AMERICA had a “Star Wars” day • ESPN featured the trailer • The Radio Disney Music Awards had Star Wars as part of the program…
- 11. •STAR WARS @ THE WHITE HOUSE •“DISNEY OWNS EVERYTHING” Mass Communication Trend: CONCENTRATION (SYNERGY)
- 12. Audience Fragmentation & Technology •Narrowcasting: • The opposite of “Broadcasting” = going for smaller audiences such as specialized cable TV channels, “radio” stations & podcasts, magazines, etc.; also know as NICHE MARKETING or TARGETING •Zonecasting: • Technology delivering different commercials to specific neighborhoods
- 13. Hypercommercialism •Recouping the costs involved in acquiring numerous or large media outlets (e.g., through the selling of more advertising on existing and new media and identifying additional ways to combine content and commercials) leads to hypercommercialism. •Product placement: • Using products within the content as “background” •Brand entertainment: • When brands are “characters” in the programming and name-checked specifically •A typical show contains more than 4 minutes of product placement and nearly 15 minutes of commercials per hour
- 14. •“COST OF ENTRY” = what it financially costs to make mass media •In the newly evolving mass communication, content providers are just as likely to be individuals who believe in something or have something to say as they are big media companies in search of audiences and profits = “the people formerly known as the audience” Mass Communication Trend: PROCESS EVOLUTION
- 15. • Content providers can now be lone individuals aided by low cost of entry • As a result, messages can now be quite varied, idiosyncratic, and freed of the producers' time demands • Feedback can now be instantaneous and direct, and, as a result, audiences, very small or very large, can be quite well known to content producers and distributors Mass Communication Trend: PROCESS EVOLUTION
- 16. • Do you trust the “Mass Media”? No matter your answer, who do you trust to help form your “reality”? IN-CLASS STUDY FOCUS QUESTIONS