Web host
- 2. Contents •Stages in Web Development •Introduction •Things to have before web hosting •Ways of web hosting •Host Types •Factors to evaluate web hosts
- 3. Stages in Web Development
- 4. xxx
- 5. Web Hosting • Web Hosts Provide Data Space on their server to host or run our websites. •If you want other people to view your website, you have to copy website code in the data space which is provided by host or server.
- 6. Things to have before web hosting The Web Site code Domain Name
- 7. Web Site code We can develop website in any web technology. For example JAVA, ASP.NET, HTML, PHP, Ruby On Rails ,Android etc. for Front End. & SQL Server, MYSQL, Oracle etc for Back End
- 8. Domain Name •A domain name is a unique name for your web site. •Your domain name should be easy to remember and easy to type. •Domains can be registered from domain name registration companies. Such as Domain.com, Godaddy.com etc. •These companies provide interfaces to search for available domain names, and they offer a variety of domain name extensions that can be registered at the same time.
- 9. xxx
- 10. Hosting your own Web site Hardware Expenses •Don't expect that a low cost PC will do the job. You will also need a permanent (24 hours a day ) high-speed connection. Software Expenses •Remember that server-licenses often are higher than client-licenses. Also note that server-licenses might have limits on number of users. Labor Expenses • You have to install your own hardware and software. You might also have to deal with bugs and viruses.
- 11. Using an Internet Service Provider •Renting a server from an Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a common option. •Most small companies store their web site on a server provided by an ISP. Here are some advantages: Connection Speed Most ISPs have very fast connections to the Internet. Powerful Hardware ISPs often have powerful web servers that can be shared by several companies. Necessary backup servers. Security and Stability ISPs are specialists on web hosting. Expect their servers to have more than 99% up time, the latest software patches, and the best virus protection.
- 12. What should you look in for a host? •24-hour support Make sure your ISP offers 24-hours customer care support. •Daily Backup Make sure your ISP runs a daily backup routine, otherwise you may lose some valuable data. •Bandwidth or Content Restrictions Study the ISP's bandwidth and content restrictions. If you plan to publish pictures or broadcast video or sound, make sure that you can.
- 13. xx •E-mail Capabilities Hosting solutions should include e-mail accounts for each person in your company. E-mail addresses should appear something like this: john@mycompany.com •Database Access Make sure web host supports the appropriate database of your website. So these are the things we have to consider while choosing the host.
- 14. Types of Web Hosting Free Hosting Shared (Virtual) Hosting Dedicated Hosting Collocated Hosting
- 15. Free Hosting Some ISPs offer free web hosting. Free web hosting is best suited for small sites with low traffic, like personal sites. It is not recommended for high traffic or for real business. Technical support is often limited.
- 16. Shared (Virtual) Hosting Shared hosting is very cost effective. With shared hosting, your web site gets its own domain name, and is hosted on a powerful server along with maybe 100 other web sites.
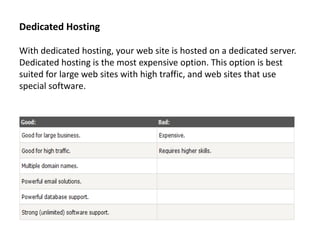
- 17. Dedicated Hosting With dedicated hosting, your web site is hosted on a dedicated server. Dedicated hosting is the most expensive option. This option is best suited for large web sites with high traffic, and web sites that use special software.
- 18. Collocated Hosting Collocation means "co-location". This is pretty much the same as running your own server in your own office, only that it is located at a place better designed for it.
- 19. Before you choose your web host, make sure that: Functionality Reliability Bandwidth and server scalability Security Backup and disaster recovery Cost effective
- 21. Thank You