What is Li-Fi ?
- 1. ByBy AvinandanAvinandan JanaJana B. Tech (CSE) - 6B. Tech (CSE) - 6thth SemSem Roll No: 18200116007Roll No: 18200116007 CS681CS681
- 2. A Presentation on LI-FI TECHNOLOGY for the partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science And Engineering.
- 3. Contents Introduction History Present Scenario Working Process Li-Fi vs Wi-Fi Applications Challenges for Li-Fi Conclusion
- 4. Introduction What is Li-Fi ? Light-Fidelity LI-FI is transmission of data through illumination, sending data through a LED light bulb that varies intensity faster than human eye can follow.
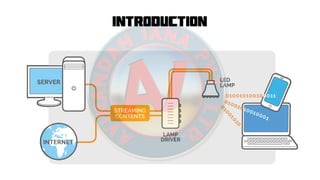
- 5. Introduction
- 6. History of Li Fi The technology truly began during the 1990's in countries like Germany, Korea, and Japan where they discovered LED's could be retrofitted to send information. Prof. Harald Haas continues to wow the world with the potential to use light for communication .
- 7. Present Scenario Radio Spectrum is congested but the demand for wireless data double each year. Every thing, it seems want to use wireless data but the capacity is drying up. 1.4 Million Base Stations 5 Billion
- 8. Radio Spectrum Issues Capacity • Radiowaves • Cost and Expensive • Less Bandwidth compared to other spectrums • Insufficient spectrum for increasing data Efficiency • Millions of base stations consume huge amount of energy for 1.Transmitting the radio waves 2.To cool the base station cabins • 5% Efficiency
- 9. Radio Spectrum Issues Availability • Available within the range of Base stations • Limited availabity • Unavailable in aircrafts Security • Less secure(passes through the walls)
- 11. Why only Visible Light Communication Radio Waves Infrared Rays Visible Rays Ultraviolet Rays X- Rays Gama Rays Gama rays cant be used as they could be dangerous. X-rays have similar health issues. Ultraviolet light is good for place without people, but other wise dangerous for the human body. Infrared, due to eye safety regulation, can only bse used with low power.
- 12. Working Process Operational procedure is very simple, if the led is on, you transmit a digital 1, if its off you transmit a 0. The LEDs can be switched on and off very quickly, which gives nice opportunities for transmitting data. Hence all that us required is some LEDs and a controller that code data into those LEDs. We have to just vary the rate at which the LED’s. Flicker depending upon the data we want to encode. Thus every light source will works as a hub for data transmission .
- 13. How Li Fi Works
- 14. How Li Fi Works On one end all the data on the internet will be streamed to a lamp driver when the led is turned on the microchip converts the digital data in form of light. A light sensitive device (photo detector) receives the signal and converts it back into original data. This method of using rapid pulses of light to transmit information wirelessly is technically referred as Visible Light Communication .
- 15. Comparison between Lifi and Wifi Feature LiFi WiFi Interference Do not have any interference issues similar to radio frequency waves. Will have intereference issues from nearby access points(routers) Technology Present IrDA compliant devices WLAN 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ad standard compliant devices Data transfer speed About 1 Gbps WLAN-11n offers 150Mbps, About 1-2 Gbps can be achieved using WiGig/Giga-IR Frequency of operation 10 thousand times frequency spectrum of the radio 2.4GHz, 4.9GHz and 5GHz Coverage distance About 10 meters About 32 meters (WLAN 802.11b/11g), vary based on transmit power and antenna type System components Lamp driver, LED bulb(lamp) and photo detector will make up complete LiFi system. requires routers to be installed, subscriber devices(laptops,PDAs,desktops) are referred as stations
- 16. Application Areas Li Fi technology is still in its infancy .However some areas where it seems perfectly applicable are: 1 . Traffic Lights: Traffic lights can communicate to the car and with each other. Cars have LED-based headlights, LED- based cack lights, and cars can communicate with each other and prevent accidents in by exchanging information.
- 17. Application Areas 2. Intrinsically Safe Environment: Visible Light is more safe than RF, hence it can be used in places where RF can't be used such as petrochemical plants.
- 18. Application Areas 3. Hospitals (In Few Medical Equipements):
- 19. Application Areas 4. Airlines: Whenever we travel through airways we face the problem in communication media ,because the whole airways communication are performed on the basis of radio waves. To overcome this drawback on radioways , li-fi is introduced.
- 20. Application Areas 5. Street Lamps (As free Access Points): • There are millions of street lamps deployed around the world. • Each of these street lamps could be a free access point.
- 21. Limitations or Challenges Light can't pass through objects. Interferences from external light sources like sun light, normal bulbs, and opaque materials in the path of transmission will cause interruption in the communication. Li-Fi requires line of sight High installation cost of the VLC systems. A major challenge facing Li-Fi is how the receiving device will transmit back to transmitter.
- 22. Conclusion The possibilities are numerous and can be explored further. If this technology can be put into practical use, every bulb can be used something like a Wi-Fi hotspots to transmit wireless data.