What IS Strategic Planning?
- 1. Lesson 1: What IS Strategic Planning? Introduction to Strategic Planning Debbie Narver
- 2. What are the problems and causes of failure in strategic planning The criteria for effective strategic plans An everyday example What we will cover?
- 3. • Often a misunderstood and misused process • “Bad habits” have become accepted as the norm Problems and Failures with Strategic Planning
- 4. Scenario 1 Our planning calendar says it’s time to do our strategic plan. So, let’s invite all of our stakeholders to a session and get it done. We will ask everyone what they think we should do for the next 3 to 5 years, and write it on flipchart. Once we are done, we will produce a nice report and give everyone a copy.
- 5. Scenario 2 Let’s hire a consult to do our strategic plan. That person can go around asking everyone what they think we should do in the next 3 to 5 years, then write up a really nice report with graphics and buzz words.
- 6. No clear purpose It’s not linked to vision and goals Opinions rather than based on real and objective information Lack of a structured and systematic approach Not linked to action (implementation) Not aligned with the current reality, such as resources No follow up evaluation What causes failure with Strategic Planning?
- 7. • Based on best practices Criteria for an Effective Strategic Plan
- 8. What IS Strategy • Definition from Essentials of Strategic Management, C. Hills and G.Jones, 2008 “A set of actions that managers take to increase their company’s performance relative to rivals”
- 9. How will we achieve or vision and mission? How can we be better than the competition? Creates focus. We can’t be all things to everyone (ever tried???) Be proactive to avoid risk and leverage opportunity Broad and long term view Guides operational decision making, budgets, priorities Why is it important?
- 10. Lowest cost Differentiation – what is unique and valuable? To whom? Niche (Focus) – excel in a narrow market, unique customer segment Partnerships or Collaboration Mergers and Acquisitions Adding or removing lines of business Automation Early adopter (first to market) Examples of Strategy
- 11. Wish list To-do list Audit Operational plan Project plan Policy What it is NOT
- 12. Planning Cycle Executive Corporate Strategic Plan Business Unit Goals and Targets Employee Performance Plan Vision, Mission, Values How to achieve superior performance Guides operational decision making and performance management
- 13. • Let’s walk through the concept with something familiar An every day example
- 14. Strategies define HOW we achieve our goals We often get bogged down in the detail (to-do list) before clarifying the big picture. Let’s look at an everyday example.
- 15. Healthy Me Fitness Quit Smoking Lose Weight Vision Goals
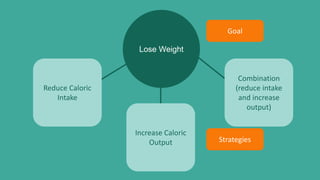
- 16. Lose Weight Reduce Caloric Intake Increase Caloric Output Combination (reduce intake and increase output) Goal Strategies
- 17. My Strengths My Weaknesses • Like to be active • Good at working in groups • Enjoy cooking • Get bored with routines • Hate mornings • Lots of social eating • Love chocolate
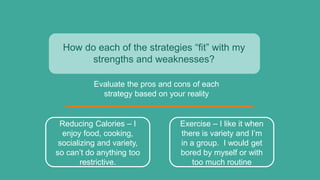
- 18. How do each of the strategies “fit” with my strengths and weaknesses? Evaluate the pros and cons of each strategy based on your reality Reducing Calories – I enjoy food, cooking, socializing and variety, so can’t do anything too restrictive. Exercise – I like it when there is variety and I’m in a group. I would get bored by myself or with too much routine
- 19. Once we decide on a Strategy, then we can talk about specific actions Too often, people jump in with ‘we need to do this project and that project’. And that’s where the endless wish list happens. That’s often where we disconnect from the reality of our strengths, weaknesses and resources. Let’s continue with our example.
- 20. Combined strategy (reduce intake and increase output) Reduce Caloric Intake – research and decide on a nutritional plan that meets my needs for variety Increase Caloric Output – sign up for group fitness classes. Get my friends involved. Connect with other like minded people for support and encouragement Strategy Tactics
- 21. Learn at your own pace, and from any location with engaging & convenient video based training Visit our website to learn about leadership training www.nmcstrategicmanager.com Learn How to Lead Strategic Planning
Editor's Notes
- The following slides are layouts you can copy-paste into your own presentations to ensure your formats and animations are always correct. You can use them as is, or you can chop-and-paste elements as you go. This slide is the standard format for the very first slide of every lecture: Just fill in the relevant information.
- Text Layout.
- Text Layout.
- Here is an example of how to format font. Source Sans Pro is our font, and can be downloaded for free from here; http://www.google.com/fonts#UsePlace:use/Collection:Source+Sans+Pro
- Another layout for bullet points.
- Here is an example of how to format font. Source Sans Pro is our font, and can be downloaded for free from here; http://www.google.com/fonts#UsePlace:use/Collection:Source+Sans+Pro
- If there are related topics with only a little bit of information about them, if they can fit comfortably on one slide you can do that
- This is one layout to break up walls of bullet points, which can bore students and be hard to look at for too long.
- Here is an example of how to format font. Source Sans Pro is our font, and can be downloaded for free from here; http://www.google.com/fonts#UsePlace:use/Collection:Source+Sans+Pro