Workshop on Network Security
- 2. Are We Secure ?
- 3. What you should know about hacking? • The impact of hacking is much worse than we could possibly imagine.. • A single ID compromised can lead to the devastation of your reputation and even money..
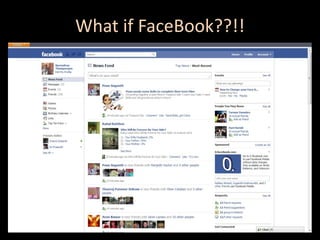
- 4. What if your Gmail account is hacked!!
- 6. Agenda • Social Engineering • ARP Poisoning – MITM • Injection attacks • Cross Site Scripting • Wireless Security • Cross Site Request Forgery • Google Hacking • Linux vs. Microsoft • The Servers FaceOff
- 7. To catch a hacker, we should think like one • What does a hacker want? Aaha!! Got it • Why does he want it? • How he gets it?
- 8. • Use at least eight characters, the more characters the better. (safe from Brute Force attacks) • Don't use a word found in a dictionary. (Safe from Dictionary attacks) • Never use the same password twice. (safe for obvious reasons) • Use a random mixture of characters, upper and lower case, numbers, punctuation, spaces and symbols.
- 9. Social Engineering is the first attack of the session
- 10. • Psychologically manipulating people into performing some action and extracting confidential information, instead of breaking in or using technical cracking skills..
- 11. 1. Security Question • You got 500 Facebook Friends who could answer all these questions!!
- 12. 2. Social Networking • Vulnerability : Human tendency to share intimate details of human life. • Though few sites allow us to set privacy controls on visibility, still most of our details are shared to the applications. • So any hacker could exploit this to find information about us.
- 13. • Cyber attack on Google in December 2009. • Chinese rebels’ accounts were accessed. • Led to Google pulling out from China. • A combination of Social Engineering and Zero- day vulnerabilities in IE6
- 14. Protecting yourself • Be aware that such attacks exist.
- 16. DISCLAIMER • Hacking is Illegal • This workshop is for Educational Purposes Only • Only use this stuff on your websites and your own networks.
- 18. ARP Poison Routing (APR) MAC Address IP Address Address Resolution Protocol
- 19. ARP Poisoning • Usually : Victim Server • In MITM : Victim Attacker Server • Thus the Attacker becomes the “Man in the Middle” (MITM) • This is done using ARP poisoning.
- 20. Technique - MITM
- 21. Counter Measures • All Your ARP Are Belong To Us ! ! • Encryption • SSL • Always Look out for the SSL Lock , if you are transferring confidential data. • Public Key Cryptography • MD5
- 23. PHP - Review • HTML can only display static content. PHP is used for processing. • PHP is a server side scripting language.
- 25. • Exploiting the weakness present in the code used for validation. • Technology review: – PHP
- 26. Injection attack • THUS A SIMPLE TEXTBOX BECOMES A PORTAL TO THE WEBSERVER. • VULNERABILITY : Input from the user is processed as such by the PHP script in the server.
- 28. 1. DIRECTORY TRAVERSAL Directory File
- 29. Traversing Directories in Windows and Linux – cd .. Takes us to the parent directory – cd pages Takes us into the Directory “pages” in the current directory – cd ../etc/files Goes back to parent directory then enters “etc” directory and then into “files” directory.
- 30. Website password.txt Pages Index.html Jive.html Choose.php Pulsar.html Stunner.html
- 31. • Apache Tomcat was vulnerable to Directory Traversal attack till version 6.0.18 (fixed July 30,2010) • RAD platform ColdFusion was found vulnerable to DT technique (fixed August 13th , 2010)
- 32. Protection mechanisms • Allow only Possible inputs.. • For the chosen scenario, make a list of Bike names.
- 34. SQL Injection
- 35. A little bit of SQL queries • With SQL, we can query a database and have a result set returned SELECT last_name FROM users WHERE user_id= 10; • Gives a result set like this: last_name rahul
- 36. What is SQL Injection? The ability to inject SQL commands into the database engine through an existing application.
- 37. How does SQL Injection work? Comments : # , -- username: ' or 1=1 # Password: anything Final query would look like this: SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ' ' or 1=1 #AND password = 'anything'
- 38. SQL Injection Defense • Input Validation • Reject "select", "insert", "update", "shutdown", "delete", "drop", "--", “#'" • Implement stringent "allow only good" filters • If the input is supposed to be numeric, use a numeric variable in your script to store it. • Magic quotes gpc is an awesome inbuilt input filter for PHP .
- 39. Cookies and Sessions • A cookie(client-side) can keep information in the user's browser until deleted. Used for Authentication, site preferences ,focusing Ads. • Sessions (server-side) assigs each user a unique number, called session id. • This session id is stored in a cookie and passed in the URL between pages while the user browses.
- 41. XSS
- 42. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) • What is it?: The Web Application is used to store, transport, and deliver malicious active content to an unsuspecting user. • XSS typically results from a web application that takes user input from one user and displays it to another user (or set of users ).
- 43. Ways of Launching Cross-Site Scripting Attacks Attacker's script must be sent to the victim o Inter-user communication within the target site (i.e., message board, etc.) o URL provided on a third-party web site (either clicked on by victim user or automatically loaded when visiting a malicious web site) o URL embedded in an email or newsgroup posting
- 45. Defending XSS • Remove from user input all characters that are meaningful in scripting languages: – =<>"'(); – You must do this filtering on the server side – You cannot do this filtering using Javascript on the client, because the attacker can get around such filtering • More generally, on the server-side, your application must filter user input to remove: – Quotes of all kinds (', ", and `) – Semicolons (;), Asterisks (*), Percents (%), Underscores (_) • Your best bet – define characters that are good and needed for the particular input (alpha and numeric), and filter everything else out .
- 48. • The ever changing network scenario..
- 50. What’s so special about Wireless networks? • Use internet anywhere, anytime. • Save a lot of money. • No need to carry cables. • IT IS ALWAYS THERE
- 51. The major problem in wireless networks – Plain text packets • Wireless devices broadcast information. • Access Anywhere, at the same time ACCESS TO ANYONE!!
- 52. Need for Wireless Security
- 53. Evolution of Wireless Security 1. Open SSID 2. Hidden SSID 3. WEP 4. WPA 5. WPA2
- 54. 1. Open SSID • The SSID (Service Set Identifier) is a name for the wireless network. SSID SSID • Open SSID – SSID is broadcasted SSID by the access point. SSID • So it is visible to everyone. • And so anyone can connect to our network.
- 55. 2. Hidden SSID • First layer of security. • The user should know the name of the SSID to connect to the internet. • Problem : Hidden SSIDs could be found using Packet Sniffers.
- 57. 3. WEP – Wired Equivalent Privacy • Both the client PC and the Access point share a common key (Shared Key). Shared Key • The shared key generates a key-stream using RC4 algorithm. • Then the key-stream is XORed with the plain text to create the cipher text. • The cipher text is sent to the receiver.
- 58. Key unchanged Same key-stream every time • If the shared key used is not changed for every frame transmitted, then the data will be XORed with the same key every time!! • So we use an Initialization Vector (IV) which changes for every frame sent thus making the key-stream unique for every frame using RC4 algorithm.
- 59. WEP Simplified
- 60. WEP Vulnerability • IV changes for each frame transmitted. • But IV is made up of 24 bits – Therefore only 16 million combinations are possible. So surely the key-stream has to repeat after a while. • If two cipher text frames using same key- stream are captured, then using statistical analysis the plain text can be found.
- 61. • Searching for Wifi Networks in a moving vehicle. • Once a Wifi network is found, the place is marked with necessary details to connect to that network. (WAR-CHALKING)
- 63. Picture showing availability of an Open SSID network with bandwidth 1.5 Mbps.
- 64. Is it not CRUEL?
- 65. Cracking the WEP Key • Interested in knowing how your home wireless network is getting poached? • Now on to a Live Demo!
- 66. So came WPA – Wifi Protected Alliance • WPA – Temporal Key Integrity Protocol – TKIP (Personal) – EAP (Enterprise) • WPA 2 – (Counter mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Protocol) – CCMP (Personal) – EAP (Enterprise)
- 68. CSRF
- 69. CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery) • A malicious exploit of a website whereby unauthorized commands are transmitted from a user that the website trusts. • XSS exploits the trust a user has for a particular site, CSRF exploits the trust that a site has in a user's browser.
- 70. Bank Forgery
- 71. Social Networks soicalnetwork.com Delete certain friends https://social.com/deletefriends.p Add a person as friend hp?id=66 https://social.com/addfriend.php? id=44 Change the password https://social.com/changepass ?new_pass=hacked attacker’s post(CSRF Code) at blog.net 71
- 72. CSRF Defenses • Secret Validation Token <input type=hidden value=23a3af01b> • Referer Validation Referer: http://www.facebook.com/home.php
- 75. • The best search engine. • Google hacking is not a exact hack. It just makes hacking easy. • VULNERABILITY : We can google ANYTHING!!
- 76. • Version of the server our website uses. • Error messages which contain too much information. • Logon Portals • Files containing passwords.
- 77. 1. Google Caches • Google caches pages whenever its crawler finds a new page in the internet. • When Cached pages are viewed then the IP address of the hacker is not logged into the system.
- 78. 2. Download anything from internet • “parent directory” akon mp3 –xxx –html –htm –php –shtml –opendir –md5 –md5sum • The above command returns the directory listing of all files under ‘Akon MP3’. Rest is “Right click” “Save Link As”
- 79. 3. Get server information • Google provides information about the server which runs a website.. Some times even passwords • Moreover some error logs in the website’s can be exploited to find the actual internal implementation of a website..
- 80. Secure against Google hacks • The password file should be saved in any name other than “password.txt” “Pass.db” or any other obviously funny names. • Exceptions should be handled properly.
- 84. LINUX vs. MICROSOFT • Linux has NO open ports by default. But windows has open ports for Windows File Sharing even if no files are shared. • Windows is susceptible to NULL session attack on port 139. • Windows gives the root user the COMPLETE power to rule the PC!!
- 85. And that includes me too :P
- 86. Are We Secure ?