World-Biomes
- 1. Antarctic Mateo Karnisauskis & Ignasi Argilès
- 2. LOCATION look at the image Less than 5% of Antarctica is free of ice;
- 3. Animals in the antarctica A variety of animals live in Antarctica for at least part of the year, including seals (...) penguins whales south georgia pipits albatrosses antarctic petrels
- 6. ENVIRONMENTAL THREATS Some species of Antarctic animals have been taken to the verge of extinction for economic benefit. Others have been killed incidentally or disturbed, soils have been contaminated, untreated sewage has been discharged into the sea and rubbish that will not decompose or break down for hundreds of years has been left behind in even the remotest parts. ~Fishing is one problem :( ~Pollution ~Exploitation and exploration ~Tourism is another problem ~Mining and oil that's another problem ~And human impacts...
- 7. Thank You for watching!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
- 9. Description of the Arctic: The Arctic is a very cold, windy, and often snowy biome located around the North Pole.
- 10. Location: The Arctic is located in the North Pole, parallel to the Equator and 23 degrees 28 minutes from the North Pole, that is, above about 75 degrees North Latitude).
- 11. Fauna: Arctic fox: Arctic Tern: Arctic Hare: Arctic Wolf: Alaskan Malamute: Ermine:
- 12. Flora: There is a little number of flora, but the most numerous plants are species of algae, moss, lichen and mushroom. They grow horizontally.
- 13. Environment Problems Polar bears are affected by decreasing sea ice The global population of polar bears is predicted to decrease by 30% in the next 45 years. Arctic and surrounding seas produce more than 10% of global marine fisheries catches by weight The Arctic and surrounding seas also account for 5.3% of the world's crustean catch by weight.
- 14. People who live there:
- 17. What is a Chaparral? A Chaparral is a shrubby coastal area that has hot dry summers and mild, cool, rainy winters. Chaparrals consist of regions of tall, dense shrubs with leathery leaves or needles.
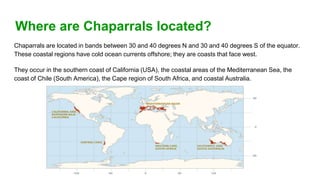
- 18. Where are Chaparrals located? Chaparrals are located in bands between 30 and 40 degrees N and 30 and 40 degrees S of the equator. These coastal regions have cold ocean currents offshore; they are coasts that face west. They occur in the southern coast of California (USA), the coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea, the coast of Chile (South America), the Cape region of South Africa, and coastal Australia.
- 19. Fauna Most are animals and desert grassland types that can adapt to the hot and dry weather. Birds make their nests in the ground to protect themselves from the heat and predators. Furry animals have short fur that can change the length to suit the season or in accordance with their environment. Reptiles hunt at night to avoid the heat.
- 21. Flora Plants must adapt to heat, little moisture, and poor soil. Plants have small, hard leaves which hold moisture. Because brush fires are frequent, many plants are small. Examples of plants: oak, scattered scrub, large shrubs, cacti.
- 22. GOODBYE
- 24. LOCATION Prairies are located in the interior of North America.
- 25. DESCRIPTION OF THE BIOME A prairie is a temperate grassland, plains of grass that get hot in the summer and cold in the winter. ( 0 ° degrees to 40º degrees) .
- 26. FAUNA Many types of animals live in the Prairies but here are the most important. We have put them here because they rather affect the food chain and some of them are beautiful. RED FOX GRAY WOLF PRAIRIE DOG BISO N
- 27. FLOR The grass is the dominant plant but also there are other plants. BIG BLUESTEM GRASS Andropogon gerardii BUFFALO GRASS Bouteloua dactyloides MILKWEED Asclepias syriaca FLEABANE Erigeron glaucus
- 28. People who live there Indian tribes lived in the prairies which were thrown to other places, and the first ranchers were installed who took care of their lands to have resources. Today there are prairies which are empty of people but there are others in which there are farms, ranches and even towns
- 29. CURIOSITI ES Twenty-five percent of the Earth is covered by the prairie biome. Since prairies biomes have rich soil, much of them are used for farming. There is only 2% of the original prairies left in North America. Prairies biomes are normally situated between a forest and a desert. In fact, prairies surround every desert in Asia.
- 31. SAVANNA Cloe Balagué and Laia Santandreu
- 32. DESCRIPTION The savanna is a hot, seasonally dry grassland with scattered trees. This environment is intermediate between a grassland and a forest. Savannas have an extended dry season and a rainy season.
- 33. LOCATION There are located in Africa, Madagascar, Australia, South America, India, and the Myanmar-Thailand region of Southeast Asia.
- 34. FAUNA ● cheetah ● baboon ● african elephant ● antelope ● boa constrictor ● giraffe ● lion
- 35. FLORA ● Senegal Gum Acacia ● Bermuda Grass ● Elephant Grass ● Manketti Tree ● Umbrella Thorn Acacia
- 36. ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES THAT AFFECT IT ➔ The global warming ➔ Agriculture ➔ Poaching ➔ Grazing ➔ Exotic plant species ➔ Climate change
- 37. PEOPLE WHO LIVE THERE Dogon tribe lives in majestic cliffs that rise in the Savanna. They live entirely apart from the other tribes of the Republic of Mali.
- 39. TAIGA Habi Siby, Mireia Arrebola
- 40. DESCRIPTION A taiga, also called a boreal forest or northern coniferous forest, is a cold woodland or forest.
- 41. LOCATION This biome spans the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. Taigas are generally located south of tundras and north of temperate deciduous forests and temperate grasslands.
- 43. FLORA In the taiga, grow mainly conifers, moss and lichens. There are many types of trees, but most of them are pines. ·Willow ·Wild rose ·Paper birch...
- 44. IT IS ENDANGERED? There are some endangered animals and plants, this are some examples: Animals: Siberian tiger, Peregrine falcon, Snow leopard… Plants: Labrador tea, Long leaf pine, Lodgepole pine...
- 45. FEATURES The taiga is characterized by a cold, harsh climate, a low rate of precipitation (snow and rain), and short growing season.Taigas are relatively low in animal diversity because of the harsh winters.
- 46. PEOPLE WHO LIVE THERE There are a few large cities in the southern parts of the taiga, such as Moscow and Toronto, but most of it is relatively unpopulated. There are also a few native communities of people who still live indigenously in the taiga.
- 47. Goodbye
- 48. Katie and Alex
- 50. Temperate forests are famous because of their leaves in Autumn, their colors vary between red, orange, yellow and brown.It usually rains a lot, and the soil is very rich in nutrients because lots of little animals and leaves fall on the floor and decompose
- 52. HEDGEHOG
- 53. SQUIRREL
- 54. SKUNK
- 55. BEAVER
- 56. RACOON
- 57. FOX
- 59. MOOSE
- 60. BEAR
- 61. WOLF
- 63. OAK
- 64. ASPEN
- 65. WALNUT TREE
- 66. CHESTNUT S
- 67. BIRCH TREE
- 68. ELM
- 69. TULIP TREE
- 70. BEECH TREE
- 71. SYCAMORE
- 73. 1-DEFORESTATION
- 74. 2-HUNTING
- 78. There aren’t any indigenous tribes in the temperate forest, but there are people living there to farm, relax... PEOPLE LIVING THERE
- 80. THE TUNDRA By: Gabryela, Andrea and Arantxa
- 81. Description of Tundra ● The tundra is a cold, treeless area; it is the coldest biome. The tundra is characterized by very low temperatures, very little precipitation (rain or snow), a short growing season, few nutrients, and low biological diversity.
- 82. Location ● The tundra is located near the North Pole, in the top of the world. This enormous biome covers a fifth of the Earth’s surface.
- 83. Fauna ● The snowy owl (Nyctea scandiaca) is a bird that lives in the tundra of North America. ● The Arctic fox (Alopex lagopus) is a furry mammal that lives in the far north, in the tundra.
- 84. Flora ● Arctic Tundra: Because the climate in the Tundra Biome is particularly inhospitable settings, the flowers found within the biome are very few. ● Alpine Tundra: The plants that grow within this Tundra Biome are called Alpine Plants. The most abundant plant is the Caribou moss.
- 85. Problems that affect the Tundra ● Lichens are a dominant life form on the tundra, and they are particularly vulnerable to air pollution. Because of this, lichens have historically been used as air pollution indicators. Air pollution has also led to a persistent 'arctic haze' that contributes to acid rain and settles on the ground, hastening snowmelt.
- 86. Problems that affect the Tundra (II) ● In addition to global concerns, ecosystem imbalances can have profound regional impacts. For example, the snow geese nesting on Canadian tundra have increased by 5 to 7 percent annually since 1965
- 87. People who live in the Tundra ● Inuit: They live along the coast and hunt caribou, seal, whales and fish. They speak Inuktitut which includes seven different dialects. ● Yakut:They live in Siberia tundras. They hunt to get animals furs. They change locations twice a year.
- 88. THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION
Editor's Notes
- mireia
- habi
- habi
- mireia
- habi siby millà
- mireia
- mireia arrebola nogués