wound healing PPT
- 2. “ God heals, and the doctor takes the fees ” Benjamin Franklin(American Statesman, scientist, Philosopher)
- 3. Phases of Healing Inflammatory (Reactive) Haemostasis Inflammation Proliferative (Regenerative/Reparative) Epithelial migration proliferation Maturation Maturational (Remodeling) Contraction scarring Remodeling
- 4. Cutaneous Wound Healing 1. By Primary Intention 2. By Secondary Intention 3. By Tertiary Intention
- 6. Secondary Union differs from Primary Union by: Larger clot or scab rich in fibrin or fibronectin More intense inflammation Much larger amounts of granulation tissue formed Involves wound contraction
- 8. Factors affecting Wound Healing Infection Nutrition ( proteins, vit.C, vit.A, Zn, Fe) Steroids / Adriamycin Mechanical factors (a) Increased pressure/torsion) (b) Ischemia Malnutrition Advanced age Ionising Radiation Diabetes Mellitus
- 9. Growth Factors affecting Wound Healing at Different Stages Epithelial Proliferation: EGF TGFa KGF HGF Monocyte chemotaxis: PDGF FGF TGFb Fibroblast Migration: PDGF FGF TGFb Fibroblast Proliferation: PDGF FGF EGF TNF Angiogenesis: VEGF Ang FGF Collagen Synthesis: TGFb PDGF Collagen secretion: PDGF FGF EGF TNF TGFb inhibits
- 10. Growth Factors in Wound Healing Increase size of cells Increase number of cells Inhibit apoptosis Pleiotropic effects i.e initiate cell proliferation, migration, differentiation, contractility, enhance synthesis of specialized proteins eg. Collagen in fibroblasts Act in autocrine, paracrine, or endocrine manner
- 11. STEM CELLS Homeostatic relation between replication and differentiation of stem cells Cells differentiate progressively as they migrate into the upper layers of the epithelium In the skin stem cell niches are in the basal layer Characteristics of Stem cells 1. Self renewal capacity 2. Asymmetric replication.
- 12. Regenerative MedicineRegenerative Medicine Goal:Goal: Regeneration and repopulation of damaged organ using embryonic or adult stem cells. Therapeutic CloningTherapeutic Cloning Patients cell Enucleated oocyte Nuclear transfer embryo Nuclear transfer blastocyst Embryonic stem cells Blood cells Neurons Muscle cells
- 13. Potential Therapeutic Strategies 1. Transplanting stem cells into area of injury 2. Use of stem cell systems to produce large amounts of differentiated cells for transplantation
- 14. Repair By Connective Tissue includes: Angiogenesis 1. Vasculogenesis 2. Angiogenesis) Deposition of ECM Migration and Proliferation of Fibroblasts Maturation and Reorganisation of Fibrous Tissue.
- 15. Fetal Wound Healing Younger the fetus less noticeable is the scar Fetal fibroblasts even in adult transplantation heals with the absence of inflammation Theory: that wound fibroblasts do not become myofibroblasts until late in gestation. IL6 is high in adult stimulated fibroblasts compared to fetal stimulated ones with coincides with increased inflammation in adults Thrombospondin 1 decreases with increase in gestation. It destabilizes matrix contracts in the EC space, facilitates mitogenesis and chemotaxis. Promotes cell associated protease and self supports matrix turnover. Thus inflammation would decrease and there would be less scarring
- 16. Aberrations of HealingAberrations of Healing Keloids: Females>Males Blacks>Whites/ Familial Outgrows the wound Rarely subsides leads to pathologic scarring in other areas of the body. In bones- Osteoarthritis common on the face shoulders back and sternum Hypertrophic Scar Females=Males Not race related/ familial Remains within the wound Subsides with time Flexor surfaces affected
- 17. 1.compression bandages 2. intralesional Triamcinolone 3. Excision and skin grafting 4. Laser 5. Surgery f/b post op interstitial radiotherapy Excessive granulation tissue which protrudes above the level of the skin & hinders re epithelialisation is called “EXUBERANT GRANULATION or PROUD FLESH! Rx: Cautrise or surgically resect the tissue Rx of Aberrations
- 19. Newer Concepts Low level laser therapy. Negative pressure wound therapy(NPWT).
- 20. Collagen & chondroitin sulphate : Integra Apligraftrade: skin substitute containing collagen and seeded cells Alloderm: immunologically inert, nonliving, allogenic, acellular dermal matrix with intact basement membrane prepares wound bed for grafting
- 21. Tegaderm Used for simple shallow wound dressing Protects from water loss mechanical injury and drying
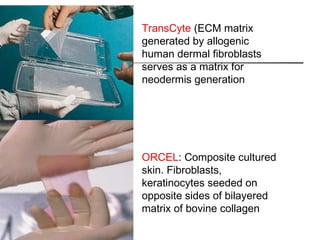
- 22. TransCyte (ECM matrix generated by allogenic human dermal fibroblasts serves as a matrix for neodermis generation ORCEL: Composite cultured skin. Fibroblasts, keratinocytes seeded on opposite sides of bilayered matrix of bovine collagen
- 23. Dermagraft living allogenic dermal fibroblasts grown on a degradable scaffold. Good resistance to tearing
- 24. E-Z Derm Biosynthetic porcine derived xenograft Collagen has been crosslinked with aldehyde Can be conveniently stored at room temperature long shelf life. perforated or non- perforated Partial thickness, donor sites, sandwich autografts, and to cover full thickness wounds prior to grafting. OASIS comprised of small intestine submucosa acellular collagen matrix. Chance of rejection
- 25. OPSITE
- 26. beta-Glucan stimulates the macrophage activity and promotes rapid wound healing. Beta-Glucan Collagen mesh or Glucan II (Beta-Glucan) mesh. Rapid healing without dressing changes painless treatment.
- 27. HONEYSOFT Natural dressing Honey-impregnated dressing Chronic unhealing wounds. Impregnated into a compress of EVA (ethylenevinylacetate) mesh Honey cleans the wound without disturbing it Removing the dressing causes no damage no known side effects
- 28. Hyperbaric Medicine Systemic delivery of oxygen to the tissues unit which has been compressed to approximately 2-2.4 ATA. Stimulates angiogenesis and fibroblast migration, enhances neutrophil and antibiotic killing action, and suppresses alpha toxin production in gas gangrene.
- 29. Total Contact Casting A treatment used for successful offweighting of plantar foot ulcerations. Provides decreased plantar surface pressures over wounded areas of the foot, by redistributing weight bearing over the entire lower leg.
- 30. a novel hydrogel, to seal wounds and at the same time deliver an antibacterial punch "They're like rebar when you're building something with concrete, They give the cement something to hang onto." "MAX8," encapsulate living cells in the hydrogel and then inject the gel into secondary sites without harming the cells.