Zara : Fast Fashion
- 1. ZARA : FAST FASHION Presented By: Avinash Shaw Mohit Chandra Prabhat Gupta Sumeet Agarwal Sumona Goash
- 2. AGENDA Company Overview Zara Business Model Key Success Factors SWOT Analysis Competitors Analysis Conclusion
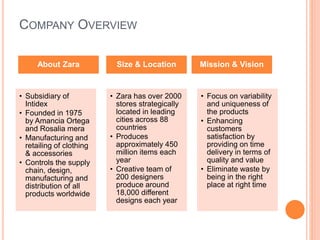
- 3. COMPANY OVERVIEW About Zara • Subsidiary of Intidex • Founded in 1975 by Amancia Ortega and Rosalia mera • Manufacturing and retailing of clothing & accessories • Controls the supply chain, design, manufacturing and distribution of all products worldwide Size & Location • Zara has over 2000 stores strategically located in leading cities across 88 countries • Produces approximately 450 million items each year • Creative team of 200 designers produce around 18,000 different designs each year Mission & Vision • Focus on variability and uniqueness of the products • Enhancing customers satisfaction by providing on time delivery in terms of quality and value • Eliminate waste by being in the right place at right time
- 4. ZARA INDIA Inditex and Tata Group joint venture First Store was opened in Mumbai in 2010 18 outlets presently (Avg. sales 47 Cr per store) First brand to cross 100 million sales mark
- 5. BUSINESS MODEL Conventional Business Model Zara’s Business Model Supply Chain Reliant on outsourcing production Highly responsive, vertically integrated supply chain Time to Market High due to outsourcing. Industry avg. is 6 months Lead time for new products launches are approx. 2-3 weeks Marketing Ads primarily for range & assortments and various discounts offers Ads only for yearly sales and to announces of new stores Design Teams Design conceptualized by small elite team. Common for all segments Dedicated teams for different segments Product Life Span Long life span because new products launch per year stood approx. 2000-4000 Short life span because of more product launches. On avg. 11K yearly Sales Forecast It is forecasted before arrival of new sessions Not done due to flexible response time and supply chain IT Spending 2% of revenue as IT applications are outsourced by vendors 0.5% of revenue due to in-house applications development
- 6. SUPPLY CHAIN STRATEGY Responsive supply chain and logistics: Provides shipments globally within 24-48 hours Vertical integration: Toyoto helped Zara to install JIT systems in its Spain factories to make their process even more smoother Communication: High communication from stores to headquarters means lower inventories and shipments of correct merchandising Fast inventory turnover: Small batches of merchandising can turnout products in as little as 2 weeks
- 7. RETAILING Cost Leader: Low price in sophisticated stores in prime location Location: The stores are located in highly visible locations Zara invest in prime locations, including the premier shopping streets and upscale shopping centres Display window: Attract shopper inside and allow them to see the type of garment offered.
- 8. KEY SUCCESS FACTORS Utilizing the advantage of geographical condition Vertical integrated distribution strategy Production in small quantities, Scarce supply Just-in-time manufacturing system Frequent change in store layout
- 9. SWOT ANALYSIS Strengths • High Brand Value • Strong Distribution channel • Vertically integrated (operation ,manufacturing) • low cost with most innovative and fashionable designs Weakness • Low advertisement • Centralize Distribution system • Ecommerce Visibility Opportunities • Growing branded apparel market • Expand in new segments • Online marketing and E- tailing Threats • Primary Challenge is high quality retail spaces • Local and Global Competitors • Large amount of consumers are switching to different brands
- 10. COMPETITORS ANALYSIS Product Male, Female, Kids Male, Female Male, Female, Kids Production Outsourced Outsourced 60% in house 40% outsourced Turn around time 56 days 56 days 2-3 weeks Net Margins 9.6% 7.07% 10.47% Global Share 1.6% 1.2% 1.4% Price Value for Money Expensive Expensive
- 11. CONCLUSION Responsive supply and logistics, vertical integration, communication and fast inventory turnover are some of Zara’s most unique and effective strategies Having a centralized distribution and JIT production schedule creates more efficient process High investment into technology enables Zara to operate the way they want
- 12. Thank You