Zoha 244
- 1. EPS SITES BY ZOHA KHAN OF GRADE 6 PROJECT ON PLANT MORE TREES
- 2. WHY WE HAVE TO SAVE PLANTS Most trees and shrubs in cities or communities are planted to provide beauty or shade. These are two excellent reasons for their use. Woody plants also serve many other purposes and it often is helpful to consider these other functions when selecting a tree or shrub for the landscape. The benefits of trees can be grouped into social, communal, environmental, and economic categories.
- 3. POEM Trees absorb pollution protect water catchments Trees produce life – giving oxygen Trees mitigate climate change Trees help to cool cities Trees are culturally important Trees provide habitat for wildlife Trees are a legacy for future generations
- 4. IMPORTANCE OF PLANTS Although rainforests make up only about six percent of the Earth's surface, they account for at least 50 percent of all of the species of organisms on our planet, if not more. There are also hundreds of species yet to be discovered.
- 5. PLANTS THEY ARE IMPORTANT MEDICINAL PLANTS – Medicinal plants help us by giving medicine . The different parts of different plants gives us medicine For e.g.. Leaves and fruits of neem etc. FLOWERING PLANTS – Flowering plants help to increase beauty of nature in flower in plants all the flower plants come . For e.g.. Rose , sun flower , lotus etc. FRUIT PLANTS – Fruit plant gives us all kinds of fruits all the plants that gives us fruit comes in fruit plant. For e.g. apple tree , mango tree , banana tree etc.
- 6. USES OF PLANTS We use plants a lot for many things like wood, medicine, fruits etc.
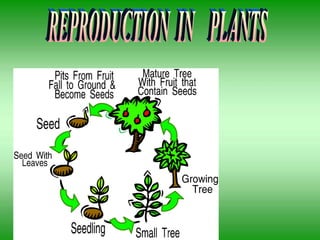
- 9. REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS
- 10. HOW WE CAN PLANT TREES By giving proper quantity of water and sunlight
- 11. WE THE E.P.S STUDENTS ARE WORKING TO SAVE PLANTS FOR BETTER ENVIROMENT
- 12. HOW WE ARE SAVING PLANTS First we went to nursery trip to take ideas that how we can save plant and to see different kinds of plants. video
- 13. SAVING PLANT After taking ideas we create our own nursery . Whole class contribute plants and we also ask other classes to contribute some plants for better environment and it is also a kind of community and service. video
- 14. PLANT CONSEVATION DAY After doing small activities we plan to celebrate plants conservation day . For plant conservation day we make banners , slogans etc .
- 15. PEOPLES FROM ANY PLACE CAN PLANT TREES FOR STOPING GLOBAL WARMING
- 16. WE WILL HELP YOU
- 17. PARTS OF PLANTS
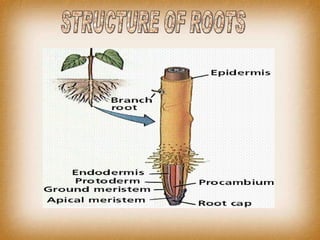
- 18. ROOTS The root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial (growing above the ground) or aerating (growing up above the ground or especially above water). Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either (see rhizome ). So, it is better to define root as a part of a plant body that bears no leaves, and therefore also lacks nodes .
- 20. STEMS A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant . The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes, the nodes hold buds which grow into one or more leaves , inflorescence (flowers), cones or other stems etc. The internodes distance one node from another. The term shoots is often confused with stems; shoots generally refer to new fresh plant growth and does include stems but also to other structures like leaves or flowers.
- 22. LEAVES leaf is an above-ground plant organ specialized for photosynthesis . For this purpose, a leaf is typically flat (laminar) and thin. There is continued debate about whether the flatness of leaves evolved to expose the chloroplasts to more light or to increase the absorption of carbon dioxide . In either case, the adaption was made at the expense of water loss. In the Devonian period , when carbon dioxide concentration was at several times its present value, plants did not have leaves or flat stems. Many bryophytes have flat, photosynthetic organs, but these are not true leaves. Neither are the microphylls of lycophytes . The leaves of ferns , gymnosperms , and angiosperms are variously referred to as macrophyll , megaphylls , or euphylls .
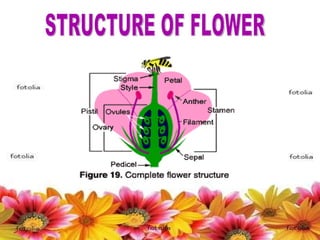
- 24. FLOWER A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom , is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants (plants of the division Magnoliophyta , also called angiosperms). The biological function of a flower is to mediate the union of male sperm with female ovum in order to produce seeds. The process begins with pollination, is followed by fertilization, leading to the formation and dispersal of the seeds. For the higher plants, seeds are the next generation, and serve as the primary means by which individuals of a species are dispersed across the landscape. The grouping of flowers on a plant is called the inflorescence .