Haptens
- 1. HAPTENS Presentation on: Presented By: Sonika Bhatnagar B.Sc Life Sc (III )
- 2. Antigen is a molecule that can bind to an antibody, B cell receptor or T cell receptor A stimulus that produces a humoral or cell- mediated immune response All immunogens are antigens but not all antigens are immunogens Some very small molecules called haptens can bind to Ab’s or TCR’s but they cannot initiate an immune response…
- 3. Haptens • The term Hapten was given by the immunologist Karl Landsteiner, who studied them in early 20th century. • It came from a Greek word Haptein meaning to fasten.
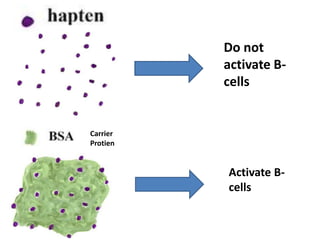
- 4. Haptens Haptens are low molecular weight molecules Small organic molecule that are antigenic but not immunogenic Which means that they can bind to immune cells but fail to induce Humoral or cell mediated immune response. Hence no antibodies are raised against them
- 5. Why Haptens are not Immunogenic? Cannot activate Helper T cells Failure to activate Helper T cells is due to their inability to bind to MHC proteins Haptens are univalent hence cannot activateB cells by themselves
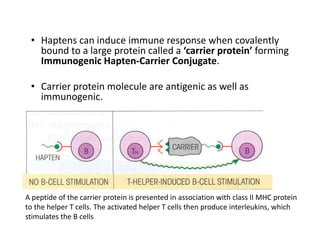
- 6. • Haptens can induce immune response when covalently bound to a large protein called a ‘carrier protein’ forming Immunogenic Hapten-Carrier Conjugate. • Carrier protein molecule are antigenic as well as immunogenic. A peptide of the carrier protein is presented in association with class II MHC protein to the helper T cells. The activated helper T cells then produce interleukins, which stimulates the B cells
- 8. Animals immunized with such a Hapten conjugate produce antibodies specific for : (1) the hapten determinant, (2)unaltered epitopes on the carrier protein (3) new epitopes formed by combined parts of both the hapten and carrier
- 9. • By itself, a hapten cannot function as an immunogenic epitope. • But when multiple molecules of a single hapten are coupled to a carrier protein (or nonimmunogenic homopolymer), the hapten becomes accessible to the immune system and can function as an immunogen. Hapten Carrier molecule Immunogen
- 10. Pioneering work of Karl Landsteiner Hapten molecule injected Carrier Molecule injected Hapten-Carrier Conjugate injected Anti-serum Anti-serum Anti-serum
- 11. Pioneering work of Karl Landsteiner (contd…)
- 12. By observing which hapten modifications prevented or permitted cross- reactions, Landsteiner was able to gain insight into the specificity of antigen antibody interactions Pioneering work of Karl Landsteiner (contd…) • Landsteiner immunized rabbits with a hapten-carrier conjugate and then tested the reactivity of the rabbit’s immune sera with that hapten and with closely related haptens coupled to a different carrier protein • He was thus able to measure, specifically, the reaction of the antihapten antibodies in the immune serum and not that of antibodies to the original carrier epitopes • Landsteiner tested whether an antihapten antibody could bind to other haptens having a slightly different chemical structure. Such reactions are called a cross-reaction • Antibodies developed against aminobenzene or its derivatives react only with the original hapten and do not cross react with any other derivative.
- 13. Examples of Haptens Many biologically important substances which can function as haptens are:- • Drugs- such as Penicillin • peptide hormones • steroid hormones Some important Haptens are: • Dinitrophenol • Aminobenzene • o-aminobenzoic acid • m-aminobenzoic acid • P-aminobenzoic acid
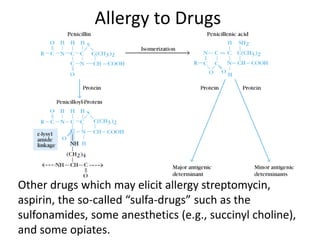
- 14. • The formation of drug-protein conjugates in the body can produce drug allergies that may be life- threatening. Haptens in Real life... • Immunologist’s favourite, as it can be used as- DIAGNOSTIC TOOL Enzyme-multiplies Immunoassay Technique (EMIT)
- 15. Allergy to Drugs Other drugs which may elicit allergy streptomycin, aspirin, the so-called “sulfa-drugs” such as the sulfonamides, some anesthetics (e.g., succinyl choline), and some opiates.
- 16. Application of Haptens in Pregnancy test
- 17. References • http://books.google.co.in/books?id=QCFwJYk2m4YC&pg=PA3 7&lpg=PA37&dq=example+of+peptide+hormone+as+hapten &source=bl&ots=INNSWFE6O_&sig=AMmrqCTXEk- WUf6wF6Mqo90acL8&hl=en&sa=X&ei=brBOVKPLCaLbmAXy mYGYBA&ved=0CCsQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=example%20of %20peptide%20hormone%20as%20hapten&f=false • http://www.slideshare.net/RajkumarNarasinghan/antigen- 15639219?qid=f2c646e7-0642-4990-8372- c4c88e4a6e2d&v=default&b=&from_search=10 • http://www.slideshare.net/taha244ali/2-antigens- immunogens-epitopes-and-haptens • Immunology Kuby 6th Edition