氯丙嗪:修订间差异
无编辑摘要 |
|||
| 第60行: | 第60行: | ||
<!-- Side effects and mechanism--> |
<!-- Side effects and mechanism--> |
||
常見副作用包含[[錐體外症候群]]、{{tsl|en|sedation|鎮靜|嗜睡}}、口乾、[[姿位性低血壓]],以及體重增加等等<ref name=AHFS2015/>。嚴重副作用則則可能導致{{tsl|en|tardive dyskinesia|遲發性不自主運動}}等永久運動功能障礙、{{tsl|en|neuroleptic malignant syndrome|抗精神藥物惡性症候群}}、以及[[白细胞减少症]]<ref name=AHFS2015/>。因[[失智症]]導致精神錯亂的老年人用藥可能會增加死亡風險<ref name=AHFS2015/>。[[妊娠]]期間用藥的安全性迄今不明<ref name=AHFS2015/>。本品屬於{{tsl|en|typical antipsychotic|典型抗憂鬱藥物}}<ref name=AHFS2015/>。 |
常見副作用包含[[錐體外症候群]]、{{tsl|en|sedation|鎮靜|嗜睡}}、口乾、[[姿位性低血壓]],以及體重增加等等<ref name=AHFS2015/>。嚴重副作用則則可能導致{{tsl|en|tardive dyskinesia|遲發性不自主運動}}等永久運動功能障礙、{{tsl|en|neuroleptic malignant syndrome|抗精神藥物惡性症候群}}、以及[[白细胞减少症]]<ref name=AHFS2015/>。因[[失智症]]導致精神錯亂的老年人用藥可能會增加死亡風險<ref name=AHFS2015/>。[[妊娠]]期間用藥的安全性迄今不明<ref name=AHFS2015/>。本品屬於{{tsl|en|typical antipsychotic|典型抗憂鬱藥物}}<ref name=AHFS2015/>。其作用機制尚未明朗,但可能與其具{{tsl|en|dopamine antagonist|多巴胺受體拮抗劑|}}的活性有關<ref name=AHFS2015/>。本品亦具有{{tsl|en|antiserotonergic|抗血清素活性|抗血清素}}以及[[抗組織胺藥|抗組織胺]]的活性<ref name="AHFS2015">{{cite web|url=http://www.drugs.com/monograph/chlorpromazine-hydrochloride.html|title=Chlorpromazine Hydrochloride|accessdate=Dec 1, 2015|author=|date=|publisher=The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208163938/http://www.drugs.com/monograph/chlorpromazine-hydrochloride.html|archivedate=8 December 2015|deadurl=no}}</ref>。 |
||
<!-- History, society and culture --> |
<!-- History, society and culture --> |
||
本品最早於1950年發現,為第一種精神疾患藥物<ref name="history05">{{Cite journal|doi=10.1080/10401230591002002|last1=López-Muñoz |first1=Francisco |last2=Alamo |first2=Cecilio |last3=Cuenca|first3=Eduardo|last4=Shen |first4=Winston W. |last5=Clervoy |first5=Patrick |last6=Rubio |first6=Gabriel |year=2005 |title=History of the discovery and clinical introduction of chlorpromazine |journal=Annals of Clinical Psychiatry |volume=17 |issue=3|pages=113–35|pmid=16433053}}</ref><ref name=Ban2007>{{cite journal|last1=Ban|first1=TA|title=Fifty years chlorpromazine: a historical perspective.|journal=Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment|date=August 2007|volume=3|issue=4|pages=495–500|pmid=19300578|pmc=2655089}}</ref>。本品列名於[[世界卫生组织基本药物标准清单]]之中,為基礎公衛體系必備藥物之一<ref name=WHO19th>{{cite web|title=WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)|url=http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/essentialmedicines/EML_2015_FINAL_amended_NOV2015.pdf?ua=1|work=World Health Organization|accessdate=8 December 2016|date=April 2015|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20161213052708/http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/essentialmedicines/EML_2015_FINAL_amended_NOV2015.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=13 December 2016|df=dmy-all}}</ref>。氯丙嗪的發現為精神醫療的{{tsl|en|history of psychiatry|精神醫學歷史|重大里程碑}}<ref>{{cite journal|last1=López-Muñoz|first1=F|last2=Alamo|first2=C|last3=Cuenca|first3=E|last4=Shen|first4=WW|last5=Clervoy|first5=P|last6=Rubio|first6=G|title=History of the discovery and clinical introduction of chlorpromazine.|journal=Annals of Clinical Psychiatry|date=2005|volume=17|issue=3|pages=113–35|pmid=16433053|doi=10.1080/10401230591002002}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last1=Shorter|first1=Edward|title=A historical dictionary of psychiatry|date=2005|publisher=Oxford University Press|location=New York|isbn=9780198039235|page=6|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=M49pEDoEpl0C&pg=PA6|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170214213428/https://books.google.com/books?id=M49pEDoEpl0C&pg=PA6|archivedate=14 February 2017|df=dmy-all}}</ref>。本品屬於[[通用名藥物]]<ref name=AHFS2015/>,其於[[開發中國家]]的每日劑量批發價約介於 0.02 至 0.12 美金之間<ref>{{cite web|title=Chlorpromazine HCL|url=http://erc.msh.org/dmpguide/resultsdetail.cfm?language=english&code=CPZ100T&s_year=2014&year=2014&str=100%20mg&desc=Chlorpromazine%20HCl&pack=new&frm=TAB-CAP&rte=PO&class_code2=24%2E1%2E&supplement=&class_name=%2824%2E1%2E%29Medicines%20used%20in%20psychotic%20disorders%3Cbr%3E|website=International Drug Price Indicator Guide|accessdate=1 December 2015|deadurl=no|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170329013315/http://erc.msh.org/dmpguide/resultsdetail.cfm?language=english&code=CPZ100T&s_year=2014&year=2014&str=100%20mg&desc=Chlorpromazine%20HCl&pack=new&frm=TAB-CAP&rte=PO&class_code2=24.1.&supplement=&class_name=%2824.1.%29Medicines%20used%20in%20psychotic%20disorders%3Cbr%3E|archivedate=29 March 2017|df=dmy-all}}</ref>。在美國同樣劑量則約需 2 美金<ref name=AHFS2015/>。 |
|||
==藥理學== |
==藥理學== |
||
2018年1月1日 (一) 12:24的版本
 | |
 | |
| 臨床資料 | |
|---|---|
| 商品名 | Largactil, Thorazine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682040 |
| 核准狀況 | |
| 懷孕分級 |
|
| 给药途径 | 口服(藥丸或糖漿)、肛門塞劑、肌肉注射、靜脈注射 |
| ATC碼 | |
| 法律規範狀態 | |
| 法律規範 |
|
| 藥物動力學數據 | |
| 生物利用度 | 10–80% (口服,視體質而定)[1] |
| 血漿蛋白結合率 | 90–99%[1] |
| 药物代谢 | 肝臟,大多經CYP2D6[1] |
| 生物半衰期 | 30 小時[2] |
| 排泄途徑 | 尿液(24小時內排除43–65%)[1] |
| 识别信息 | |
| |
| CAS号 | 50-53-3((自由基團) 69-09-0 (鹽酸鹽)) |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.042 |
| 化学信息 | |
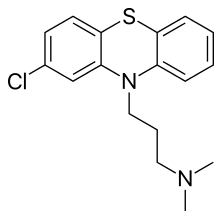
| 化学式 | C17H19ClN2S |
| 摩尔质量 | 318.86 g/mol (自由基團) 355.33 g/mol(鹽酸鹽) |
| 3D模型(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
氯丙嗪(Chlorpromazine,簡稱CPZ),常見商標名 Thorazine 或 Largactil ,為一種精神科藥物[2]。本品一般用於治療精神分裂症等思覺失調[2]。其他用途還可用做治療躁鬱症、過動症、恶心、呕吐、術前焦慮,或是其他方法無法控制的打嗝症狀等等[2]。本品可以口服、肌肉注射,或靜脈注射[2]。
常見副作用包含錐體外症候群、嗜睡、口乾、姿位性低血壓,以及體重增加等等[2]。嚴重副作用則則可能導致遲發性不自主運動等永久運動功能障礙、抗精神藥物惡性症候群、以及白细胞减少症[2]。因失智症導致精神錯亂的老年人用藥可能會增加死亡風險[2]。妊娠期間用藥的安全性迄今不明[2]。本品屬於典型抗憂鬱藥物[2]。其作用機制尚未明朗,但可能與其具多巴胺受體拮抗劑的活性有關[2]。本品亦具有抗血清素以及抗組織胺的活性[2]。
本品最早於1950年發現,為第一種精神疾患藥物[3][4]。本品列名於世界卫生组织基本药物标准清单之中,為基礎公衛體系必備藥物之一[5]。氯丙嗪的發現為精神醫療的重大里程碑[6][7]。本品屬於通用名藥物[2],其於開發中國家的每日劑量批發價約介於 0.02 至 0.12 美金之間[8]。在美國同樣劑量則約需 2 美金[2]。
藥理學
现在氯丙嗪被归入第一代抗精神病药,它们的药理机制是阻断脑内多巴胺受体,从而发挥抗精神病作用。
不良反應
该类药物一般都伴有锥体外系副作用。针剂的体位性低血压副作用较明显。长期服用后戒断会出现肌肉抽搐。
劑型及用量
有片剂和针剂,25mg/片,50mg/针。
用于治疗精神病时起始剂量较低,根据病人情况逐渐加量至治疗剂量,治疗剂量一般在300mg至600mg之间。该药有较强的镇静作用,故也常用于镇静。针剂通常用于不合作病人,另外针剂通常与鹽酸異丙嗪(也叫非那根)合用,组成冬非合剂。
參考文獻
- Baldessarini, Ross J.; Frank I. Tarazi. Pharmacotherapy of Psychosis and Mania. Laurence Brunton, John Lazo, Keith Parker (eds.) (编). Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics 11th. New York: McGraw-Hill. 2006. ISBN 978-0071422802.
- Bezchlibnyk-Butler, K. Z. Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs (German Edition)
- Rote Liste (German Drug Compendium)
- Benkert, O. and H. Hippius. Psychiatrische Pharmakotherapie (German. 6th Edition, 1996)
- Physician's Desktop Reference (2004)
- Heinrich, K. Psychopharmaka in Klinik und Praxis (German, 2nd Edition, 1983)
- Römpp, Chemielexikon (German, 9th Edition)
- NINDS Information Homepage (see External links section)
- Plumb, Dondal C. Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook (Blackwell, 5th Edition, 2005)
- Methods of Execution. Clark County, IN Prosecuting Attorney web page. [2008-08-03].
外部連結
- Medlineplus article on chlorpromazine
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) Tardive Dyskinesia information page
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal - Chlorpromazine
- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 PRODUCT INFORMATION LARGACTIL (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Sanofi Aventis Pty Ltd. 28 August 2012 [8 December 2013]. (原始内容存档于30 March 2017). 已忽略未知参数
|df=(帮助) - ^ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 Chlorpromazine Hydrochloride. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. [Dec 1, 2015]. (原始内容存档于8 December 2015).
- ^ López-Muñoz, Francisco; Alamo, Cecilio; Cuenca, Eduardo; Shen, Winston W.; Clervoy, Patrick; Rubio, Gabriel. History of the discovery and clinical introduction of chlorpromazine. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 2005, 17 (3): 113–35. PMID 16433053. doi:10.1080/10401230591002002.
- ^ Ban, TA. Fifty years chlorpromazine: a historical perspective.. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment. August 2007, 3 (4): 495–500. PMC 2655089
 . PMID 19300578.
. PMID 19300578.
- ^ WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List) (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015 [8 December 2016]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于13 December 2016). 已忽略未知参数
|df=(帮助) - ^ López-Muñoz, F; Alamo, C; Cuenca, E; Shen, WW; Clervoy, P; Rubio, G. History of the discovery and clinical introduction of chlorpromazine.. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 2005, 17 (3): 113–35. PMID 16433053. doi:10.1080/10401230591002002.
- ^ Shorter, Edward. A historical dictionary of psychiatry. New York: Oxford University Press. 2005: 6. ISBN 9780198039235. (原始内容存档于14 February 2017). 已忽略未知参数
|df=(帮助) - ^ Chlorpromazine HCL. International Drug Price Indicator Guide. [1 December 2015]. (原始内容存档于29 March 2017). 已忽略未知参数
|df=(帮助)
