Abstract
While engineered quantum systems are a general route to the manipulation of multipartite quantum states, access in a physical system to a continuous quantum phase transition under sufficient control offers the possibility of an intrinsic source of entangled states. To this end we realize the quantum version of the linear-zigzag structural transition for arrays of up to five ground state-cooled ions held in a linear Paul trap and we demonstrate several of the control requirements towards entangled-state interferometry near the critical point. Using in situ spectroscopy we probe the energy level structure and occupation of the soft mode associated with the structural transition, and show a stable critical point and majority ground state occupation crossing the transition. We resolve biases arising from trap electrode asymmetries that change the nature of the transition, show that they can be suppressed by varying the ion number, and demonstrate control of the transition bias using optical dipole forces.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
By virtue of their Coulomb interactions, laser-cooled trapped arrays of ions intrinsically present a strongly interacting condensed matter system that forms a variety of Wigner ion-crystal configurations1,2,3,4,5 and at the same time is dilute enough to be optically manipulated down to single atom resolution. The ion-crystal configurations are separated by a hierarchy of structural phase transitions driven by either the confinement geometry or ion density3,4,6,7,8,9. In a linear radio-frequency Paul trap the first such transition is the 1D linear to 2D zigzag transition6,7, which for small arrays of ions is the mesoscopic analog of a continuous phase transition10,11. Prior experiments with the linear-zigzag (LZ) transition have focused on its classical behavior including both equilibrium properties6,9,12 and dynamics13,14,15,16,17. Here, using ground-state cooling we investigate the transition in the quantum regime, and we assess the feasibility of the system for double-well interferometry18 and the sensing of ambient electric field noise in the ion-trap environment. As an important step towards interferometry, we investigate the near-adiabatic crossing of the LZ transition in the ground state, which in the ideal scenario prepares a Schrödinger cat superposition of the symmetry broken zigzag structures.
The predominant paradigm underlying quantum control of trapped arrays of ions, including in quantum computing and quantum simulations, uses the set of vibrational normal modes of the ion crystal in the linearized small oscillation limit19. Near the LZ critical point this work explores the opposite limit where the nonlinearity in the interactions dominates the effective potential of the relevant zigzag vibrational mode. As a further contrast, dynamical Schrödinger cat states involving entangled states of spin and coherent motion20 and generalized Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) states of spin21,22 have both been previously prepared in ion traps. Here, the limit of quantum state preparation in an ion trap can be explored down to dc excitation frequencies due to the softening of the zigzag mode at the LZ transition, and coherent state manipulation on the zigzag side of the transition would provide a testbed to probe sources of static and fluctuating bias affecting the double-well zigzag potential18. Unlike prior quantum dynamics studies near the critical point for a three-ion rotor mode23, the LZ transition is a system that is readily extensible to a varied and larger number of ions, and in situ measurement of near ground-state energies is shown here to be feasible close to the critical point.
Our experiments are simultaneously motivated by the fact that the LZ transition at ultracold temperatures is marked by a sharp spectral signature in the zigzag mode with strong dependence on the trap potential parameters. This allows for sensitive in situ and broadband electric field noise measurement, which is of direct consequence to the performance of trapped ion quantum computers19,24, and offers advantages over the standard sensing technique based on the center-of-mass mode of a single trapped ion25,26. First, the measurement of slow drifts in the strength of the ion-trap potential can be achieved with more than an order-of-magnitude improvement in single-shot sensitivity without the need for high-order motional Fock-state superpositions27. Second, as a resonant absorptive sensor the zigzag mode near the LZ transition offers wide frequency tunability from dc to 1 MHz for only minimal adjustment of the trap voltages (~1 V), which is advantageous in the characterization of the spectral dependence of noise to identify its sources26.
The potential energy for N ions in a linear radio-frequency (rf) Paul trap is expressed in dimensionless form as
where riâ=â(xi,âyi,âzi) is the position of the ith ion and the terms, in order, describe the harmonic rf pseudopotential, Coulomb interactions and perturbative imperfections Vpert in the trap potential. The aspect ratio of the harmonic trap is characterized by the quantities \({\alpha }_{{{{\rm{x}}}}({{{\rm{y}}}})}\,=\,{({\omega }_{{{{\rm{x}}}}({{{\rm{y}}}})}/{\omega }_{{{{\rm{z}}}}})}^{2}\) in terms of the secular trap frequencies νââ=âÏâ/2Ï, ââââ{x,ây,âz}. The dimensionless potential is expressed in terms of the Coulomb length \({d}_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}={\left(\frac{{q}^{2}}{4\pi {\epsilon }_{0}m{\omega }_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}^{2}}\right)}^{1/3}\), which sets the axial ion spacing, and the corresponding Coulomb energy \(\frac{{q}^{2}}{4\pi {\epsilon }_{0}{d}_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}}\). The perturbation potential captures the effect of deformations of the electrode geometry away from an ideal linear trap, with select terms in a polynomial expansion leading to symmetry breaking of the LZ transition.
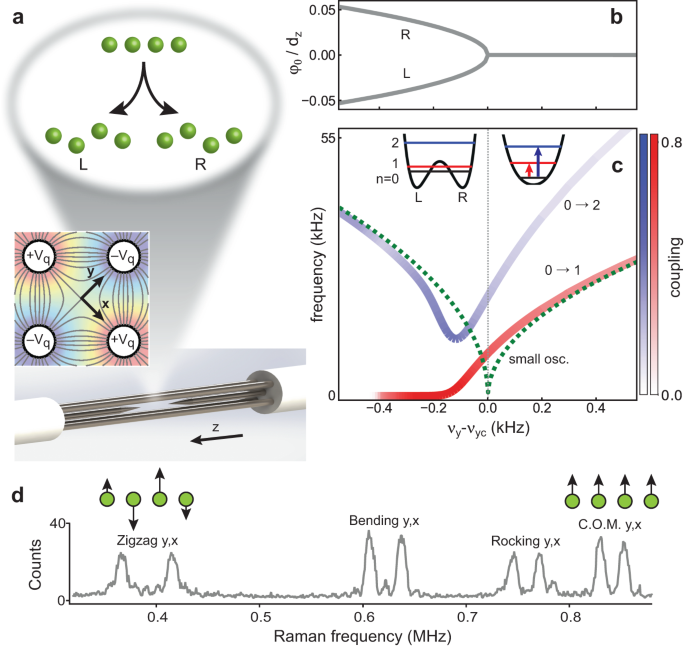
The LZ transition for an ion crystal with a fixed number of ions is controlled by the trap aspect ratio. This can be modified by applying a dc quadrupole potential in the transverse trapping plane to weaken the transverse confinement along only one of the principal axes, here assumed to be the y-axis (Fig. 1a). We therefore restrict our discussion of the LZ transition to the yâââz plane and refer to the relevant control parameter αy hereafter as α. For strong transverse confinement the ions form a linear string along the axial z-direction of the linear trap. At a critical point αc which depends on the number of ions12, the ions undergo a structural phase transition to a 2D zigzag configuration (Fig. 1a). The dynamics of the linear ion string restricted to 2D can be described in terms of its 2N collective vibrational modes. The transverse-y zigzag mode represents a âsoft mode"28 that classically goes to zero frequency (i.e. softens) at the LZ critical point according to \({\nu }_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}={\nu }_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}\sqrt{\alpha -{\alpha }_{{{{\rm{c}}}}}}\)11. This creates a dynamical instability that drives the transition12, and below the critical point the crystalâs equilibrium structure takes on a frozen-in version of the zigzag mode11,28. Near the transition the zigzag mode dominates the ion crystal dynamics for slow quenches. A coupled-mode analysis and adiabatic elimination of the other modes leads to an effective field theory for the zigzag mode11,18 (see Methods). The associated dimensionless potential as a function of the zigzag order parameter Ï (the normal mode coordinate) up to fourth order is
where the quadratic term is C2â=âαâââαc, and other coefficients are constant. This derivation ignores spatial variation of the order parameter and propagation effects along the ion string29,30, which are not relevant for the small ion strings and slow quenches considered here. Asymmetries in the non-ideal trap from Vpert give rise to the linear and cubic bias terms. If C1 and C3 are zero, the mesoscopic equivalent of a second-order phase transition is realized for small numbers of ions. The mean order parameter ãÏã, obtained from minimization of U, is zero on the linear side and continuously acquires a non-zero value on the zigzag side of critical point (Fig. 1b). On the zigzag side of the transition there are two symmetry-broken, and in the ideal case energy-degenerate, states corresponding to the minima of the quartic double-well potential that forms across the transition. We define the two equilibrium configurations as âleft" (L) and âright" (R). In the zero temperature limit, it is relevant to consider the quantum energy levels for the effective potential across the transition, as shown in Fig. 1c for the example of four ions. Near the critical point the frequency splitting between the ground state, \(\left\vert 0\right\rangle\), and first excited state, \(\left\vert 1\right\rangle\) deviates from the equivalent classical small oscillation frequency. The level splitting remains finite at the critical point before approaching zero in the zigzag phase as tunnel coupling between the two sides of the double well, associated with the states \(\left\vert {{{\rm{L}}}}\right\rangle =\left(\left\vert 0\right\rangle -\left\vert 1\right\rangle \right)/\sqrt{2}\) and \(\left\vert {{{\rm{R}}}}\right\rangle =\left(\left\vert 0\right\rangle +\left\vert 1\right\rangle \right)/\sqrt{2}\), is suppressed by the intervening barrier. At the point of optimum tunneling the two lowest levels are just captured below the double-well barrier. For νyâ=â0.75 MHz a tunnel splitting of 3 kHz is expected at this point and the order parameterâs magnitude is |ãÏã|â=â0.03âââ0.02 or 100â50 nm for 3â5 ions.
a Schematic realization of the 1D linear to 2D zigzag structural transition for a four-ion crystal confined in a linear rf Paul trap, consisting of four rod electrodes and two endcap needles. Color inset shows a cross-section of the trap superposed with the transverse quadrupole electric field generated from rod voltagesâ±âVq and used to weaken the transverse confinement along the y-axis to induce the transition. b Classical energy-minimum values of the zigzag order parameter, proportional to the transverse zigzag displacement from the z-axis, as a function of control parameter νyâââνyc for a four-ion crystal. νy is the transverse-y secular trap frequency. c Simulated quantum energy-level spectrum for the first two excited states of the transverse-y zigzag mode of a four-ion crystal, calculated relative to the ground state. A small linear bias C1â=â10â14 is assumed. Color shading of the levels indicates the strength of Raman sideband coupling to the ground state for a central ion (see sidebar scale). Also shown is the classical small-oscillation prediction and the form of the zigzag potential on either side of the transition. Simulations in (b) and (c) assume νycâ=â740 kHz and νzâ=â363 kHz corresponding to dzâ=â5.4âμm. d Experimental Raman first-sideband spectrum of all transverse vibrational modes, measured relative to the carrier resonance frequency, for a four-ion linear crystal (νyâââνycâ=â93 kHz, or αâ=â5.27). A Raman probe of the center-of-mass mode provides in situ assessment of the control parameter, while a probe of the zigzag mode provides access to order-parameter properties. Vertical scale is fluorescence counts averaged over 50 iterations. Second sideband resonances of the zigzag modes are not visible since they are weakly excited. See text for parameter definitions.
Small nonlinearities in the trap potential from the electrode configuration or from other ambient sources will introduce biases changing the nature of the phase transition. A small cubic term will change the transition from second to weak first order31. A linear bias will act to smooth away the discontinuity in the transition. From the perspective of double-well interferometry and entangled state preparation, we seek to realize a sufficiently symmetric double well such that quantum tunneling is not suppressed near the critical point. To estimate the relevant level of bias, we consider the optimum tunneling point for 3â5 ions where limiting the localization of the ground state to 50% requires a potential bias of â£C1â£ââ²â10â6 or â£C3â£ââ²â10â3âââ10â2 (see Methods). At the same time, stability of the potential is required together with sufficiently low noise to retain coherence.
Results
Experimental system
Our investigations of the LZ transition use 171Yb+ ions held in a stabilized linear radio-frequency (rf) Paul trap14 (Fig. 1a), which has typical secular frequencies \(\left\{{\nu }_{{{{\rm{x0}}}}},{\nu }_{{{{\rm{y0}}}}},{\nu }_{{{{\rm{z0}}}}}\right\}\) of \(\left\{864,844,303\right\}\) kHz for five ions starting on the linear side of the transition (see Methods for details). Near-ground-state cooling of the linear-string configuration is achieved through 3D Sisyphus cooling of all 3N vibrational modes to the few-phonon level14 followed by simultaneous resolved sideband cooling of the transverse-y and axial modes except the center-of-mass (COM) ones. We estimate a ground-state occupationââ³â0.9 for the sideband cooled modes including the transverse-y zigzag mode of interest32. Following the cooling process, the approach to and crossing of the LZ transition is controlled by a ramp of a transverse dc quadrupole potential applied through the trap rods (Fig. 1b)14 with minimal effect on the axial confinement (â£Îνzâ£/νzâ<â0.03%). The secular frequency along the y-axis weakens to 760 kHz near the critical point while the orthogonal x-axis simultaneously strengthens to 940 kHz such that the LZ transition is effectively confined to the 2D yâââz plane. While the ramp implementation is expected to be adiabatic for endpoints near the critical point, we do not optimize the ramp for endpoints deeper in the zigzag side of the transition. At a given final ramp value of the dc quadrupole voltage, the vibrational modes of the ion crystal are probed by driving stimulated two-photon Raman sideband transitions between the internal hyperfine states \({}^{2}\,{S}_{1/2}\left\vert F=0,{m}_{F}=0\right\rangle \equiv \left\vert \downarrow \right\rangle\) and \({}^{2}\,{S}_{1/2}\left\vert F=1,{m}_{F}=0\right\rangle \equiv \left\vert \uparrow \right\rangle\) of the ions, separated by νhfâââ12.6 GHz32. Subsequent readout of the transition is obtained by state-selective fluorescence of the internal state of the ions33. For individual laser addressing of the ith ion, the Raman coupling drives the transition \({\left\vert \downarrow \right\rangle }^{\bigotimes N}\left\vert {n}_{k}\right\rangle \to \left\vert \downarrow \ldots {\uparrow }_{i}\ldots \downarrow \right\rangle \left\vert {n}_{k}^{{\prime} }\right\rangle\) at resonance \({\nu }_{{{{\rm{hf}}}}}+({n}_{k}^{{\prime} }-{n}_{k}){\nu }_{k}\), involving the vibrational states \(\left\vert {n}_{k}\right\rangle\) and \(\left\vert {n}_{k}^{{\prime} }\right\rangle\) of the kth mode of the ion crystal. In practice we use a technically simpler global illumination of the ions, which gives rise to a simultaneous Raman coupling of all the ions to the mode of interest (see Methods). We measure both the carrier (\({n}_{k}^{{\prime} }={n}_{k}\)) and upper sideband resonances (for example the first sideband \({n}_{k}^{{\prime} }={n}_{k}+1\)) and extract the mode frequency from the difference. The first sidebands of the COM modes are used to measure the secular frequencies of the trapâthe control parameter for the transitionâwhile the sidebands for the transverse zigzag mode give access to the spectral properties of the order-parameter dynamics (Fig. 1d).
Transition spectroscopy
We first consider the properties of the LZ transition in the vicinity of the critical point for a crystal of five ions. For this study both the first and second upper sidebands of the zigzag mode are measured as a function of secular frequency νy. A distinctive feature from the typical behavior for linear ion strings is the significant anharmonicity of the zigzag mode near the critical point due to the nonlinearities in the effective potential. This gives rise to non-uniform energy level spacings and asymmetric lineshapes. We avoid significant induced distortion of the lineshapes by limiting the drive strength of the Raman transition. Nevertheless, if the zigzag mode is in an initial distribution of Fock states, for example a thermal distribution, the onset of anharmonicity will lead to a set of unresolved sidebands dispersed into a combined asymmetric lineshape. In cases of significant asymmetry, we fit the sideband resonances with an exponentially modified Gaussian to extract a resonance, width and lineshape asymmetry factor (see Methods). Assuming an initial motional distribution with a large ground state occupation, we can associate the first sideband resonance with the 0â1 energy level spacing and the second sideband with the 0â2 energy level spacing in the potential for the zigzag mode.
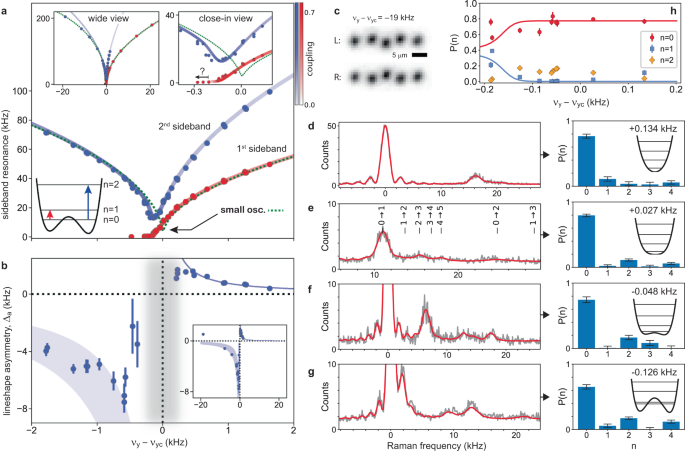
Figure 2a shows both first and second sideband resonances of the zigzag mode as a function of \({\Delta}\)νyâ=âνyâââνyc in a 4âkHz range around the critical point at νycâ=â759.94(2) kHz. The data including the region close to the transition is fit to the quantum energy level theory for a biased quartic potential (see Methods) and provides the value of the critical point used to set the origin of the plot. Expressed as a trap aspect ratio, the critical value, αcâ=â6.3007(16), is shifted upward from the expected pseudopotential value of 6.2374 by δαc/αcâ=â0.0100(2). The fractional shift is in agreement with an estimate of 0.01050(3) due to the higher order effect of the rf micromotion on the vibrational modes of the ions in the trap (see Methods and ref. 34). Quoted uncertainties include both statistical error and error associated with calibration of the trap potential. The quadrupole voltage adjustment for points near the transition is equivalent to a variation of 50 ppm of the transverse secular frequency, providing an indirect characterization of the stability of the trap potential over several hours.
a Frequency of first and second upper Raman sidebands for the transverse-y zigzag mode as a function of secular trap frequency νy relative to critical value νycâââ760 kHz. Insets show the full range of data acquisition and a close-in view near the critical point. For points denoted by â?", see âMethodsâ. Solid lines are quantum energy-level differences of nâ=â1 and nâ=â2 number states with respect to the nâ=â0 ground state for a quartic potential (Eqn. (2)) with bias â£C1â£â=â3.3âÃâ10â7. Line shading corresponds to Raman coupling strength (see side-bar scale). Green dotted line shows the classical small-oscillation prediction for the full pseudopotential (Eqn. (1)) with equivalent bias. b Asymmetry in the combined Raman lineshape for unresolved second upper sidebands from multiple initial number states. Inset shows the full range of data acquisition. Blue lines indicate expected scaling of the asymmetry due to anharmonicity of the quartic potential. Width of the line on the zigzag side shows a factor-of-two range in scaling prefactor. Vertical gray shaded region indicates where sideband peaks are (partially) resolved, as shown in (dâg). c Sample images of the two symmetry-broken equilibrium structures of the five-ion crystal far from the critical point. dâg Sample Raman sideband lineshapes near the critical point (with vertical scale of fluorescence counts averaged over 50 or 100 iterations), and fits (solid red lines) to extract C1 and Fock-state population distribution P(n) of the zigzag mode. Distributions are shown in adjacent panels along with the shape of the zigzag potential. In (e) line centers for sidebands from different initial n-levels are indicated. h Summary of measured P(n) across the transition for nââ¤â2. Lines are a quantum dynamics simulation to indicate onset of non-adiabaticity. Optimum tunneling point lies near νyâââνycâ=ââ0.100 kHz. Error bars in all cases are statistical uncertainties of one standard deviation from fits. See main text and Methods for further details.
The full dataset taken over a wider range of control parameter is shown in the left inset of Fig. 2a. The analytical prediction \({\nu }_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}=\sqrt{{\nu }_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}^{2}-{\nu }_{{{{\rm{yc}}}}}^{2}}\) for the zigzag frequency on the linear side of the transition matches the data well at points away from the critical point. Far from the transition on the zigzag side, the measured sideband frequencies deviate from the energy-level spectrum for the zigzag potential (Eqn. 2) since the potential coefficients are calculated perturbatively near the critical point. Very close to the transition, within Îνyâ~â±â0.3 kHz as seen in the right inset of Fig. 2a, the data exhibit a distinct deviation from the classical small oscillation prediction. The dependence measured for five ions close to the transition approaches that of an unbiased quantum LZ transition with the first sideband approaching zero frequency (compare Fig. 1c). Bias in the double well, which lifts the degeneracy between the lowest energy levels of the zigzag mode, can be identified by a non-zero minimum frequency of the first sideband. However, on the zigzag side of the critical point it becomes difficult to separate the low-frequency first sideband from the carrier (Îνyâ<âââ0.2 kHz in right inset of Fig. 2a); as such, the lowest frequency value that can be reliably measured provides an upper bound on the bias. Suppression of the line strength of the first sideband resonance near the critical point additionally constrains the bias in the double well, and a combined analysis (discussed in detail below) is used to obtain the fit to quantum theory with C1â=â3.3âÃâ10â7 shown in Fig. 2a.
In addition to the resonance center, the asymmetry in the lineshape of the zigzag sidebands provides insight into the zigzag potential and the motional distribution of the order parameter. The asymmetry of the fit lineshape is shown in Fig. 2b, where its sign switches across the critical point due to the change in the anharmonicity from the single to double well. The anharmonic energy-level shift in the perturbative limit should scale as \(1/{\nu }_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}^{2}\propto 1/{{\Delta }}{\nu }_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}\)35. The scaling law shows good agreement on the linear side away from the critical point but only a rough match to the behavior on the zigzag side. The 6â12 times larger asymmetry scaling factor inferred on the zigzag side is partly attributed to a factor-of-2 larger anharmonicity effect, and the remainder we expect is due to a larger motional excitation out of the ground state. The onset of increased heating of the zigzag mode across the LZ transition arises from non-adiabatic transitions due to the ramp, higher electric field noise density at low frequencies and enhanced sensitivity to electric field noise as the zigzag structure forms.
In the region closest to the critical point, the anharmonicity of the potential is sufficiently large to allow the zigzag sidebands starting from the lowest vibrational levels to be resolved (Fig. 2dâg). We take advantage of this to infer the motional population distribution, P(n), in the n-number states of the zigzag mode from the measured sideband spectrum of transitions nââânâ+âm. The fit model of the line strengths and centers is based on the quantum double-well theory including bias, and the carrier and sidebands are fit to an incoherent sum of lineshapes which include three separate phase decoherence parameters for the carrier, first and second sidebands. It is not possible to constrain independent values for the linear and cubic bias from the resolved spectra; for simplicity, we assume a null cubic bias (C3â=â0) and take the average of â£C1⣠fit values across the range of data in Fig. 2 to obtain a best-fit value of â£C1â£â=â3.3(3)âÃâ10â7. With this value of C1 we obtain the motional population distributions shown in Fig. 2dâg and aggregate measurements of motional populations in Fig. 2h. The motional populations reveal non-thermal distributions with preferential occupation of even n levels (for example Fig. 2e and h), which is indicative of non-adiabatic transitions due to the ramp or parametric heating of the zigzag mode on the linear side. The ground state is found to remain majority populated (P(0)ââ³â0.6) down to Îνyâ=ââ0.2 kHz (Fig. 2h), including the location of the optimum tunneling point near â0.100 kHz where the lowest two energy levels in the double-well model first lie below the barrier. From numerical modeling of the quantum mechanical dynamics of the ramp, we expect that it remains adiabatic down to Îνyâ=ââ0.17 kHz, which is consistent with the observed behavior of P(1) as shown in Fig. 2h.
The linewidths of the resolved sidebands give an upper bound on the coherence time for the zigzag order parameter. We find that the phase coherence time from the fits for the first sidebands is 0.3â0.5 ms and 0.3 ms for the second sidebands, both much shorter than the value of 3â5 ms for the motion-sensitive carrier. The value of 0.3â0.5 ms is roughly consistent with a preliminary assessment of the Ramsey coherence time of the first upper sideband near to the critical point. We observe that the coherence time decreases as the LZ transition is approached from the linear side. In part this is due to increased sensitivity of the zigzag mode to fluctuations in the trap potential, scaling as \(1/{\nu }_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}^{2}\). A more detailed assessment of decoherence near the critical point is left to future work.
Ion-number dependence
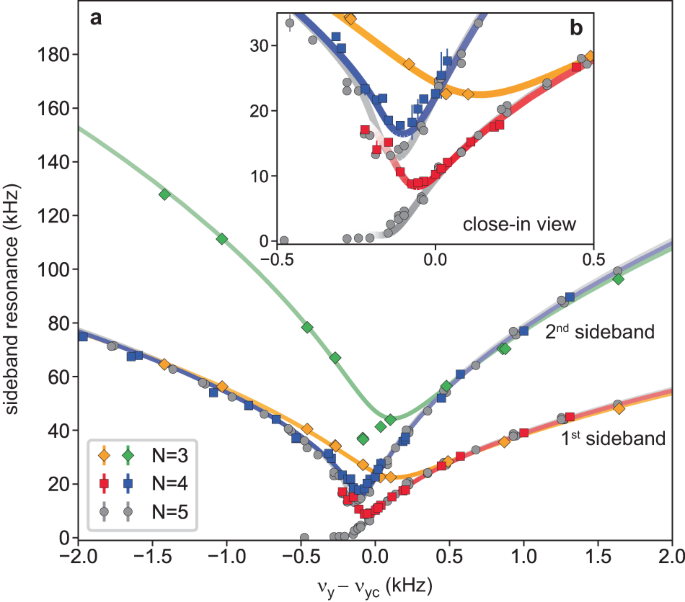
Extending the results for five ions, we have compared the transition spectroscopy for ion numbers ranging from three to five (Fig. 3). The axial confinement, and by extension the axial ion density, is adjusted to make the critical transverse secular frequency approximately the same in all cases, within a 6% range. The critical trap asymmetries αc are found to be {2.4251(4), 4.1967(6), 6.3007(15)} for 3â5 ions, corresponding to a nearly N-independent fractional shift of {0.0103(2), 0.01012(14), 0.0100(2)} from the pseudopotential prediction. This is in accord with the predicted micromotion-induced shift, which in lowest order depends only on the Mathieu parameters for the ion trap (see Methods). The main feature in the transition spectroscopy of Fig. 3 is the strong reduction in bias effect going from three to five ions. This is manifest by the qualitative sharping of the LZ transition and the reduction in the gap between the nâ=â0 and nâ=â1 energy levels near the critical point. Assuming a dominant linear biasâto be justified belowâwe perform fits to the quantum theory for the three- and four-ion cases, and extract a bias coefficient â£C1⣠of 3.62(11)âÃâ10â5 and 4.52(17)âÃâ10â6 respectively. The case of four ions exhibits a complicated spectral structure due to the particular value of the bias; from the best-fit double-well model, we find that the line strength of the 0âââ1 sideband vanishes as it approaches degeneracy with the 0âââ2 sideband, corresponding to a level crossing between the nâ=â1 and nâ=â2 states. For three ions the bias is strong enough that the lowest energy states are well localized in a single well across the LZ transition, and thus neither a suppression of the 0âââ1 sideband from an onset of symmetry breaking nor a level crossing occur. Finally, we note that we have also confirmed the general trend in bias for 3â5 ions from measurements of the asymmetry in statistical outcomes of the two zigzag configurations after crossing the LZ transition.
First and second upper sideband frequencies for the transverse-y zigzag mode are shown as a function of the transverse secular trap frequency νy referenced to the measured critical value νyc. Main figure (a) shows a wide region about the critical point while inset (b) shows a zoomed-in view. Axial confinement is chosen such that the critical values νycâ=â{717,â744,â760} kHz for 3â5 ions are close (within 6%) so that the linear-zigzag (LZ) transitions can be directly compared. Error bars on data points, representing one standard deviation (s.d.) statistical uncertainties from resonance fits, are typically smaller than the symbol size shown. Fits (solid lines) to the quantum energy level structure for a quartic potential are used to extract νyc and a bias â£C1⣠of 3.62(11)âÃâ10â5 for three ions and 4.52(17)âÃâ10â6 for four ions (all uncertainties one s.d.). For five ions, theory is shown for â£C1â£â=â3.3(3)âÃâ10â7, obtained separately from lineshape fits (see text). Theory lines are shaded according to Raman coupling for the central ion, similar to Fig. 2a. In both four- and five-ion cases the 0âââ1 first sideband coupling vanishes below the LZ transition due to the onset of the symmetry breaking effect on the wavefunctions. This is precluded for three ions since the symmetry is already fully broken by the strong bias.
Bias spectroscopy
The transition spectroscopy of Figs. 2 and 3 is insufficient to distinguish unambiguously between a linear and cubic bias in the zigzag potential. To differentiate the two forms of bias, we introduce a technique to measure the splitting in the frequency of the zigzag mode between the L and R zigzag configurations. The splitting dependence on C1 and C3, considering a classical perturbative model derived from Eqn. (2) on the zigzag side of the LZ transition and for â£Î½LâââνRâ£ââªâνL,R, is
where the axial secular frequency νz is used to set the scale (see Methods). The linear bias is characterized by a rapid \({\nu }_{{{{\rm{R}}}}}^{-2}\) decay away from the transition since it cannot affect the local curvature in the minima of the double well once the wells are deep enough.
To prepare the ion crystal deterministically in either of the zigzag configurations, we use the optical dipole force from an off-resonant laser beam focused to the order of the ion spacing and displaced transversely from a central ion in the string (see Fig. 4c and âMethodsâ). This is sufficient to bias the transition globally to achieve initialization of either configuration with >90% fidelity for 3â5 ions. The same experiment sequence as for the transition spectroscopy is used with the addition of the biasing beam applied as the critical point is traversed (Fig. 4e). The frequency splitting between the two zigzag configurations is measured as a function of proximity to the critical point on the zigzag side of the transition, and the results are plotted self-consistently in terms of the naturally biased zigzag mode frequency ν0âââνR (Fig. 4a). For both three and four ions a rapid reduction of the splitting away from the transition is observed. This is indicative of a dominant linear bias. We fit the measurements to the unapproximated version of Eqn. (3) to extract the coefficients C1 and C3 (see Fig. 4 for values). The linear bias decreases in magnitude from three to four ions in agreement with the transition spectroscopy of Fig. 3. The value of C1 for three ions, for which the bias is strongest, agrees with that obtained from transition spectroscopy, and the value for four ions agrees within a factor of 2. For five ions, data fluctuations are such that only an upper bound on the small bias coefficients is possible. While this technique is not as precise as a fit to transition spectroscopy, it provides clear evidence of a dominant linear bias for three and four ions, and justifies the fitting of the transition spectroscopy to C1 alone in these cases.
a Difference in zigzag mode frequency, νRâââνL, for an ion crystal of 3â5 ions initialized into opposite zigzag configurations, defined as left (L) and right (R) sides of the double well. Data plotted as a function of mode frequency ν0 without any applied initialization. In all cases, νRâââν0 within 0.7 kHz, which is explained by the direction of the biases. Error bars are one standard deviation (s.d.) statistical uncertainties from resonance fits (for example as shown in (b)) and omit systematic effects including drifts. Solid lines are fits to classical small-oscillation theory (see text). Bias coefficients from the fits are C1â=âââ4.0(3)âÃâ10â5 and C3â=âââ7(7)âÃâ10â4 for three ions, and C1â=âââ9.5(1.7)âÃâ10â6 and C3â=â1.7(1.4)âÃâ10â4 for four ions (all uncertainties one s.d.). Data fluctuations for five ions only allow a partial constraint on the biases: a fit of all data (solid gray line) gives C1â=â1(4)âÃâ10â5 and C3â=âââ4(5)âÃâ10â3, while a fit excluding the left-most data point (dotted line) gives C1â=âââ6(5)âÃâ10â6 and C3â=âââ2(3)âÃâ10â3. The zigzag mode experiences increasing excitation away from the critical point without substantive effect on results expected. b Sample lineshapes with fits for three ions at ν0â=â80 kHz. The L-case has been shifted vertically to clarify comparison. Vertical scale is fluorescence counts averaged over 50 iterations. c Illustration of scheme for initialization into either zigzag structure. Controlled biasing of the transition is achieved with a repulsive optical dipole potential from an off-resonant beam focused with near single-ion resolution. d Experiment sequence showing initial laser cooling, ramp of transverse secular frequency νy across the transition biased by the optical potential, and Raman spectroscopy on the zigzag side of the transition to measure νR or νL.
Connection of bias coefficients to the trap
Moving beyond an interpretation of the data in terms of the phenomenological effective potential of Eqn. (2), we have explored theoretically the origin of the zigzag bias in terms of asymmetries in the ion trap potential (see Methods). The perturbations from an ideal trap can be expressed as a polynomial expansion, \({V}_{{{{\rm{pert}}}}}(x,y,z)={\sum }_{\xi }{\lambda }_{\xi }{x}^{{\xi }_{1}}{y}^{{\xi }_{2}}{z}^{{\xi }_{3}}\), where ξâ=â(ξ1,âξ2,âξ3) is a list of the integer exponents for each term with order noâ=âξ1â+âξ2â+âξ3 and coefficient \({\lambda }_{\xi }\equiv {\lambda }_{{\xi }_{1}{\xi }_{2}{\xi }_{3}}\). Based on a 2D coupled-mode analysis in the pseudopotential limit for perturbations up to noâ=â7 and for ion crystals up to Nâ=â7, we find that the bias for the LZ transition in the yâââz plane depends on coefficients \({\lambda }_{01{\xi }_{3}}\) and \({\lambda }_{03{\xi }_{3}}\) with orders noââ¥â3 of the same parity as the ion number N. The linear bias, which will in general dominate close to the transition where â£ãÏãâ£ââªâ1, only depends on the \({\lambda }_{01{\xi }_{3}}\) coefficients. The sensitivity of the linear bias to the coefficients is strongly suppressed up to order noâ<âN, which is consistent with the observed rapid suppression of linear bias from 3 to 5 ions. The cubic bias depends on both \({\lambda }_{01{\xi }_{3}}\) and \({\lambda }_{03{\xi }_{3}}\) coefficients with sensitivities that are suppressed more weakly with N. Rotations of the trapâs principal axes and shifts in its minimum in conjunction with nonlinearities in the potential will induce additional, typically smaller, contributions to the zigzag bias. The ion trap potential has various nonlinearities that do not break zigzag symmetry but can also lead to shifts in the critical point, for example quartic terms arising from the endcaps of form z4 and y2z2 with polynomial coefficients in our case of order 10â4â10â5.
We use numerical modeling of the trap potential as well as estimates of mechanical tolerances to identify likely sources of asymmetry in the trap potential that contribute to the zigzag bias (see Methods). For our linear trap design (Fig. 1a), the bias for three ions can arise from a number of different trap asymmetries including transverse co-displacements of the endcaps or various displacements of the trap rods of order 10 μm36. We find that the same deformations are also roughly consistent with the bias measured for five ions. For four ions, the most likely source of asymmetry is from transverse counter-displacements of the endcaps of order 100 μm, which is possible given that the endcaps are not positionally well constrained in our trap design. Note that the bias for odd ions is insensitive to counter-displacements of the endcaps.
The theoretical results imply that a highly symmetric zigzag transition can be readily achieved for moderate numbers of ions N. With an improved trap with electrodes constrained to a few microns and Nââ¥â4, the linear bias C1 can be highly suppressed to below the target 10â7 level, which we already approach for Nâ=â5 in our current setup. For odd N this will still leave cubic biases at a level of <10â3 that decrease only gradually with number of ions. However, ion crystals with even N can be used to advantage to obtain a high degree of double-well symmetry with â£C3â£ââ²â10â6, since their transverse symmetry suppresses the effect of the lowest order (noâ=â3) perturbations. For example for Nâ=â6 and in our existing trap, we expect to achieve biases of C1â=ââ2.5âÃâ10â8 and C3â=â1.6âÃâ10â5.
Discussion
In summary, we have extended previous demonstrations of the LZ transition in linear ion traps to probe the region close to the critical point for ion crystals near the quantum ground state. Stabilized trap potentials, reduced thermal fluctuations and the use of a spectroscopic probe of the zigzag mode have allowed for a precision determination of the critical point beyond previous assessments of the order parameter variation through fluorescence images of the ions12,13, and have revealed the effect of small asymmetries in the trap potential on the nature of the transition. We have realized a method for measuring the motional population distribution of the zigzag mode near the critical point and demonstrated key ingredients towards the goal of double-well interferometry with this system. A direct extension of this work is to probe the decoherence of the order parameter near the LZ critical point using both a Raman Ramsey measurement of T2 relaxation of the zigzag mode and Raman sideband thermometry to assess the T1 relaxation associated with motional heating. An estimate of the fundamental decoherence limit of image current damping on the zigzag dynamics37,38 shows that it is negligible for our ion-electrode distance in comparison to the measured decoherence rate of 0.3â0.5 msâ1 near the critical point. Given that we expect the origin of the decoherence is technical in nature, improvements are possible by increasing the ion confinement with smaller trap structures to scale up the characteristic frequencies, and by the reduction of phase noise in the trapping potentials through optimization of the active trap voltage stabilization and the use of additional passive measures, including rf filtering from a higher quality factor rf resonator in a cryogenic trap system.
Extension of this work to a larger number of ions requires a consideration of the scaling of the energy gaps, which impact on diabatic excitation out of the ground state including the formation of spatial domains39. Relevant to this, a calculation of the quantum suppression of long range order in the thermodynamic limit for the case of a homogeneous ion density has been performed29. It provides an estimate of a quantum critical point for the LZ transition with a small shift below νyc, of order 0.1â1 Hz for the central ion density in our trap. A vanishing gap, however, is central to this critical behavior. The non-zero energy gap for a finite number of ions allows for adiabatic evolution of the ground state through the critical point for sufficiently slow quench time39. For our inhomogeneous case in a harmonic trap and out to Nâ=â50, we find theoretically that the location of the optimum tunnel point relative to the critical point νyc and the tunnel splitting energy remain nearly constant for a fixed central ion density (see Methods). As well, the closing of the excitation gap to the next normal mode, which brings with it the possibility of spatial variation in the order parameter, only becomes relevant for very long ion strings, outside the typical 100-ion limit in a linear trap.
Measurements of the decoherence in the zigzag mode provide an assessment of the ambient electric field noise in the trap environment, which is of general relevance to quantum information applications where the ionsâ motion is used to engineer controlled interactions. While the zigzag mode in a linear ion crystal is less sensitive to fluctuating electric fields than the COM mode due to the higher-order coupling to gradients, the zigzag mode has the useful feature near the LZ transition that it can resolve electric field noise over a wide spectral range from the transverse secular frequency down to dc with minimal variation of the dc trap voltages. In particular this can be performed without change in the rf trap voltage. Furthermore, taking advantage of the high sensitivity of the LZ critical point to both transverse and axial secular confinement, we can gain an enhancement in the measurement of drifts in the trap secular frequencies by using the zigzag mode over a direct measure of the COM modes at the cost of a small additional time overhead required to ramp to near the LZ transition. The single-shot gain over a first-sideband measurement of the transverse COM mode is Gâââνy/νzz on the linear side of the transition and reaches a maximum near the critical point due to the energy level structure. For example, we calculate for five ions a gain of up to 67.
Finally, we briefly note additional potential applications of this work. The precise detection of small trap asymmetries with the LZ transition, either via sideband spectroscopy or ultimately with double-well interferometry, should be useful to constrain the effect of trap nonlinearities in quantum computing and quantum simulation with long ion crystals40 and in linear ion trap mass spectrometry36. The spectroscopic sensitivity of the transition and the demonstrated stability of the trap potential open up the possibility to measure finer shifts in the critical point. For example, shifts in the critical point due to cross-mode coupling41 in the dispersive Kerr regime42 are small, up to 3 Hz per phonon depending on the contributing mode, but are measurable with the current setup for higher levels of mode excitation. Other potential applications in the quantum regime that build on the techniques presented here include entanglement of the internal spin of the ions and the zigzag mode using a spin-dependent optical dipole force to modify the critical point43, and quantum dynamics of topological kink defects seeded into the zigzag structure and prepared in the ground state44,45.
Methods
Ion trap system
The ion trap is a linear radio-frequency (rf) Paul trap14 consisting of four rods and two endcap needles with an ion-to-rod distance of Râ=â0.66 mm and two needle endcaps with a tip-to-tip separation of 2.5 mm (Fig. 1a). The trap operates at a radio frequency Ωrf/2Ïâ=â16.9 MHz, rf voltage amplitude Vrfâ=â770 V, and endcap voltage Vecâ=â67âââ155 V depending on ion number. The trap has typical secular frequencies νââ=âÏâ/2Ï of 864 kHz and 844 kHz along the transverse x and y principal axes and 303 kHz along the axial z axis for five ions starting in the linear phase. Stabilization of the trap potential against drifts is implemented through passive and active techniques that include a servo of the rf amplitude and provide a stability of <10 ppm over 100 s for the secular frequencies46. Real-time monitors of the trap rf and endcap voltages provide an assessment of drifts and are used as inputs to a calibrated trap potential model for calculating secular trap frequencies. Excess micromotion is monitored for, but drifts in the background electric field for the majority of datasets are small enough that we can avoid compensation adjustments that could shift the critical point.
We make use of the internal clock states in the 171Yb+ hyperfine ground state manifold, \({}^{2}{S}_{1/2}\left\vert F=0,{m}_{F}=0\right\rangle \equiv \left\vert \downarrow \right\rangle\) and \({}^{2}{S}_{1/2}\left\vert F=1,{m}_{F}=0\right\rangle \equiv \left\vert \uparrow \right\rangle\), for ground state cooling and Raman spectroscopy. The general experimental sequence for all data consists of laser cooling the ion string to near the ground state on the linear side well away from the critical point, initialization of the ions into the internal state \({\left\vert \downarrow \right\rangle }^{\bigotimes N}\), a ramp of the transverse trap frequency to the vicinity of the zigzag transition, application of the Raman sideband spectroscopic probe and finally readout of the internal state of the ions using state selective fluorescence. The total fluorescence from all ions is collected simultaneously onto a single photomultiplier tube using a 400-μs collection time and 50 or 100 experimental iterations per data point.
Ground-state laser cooling
Near ground-state cooling of the ion crystal in the linear-string configuration is achieved through Doppler pre-cooling, 3D Sisyphus cooling of all 3N vibrational modes to the few-phonon level32, and finally interleaved resolved sideband cooling of the zigzag mode of interest along the y axis, the x-zigzag mode and all other modes along the y and z axes except the center-of-mass (COM) ones. We estimate a ground-state occupation for the sideband cooled modes to be â³0.9 based on measured sideband Rabi oscillations32. Ground-state cooling of modes other than the zigzag mode of interest aids to suppress heating of the zigzag mode due to cross-mode coupling resonances that are encountered during the ramp to the linear-zigzag (LZ) transition.
Ramp across the LZ transition
The approach to and crossing of the LZ transition is controlled by a hyperbolic-tangent ramp of a transverse dc quadrupole potential applied through the trap rods (Fig. 1b)14 with minimal effect on the axial confinement (â£ÎÏzâ£/Ïzâ<â0.03%). In terms of the quadrupole voltage Vq, the secular frequency along the y-axis weakens according to \({\omega }_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}={\omega }_{{{{\rm{y0}}}}}\sqrt{1-{V}_{{{{\rm{q}}}}}/{V}_{{{{\rm{q0}}}}}}\) with Vqâ>â0 and Vq0âââ13V, and the orthogonal axis strengths as \({\omega }_{{{{\rm{x}}}}}={\omega }_{{{{\rm{x0}}}}}\sqrt{1+{V}_{{{{\rm{q}}}}}/{V}_{{{{\rm{q0}}}}}}\), such that the LZ transition is effectively confined to the 2D yâââz plane. The quadrupole voltage begins at 0 V and crosses the transition near 2.5 V. For Vq ramp endpoints close to the critical point or those passing into the zigzag phase, a two-stage ramp is used with a slower final stage over 1 ms. Using simulations (see below) we find that this provides sufficient adiabaticity for ramp endpoints near the critical point, but we do not optimize the ramps for endpoints further into the zigzag side of the transition. An example ramp sequence can be seen in Fig. 4d.
The endpoint of the voltage ramp is converted to a value of transverse secular trap νy using a calibrated trap potential model. We plot results in terms of the control parameter νy rather than the theoretically more natural trap aspect ratio α (αy in Eqn. (1)) since the axial secular frequency changes only minimally during the quadrupole voltage ramp. The in situ calibration of the trap potential model is derived from prior separate experiments using a single ion and is updated using values of COM modes measured at select points during data collection to correct for daily drifts in the calibration. The trap potential model is a parameterized version of a symmetric linear Paul trap potential up to second order in coordinates and incorporates the next leading order of the Mathieu expansion for the secular frequencies5. The calibrations achieveâ<â0.03 kHz error from the fits near the critical point. As part of the trap calibration model we implicitly infer the Mathieu a and q parameters5 for all three trap axes.
Raman spectroscopy
We use motion sensitive two-photon Raman transitions to probe the various vibrational modes in the ion crystal, including the zigzag mode. Different Raman beam pairs allow access to motional sidebands in both the axial and transverse directions. The Raman beamsâ large size provides nominal uniform illumination of the ion crystal, giving rise to global Raman sideband coupling weighted by the mode participation of each ion47. Since all N ions are simultaneously illuminated by the Raman beams, up to N vibrational states can be excited from a given initial state. While the global coupling complicates the theoretical description of the Raman transition, in practice we keep the average sideband excitation to one phonon or less by limiting the Raman pulse time to simplify the interpretation of measurements. We suppress sideband resonance shifts due to the ac Stark shift of the Raman beams (â²0.3 kHz) by measuring the carrier and sidebands at the same Raman beam power. Near the critical point, reduced Raman beam power helps to resolve close-in sidebands that lie a few kilohertz from the carrier.
Bias spectroscopy
The bias spectroscopy uses the force from an off-resonant beam, focused and offset from a central ion in the linear crystal, to achieve deterministic initialization into either the L or R zigzag configuration before the Raman probe of the zigzag mode is performed. The biasing beam is blue-detuned by 0.7 THz, and its power (1â9 mW) is adjusted to minimize spontaneous emission while still achieving a high fidelity of initialization. The application of the biasing beam is limited to the portion of the quadrupole ramp close to the LZ transition to further minimize spontaneous emission heating. For the data for three and five ions, a controllable temporal amplitude profile has also been implemented to limit non-adiabatic excitation from the bias beam. The fidelity of the zigzag initialization is confirmed over the range of bias spectroscopy data by direct imaging of the zigzag structure following a fast projection ramp deep into the zigzag region. The lineshape asymmetries for the L and R configurations are compared to ensure that the bias beam does not introduce a differential heating effect, which could incur a systematic shift in the resonance line centers. The comparison of zigzag sideband resonances between the L and R configurations is also sensitive to slow drifts in the trap potential. For example, the five-ion bias measurements shown in Fig. 4a are limited by anomalous excess drifts due to electrode contamination.
Transition spectroscopy analysis
To extract the first and second sideband frequencies of the zigzag mode across the LZ transition, as shown in Figs. 2a and 3, we fit Raman spectra to a set of incoherently summed peaks without reference to a specific model for the zigzag potential. We assume the appropriate Rabi-resonance lineshape48 for the carrier to account for the coherent sidelobes of significant amplitude, while for the sidebands we find it is an adequate approximation to use a Gaussian or exponentially modified Gaussian lineshape depending on proximity to the critical point. The exponentially modified Gaussian49, which is a convolution of a Gaussian with an exponential distribution, is motivated by a model of anharmonicity and a thermal-like distribution of number states for the zigzag mode; however, the functional form is taken as a heuristic function that is found to work well in practice. It is defined as
in terms of frequency f, resonance location f0, width w, lineshape asymmetry Îa, amplitude A and baseline offset b0. The normalization is chosen such that the lineshape area, \(Aw\sqrt{\pi }\), matches that of a Gaussian \(A\exp (-{f}^{2}/{w}^{2})\) with the same width and amplitude. If the lineshape asymmetry obtained from a fit is below a minimum threshhold (Îa/wâ<â0.5) we revert to a Gaussian lineshape. This occurs far from the critical point where anharmonicity is negligible and close to the critical point where the sidebands are sufficiently resolved. Exponentially modified Gaussian lineshapes are relevant in the intermediate region where the anharmonicity is significant but not large enough to resolve the sidebands from different initial n-number states of the zigzag mode.
Identification of the resonances for the first sideband (nââânâ+â1) and second sideband (nââânâ+â2) is done by considering continuity of data and by assuming that the initial state is majority populated in the nâ=â0 ground state for data close to the critical point. Close to the critical point on the zigzag side, sideband identification becomes challenging since below νyâââνycâ=ââ0.2 kHz the sidebands for five ions lie under the carrier lineshape or have vanishing line strength, and for four ions the 0âââ1 and 0âââ2 resonances approach degeneracy. In the case of five ions below â0.2 kHz, low-frequency peaks extracted from underneath the carrier lineshape have been included conservatively as the upper first sideband 0âââ1 and identified by the symbol â?" in the right inset of Fig. 2a, but they may be due to the lower first sideband 1âââ0 or an upper sideband nââânâ+â1 for nâ>â0.
LZ transition fit
We fit the sideband frequency dependence of the zigzag mode across the LZ transition in an iterative fashion to obtain the critical point νyc and the bias in the zigzag potential. The fitting procedure is as follows: (i) An initial value of νyc is extracted from a fit of the first-sideband data to the ideal classical dependence on the linear side, \({\nu }_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}=\sqrt{{\nu }_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}^{2}-{\nu }_{{{{\rm{yc}}}}}^{2}}\), for a data range limited to â³1 kHz above the critical point. This avoids deviations in the sideband frequency that manifest near the critical point due to bias and the effect of the quartic potential on the quantum energy-level dependence of the zigzag mode. (ii) An initial value for the bias is determined from a fit to the numerical quantum theory for the zigzag potential (Eqn. (2)) using νyc from (i). (iii) A refined value of the critical point is determined from a fit of each sideband to the quantum theory on the linear side of the transition and the results are averaged. (iv) A refined value for the bias is determined from a fit of both sidebands to the quantum model. Refinement of the critical point is <0.05 kHz for the data presented. Statistical error in the critical point from fitting and systematic error from determination of the secular trap frequencies are <0.02 and <0.03 kHz respectively for νycâ=â717âââ760 kHz. Critical trap asymmetries αc are calculated using the measured axial secular frequency. The data does not allow to distinguish a linear from cubic bias. Using additional information from bias spectroscopy, we determine for three and four ions that a linear bias dominates, and so fits to a linear bias with C3â=â0 are presented in Fig. 3. For five ions the bias is small enough that the sideband frequency dependence alone can only roughly constrain the bias. An alternative fitting approach is taken to constrain the bias further (see discussion below).
For higher data density in spectroscopy plots of the LZ transition (Figs. 2a and 3 for four and five ions), we take advantage of the stability of the experiment to combine data sets from two or more days. Data sets are combined by fitting each set for the critical point using the above method and then using the fit value as the reference for the horizontal axis, νyâââνyc, to remove small day-to-day drifts. The critical points quoted in the main text represent a weighted statistical average over values from all data sets.
Motional state and bias assessment from line centers and strengths
For the five-ion Raman spectra close to the critical point where the sideband peaks from different initial number states of the zigzag mode are resolved or partially resolved, we use the relative peak heights and center frequencies of the sidebands to extract both the motional population distribution of the number states and the bias in the zigzag potential. To do so, we perform dedicated fits of the spectra including the carrier, multiple upper sidebands and the first lower sideband as an incoherent sum of lineshapes. Refined models of the lineshapes are incorporated into the fit: both the carrier and sidebands are modeled as modified Rabi-resonance lineshapes including pure phase damping. The lineshapes are obtained from numerical solution of the optical Bloch equations48, and in practice lie between the limits of Rabi-resonance and Lorentzian forms. The value of the sideband Rabi couplings are calculated using (i) wavefunctions obtained for a given zigzag potential, (ii) a global Raman interaction arising from uniform laser illumination of the ions, and (iii) no assumption of the Lamb-Dicke approximation47. For a resolved sideband from an initial n-number state, the Raman transition with global coupling simplifies to that for a two-level system, \({\left\vert \downarrow \right\rangle }^{\bigotimes N}\left\vert n\right\rangle \leftrightarrow \left\vert {\Uparrow }_{{{{\rm{eff}}}}}\right\rangle \left\vert m\right\rangle\) where \(\left\vert {\Uparrow }_{{{{\rm{eff}}}}}\right\rangle\) is a superposition of single-excitation spin states. The effective Rabi frequency is
where the matrix element Mnm,j for the jth ion is
in terms of zigzag number states \(\left\vert n\right\rangle\), scaled zigzag normal mode coordinate Ï, Coulomb length scale dz, and effective wavenumber \({k}_{{{{\rm{eff}}}},j}={{{{\bf{k}}}}}_{{{{\rm{L}}}}}\cdot {\hat{{{{\bf{D}}}}}}_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}^{j}\), which captures the projection of the Raman wavevector kL onto the direction \({\hat{{{{\bf{D}}}}}}_{{{{\rm{zz}}}}}^{j}\) of the jth ionâs displacement in the zigzag mode. Wavefunctions Ψn(Ï) for evaluating Eq. (6) are obtained from numerical solution of the time-independent Schrödinger equation for the zigzag potential (see below). An approximate linear model for the axial components of the zigzag mode vector is used on the zigzag side of the transition. The model works well out to a zigzag mode frequency of 60 kHz on the zigzag side, which is adequate for the data range of interest.
Fit parameters for a measured carrier and sideband spectrum include a baseline offset, offset from the critical point νyâââνyc, potential parameters C1 and C3, a carrier Rabi frequency Ω0 that sets the overall coupling scale, a carrier phase damping rate γcar and carrier amplitude correction factor near unity, first and second sideband phase damping rates γ1 and γ2 and an overall relative amplitude correction to the carrier, and finally motional populations P(n) for the number states of the zigzag mode. Fit parameters and uncertainties are obtained from unweighted fits using Ï2 minimization.
We find that C1 and C3 values from the fits are strongly correlated, but the motional populations P(n) are insensitive to the choice. Without additional constraining information, we choose C3â=â0 and determine an average value of C1â=â3.3(3)âÃâ10â7 from the resulting fits to the data. We use this value to obtain final fit values for the motional distributions P(n) as shown in Fig. 2. The fits could be improved by including a set of lower sideband measurements but at the expense of longer data collection times.
Classical small-oscillation analysis
Small-oscillation analysis is performed for an N-ion crystal in the 2D pseudo-potential (Eqn. (1) reduced to the 2D yâââz plane with αââ¡âαy) to extract the equilibrium crystal structure and normal modes. The critical value \({\alpha }_{{{{\rm{c}}}}}^{(0)}\) for the LZ transition in the pseudopotential approximation is extracted from the eigenvalue spectrum of the normal modes12. Values for 3â5 ions in an ideal linear trap are \({\alpha }_{{{{\rm{c}}}}}^{(0)}=\{2.4000,4.1542,6.2374\}\). The frequency of the zigzag mode experiences a shift from the pseudo-potential value due to micromotion effects in the ion trap34,50, which in turn leads to a shift in the critical point at the percent level. We apply approximate Mathieu equations for the normal modes of a linear ion string34 to derive the micromotion-corrected frequency for the zigzag mode and the micromotion-shifted critical point
in terms of the Mathieu parameter qy along the relevant transverse y-axis. For this result we assume \({q}_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}^{2}\ll 1\), neglect small corrections due to Mathieu parameter ay, and neglect weak Ïy dependence by setting \({\omega }_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}^{2}\approx {\omega }_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}^{2}{\alpha }_{{{{\rm{c}}}}}^{(0)}\). Since the lowest order effect on the zigzag mode for linear or nearly linear ion crystals is a frequency shift, we use the pseudopotential result for the small-oscillation curve shown in Fig. 2a. Far from the critical point on the zigzag side of the transition, the micromotion-corrected frequency of the zigzag mode needs to be determined numerically from the crystal structure and normal mode vector34,50, but this is not necessary for this work.
The small-oscillation curve shown in Fig. 2a also includes a matching linear bias effect for direct comparison to the quantum model shown. The bias is added through a potential perturbation yz4 with the coefficient λ014â=âââ2.2âÃâ10â7 adjusted to match the effective linear bias coefficient C1â=âââ3.3âÃâ10â7 from 5-ion measurements. Other choices of perturbation are possible, in particular the λ012 term; however, using this perturbation instead makes negligible difference to the curve shown in Fig. 2a.
Zigzag potential
To derive the effective potential for the zigzag mode near the critical point we perform a classical, perturbative, coupled-mode analysis11,18 and adiabatically eliminate modes other than the soft zigzag mode. Using this semi-analytical method, we also obtain the sensitivity of the potential coefficients C1 through C4 (Eqn. (2)) to the polynomial terms in a Cartesian expansion of the trap perturbations, \({V}_{{{{\rm{pert}}}}}(x,y,z)={\sum }_{\xi }{\lambda }_{\xi }{x}^{{\xi }_{1}}{y}^{{\xi }_{2}}{z}^{{\xi }_{3}}\), where ξâ=â(ξ1,âξ2,âξ3) is a list of the integer exponents for each term with order n0â=ââ£Î¾â£â=âξ1â+âξ2â+âξ3. We briefly summarize the method with further details to be presented elsewhere. We Taylor-expand the 2D pseudo-potential (Eqn. (1) reduced to the yâââz plane) to order noâ=â5 or larger in the ionsâ displacements and express the result in terms of the mode coordinates Ïk of the linear crystalâs 2N normal modes, which are re-diagonalized at lowest order of coupling to account for the trap perturbations Vpert. Working from the nonlinear coupled oscillator equations near the critical point, we assume that all other modes adiabatically follow the soft zigzag mode and so adiabatically eliminate them to arrive at an effective force for the zigzag mode in terms of the zigzag order parameter, Ïââ¡âÏzz, alone. Integration of the force provides the effective zigzag potential, which is limited to 4th order. We retain up to 1st order in the polynomial coefficients λξ, which give rise to bias coefficients C1 and C3, shifts in the critical point and modifications to C4. The value of C4 also includes the effect of axial collapse of the ion crystal as the zigzag structure grows, which is encoded in the coupling between the zigzag and axial breathing modes. The effect is significant (order unity) and its inclusion extends the double-well calculation performed in ref. 18. The effects of axial confinement, trans-axial mode coupling and in particular bias extend the calculation of the zigzag potential for a uniform linear ion chain in11. Values of C4 in an ideal linear trap are {0.9307,â2.1906,â4.5409} for 3â5 ions. N-scaling is discussed more generally in a separate section below. We ignore in our fits to data the small effects of the trap perturbations on C2 (i.e. on the critical point) and on C4. Also in our calculation the coupling to the zigzag mode is limited to the effect of the mean order parameter for the non-zigzag modes, ãÏkâ zzã, and excludes the effect of fluctuations arising from terms \(\langle {\varphi }_{k}^{2}\rangle\)âfor example due to thermal fluctuationsâthat induce a shift in the critical point. We expect these effects to be small given the near-ground-state initial cooling of the relevant modes.
Quantum theory
We assume the quartic form of the effective zigzag potential U(Ï) as defined in Eqn. (2) as the starting point for quantum mechanical calculations of the zigzag mode. This implicitly ignores axial spatial variation of the zigzag order parameter Ï29, which applies for the small ion crystals being considered. The effective zigzag potential, derived from the classical coupled mode theory, also ignores the effect of quantum fluctuations from the other modes, which is reasonable given their high frequency. The values of αc and C4 in the potential are obtained from the classical theory in the absence of trap imperfections, and the bias coefficients C1 and C3 are treated as adjustable model parameters obtained from fits. The quantized energy levels and zigzag wavefunctions Ψ(Ï), used in the preparation of Figs. 1â3, are obtained as a function of α from a numerical solution of the 1D time-independent Schrödinger equation for the potential U(Ï). The wavefunctions are used to calculate Raman sideband couplings, as discussed above. Adiabaticity of the ramp across the transition (Fig. 2h) is assessed from numerical solution of the 1D time-dependent Schrödinger equation in which the applied quadrupole voltage ramp introduces a time varying trap aspect ratio α(t) to the zigzag potential. Initial conditions for the simulation shown in Fig. 2h are matched to the average of P(n) measurements on the linear side of the transition. The form of the quartic zigzag potential derived perturbatively near the critical point begins to break down significantly for â³100-kHz mode frequency on the zigzag side, which provides sufficient range for comparison to experiment.
Scaling of zigzag potential parameters
We summarize methods used to assess scaling of the properties of the effective zigzag potential with respect to ion number N and trap size R. It is convenient to consider first the quantum double well in quartic-scaled units (C4âââ1)51, from which we obtain universal values for the optimum tunnel point and the threshold biases for allowable ground-state asymmetry at the optimum point. These results are then evaluated for arbitrary N given knowledge of C4 and αc. The critical trap aspect ratio has previously been shown to scale as αcâ=â0.347N1.77 determined numerically up to Nâ=â10012. In axial Coulomb units with frequency scale \(\bar{\omega }={\omega }_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}\) and corresponding Coulomb length scale \({d}_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}=\bar{d}\equiv {(Q/4\pi {\epsilon }_{0}m{\bar{\omega }}^{2})}^{1/3}\), which is commonly used in the literature and which we consider in the main text, we find C4â=â0.077N2.64 determined numerically up to Nâ=â50 (and C4â=â0.049N2.83 for Nââ¤â10). Alternatively, the zigzag potential can be expressed in transverse Coulomb units with \(\bar{\omega }={\omega }_{{{{\rm{yc}}}}}\) and \(\bar{d}={d}_{{{{\rm{yc}}}}}\), which is convenient to assess scaling of the double-well properties with ion number N. This is in close parallel to our experiment where we keep Ïyc, and so the central ion spacing, constant. In these units the coefficients for the zigzag potential are related to the axial ones as \({C}_{n}^{({{{\rm{t}}}})}={C}_{n}{\alpha }_{{{{\rm{c}}}}}^{-(n+1)/3}\). The quartic term, \({C}_{4}^{({{{\rm{t}}}})}\propto {N}^{-0.31}\), scales weakly with ion number. This weak scaling extends to the optimum tunnel point, \({C}_{2}^{({{{\rm{t}}}})}=2{{\Delta }}{\omega }_{{{{\rm{y}}}}}/{\omega }_{{{{\rm{yc}}}}}\propto {N}^{-0.21}\), tunnel splitting, \({\Delta}\) E10/ââââNâ0.10, and the threshold biases, \(\max\{C^{{(\rm{t}})}_{1}\}\propto {N}^{-0.15}\) and \(\max\{C^{(\rm{t})}_{1}\}\propto{N}^{-0.26}\). The dependencies are even weaker for Nâ¤10. The threshold biases are determined from a threshold value of the right-well projection probability PR(0)â=ââ£ãRâ£0ãâ£2â=â0.75, equivalent to the localization â£2PR(0)âââ1â£â=â0.5, where \(\left\vert {{{\rm{R}}}}\right\rangle\) is defined as the maximally right-localized superposition of the lowest two energy eigenstates of the biased double well. Threshold values quoted in the main text are converted to axial units.
The N-scaling of the actual biases in a trap with a fixed set of electrode perturbations is more complicated since variation in the axial confinement to keep Ïyc constant can alter the trap asymmetries, and the polynomial order and bias strength of the dominant asymmetries vary with N. We write the zigzag bias coefficient in transverse Coulomb units, \({C}_{n}^{({{{\rm{t}}}})}\) for nâââ{1,â3}, as
summed over polynomial exponent lists ξ of order noâ=ââ£Î¾â£ as defined above. The sensitivities, \(\frac{d{C}_{n}}{d{\lambda }_{\xi }}\), are expressed in axial units and are obtained as described above from the zigzag potential. The coefficients, Aξ, are obtained from the trap pseudo-potential expressed in dimension-full units, \({{\Phi }}(x,y,z)={\sum }_{\xi }{A}_{\xi }\frac{{x}^{{\xi }_{1}}{y}^{{\xi }_{2}}{z}^{{\xi }_{3}}}{{R}^{| \xi | }}\), with Aξ in volts and distances in meters. A020 corresponds to {ξ1â=â0,âξ2â=â2,âξ3â=â0}. The coefficients Aξ, while proportional to λξ, exclude the axial scaling dependence. We have explored the effect of trap perturbations on zigzag bias numerically in the range Nâ=â3âââ7 and noââ¤â7 as detailed in the main text. For the linear bias coefficient, \({C}_{1}^{({{{\rm{t}}}})}\), the sensitivity exhibits strong N-dependence and for a given N is strongly suppressed up to order noâ=âN, where perturbation terms arise with unit sensitivity. The bias from these terms, however, is highly suppressed with N due to the other dependencies such that we expect the residual sensitivities to low-order perturbations (noâââ{3,â4}) to be relevant in our trap, including for 5 ions. For the cubic bias coefficient, \({C}_{3}^{({{{\rm{t}}}})}\), we expect the low-order perturbations to dominate since the sensitivities are suppressed more weakly with N.
The last two contributions in the summand of Eqn. (8) determine the scaling of the bias with trap size R and confinement strength Ïyc for a characteristic electrode perturbation of size dpert due to mechanical tolerance. For example, if we can assume fixed transverse Mathieu q-parameter and rf voltage over a limited reduction range of R, we have ÏycâââRâ1, which results in a bias enhancement of \({R}^{-({n}_{{{{\rm{o}}}}}-2)/3}\frac{{d}_{{{{\rm{pert}}}}}}{R}\) with decreasing R at relevant order no. While this represents a challenge to reducing trap size, we expect that a factor-of-4 increase in Ïyc relative to our current setup is feasible.
Bias splitting model
The bias-induced splitting in the frequency of the zigzag mode between the L and R zigzag configurations (Eqn. (3)) is obtained as follows using classical small oscillation analysis. Beginning with the zigzag potential U(Ï) in axial scaled units (Eqn. (2)) on the zigzag side of transition (αâ<âαc), we determine the local mode frequency for each side of the double well from \({\omega }_{{{{\rm{L}}}}({{{\rm{R}}}})}^{2}/{\omega }_{{{{\rm{z}}}}}^{2}={d}^{2}U/d{\varphi }^{2}\) evaluated at the two minima defined by dU/dÏâ=â0. The full dependence of the splitting, ÏRâââÏL, on C1 and C3, which we include in our analysis, is complicated; however, for a pure cubic bias and in the perturbative limit one obtains the simple relation
Similarly for a pure, perturbative linear bias one obtains
In the perturbative limit, using \({\omega }_{{{{\rm{R}}}}}^{2}-{\omega }_{{{{\rm{L}}}}}^{2}\approx 2({\omega }_{{{{\rm{R}}}}}-{\omega }_{{{{\rm{L}}}}}){\omega }_{{{{\rm{R}}}}}\) and \({\omega }_{{{{\rm{R}}}}}^{2}\approx -2{C}_{2}\) for the zigzag side of the transition, we combine the above two contributions to arrive at the main textâs Eqn. (3), which is expressed in terms of νL(R)â=âÏL(R)/2Ï and νzâ=âÏz/2Ï. The above model is limited away from the critical point by the approximations used to derive U(Ï) and deviates from a quantum calculation of the splitting between the lowest energies levels close to the critical point.
Trap potential simulation
To understand the role of the trap electrode imperfections in generating zigzag bias, we simulate the electric potentials from the trap electrodes using commercial Charged Particle Optics (CPO) software52. For a given trap electrode configuration, the potentials are least-squares fit to a set of solid harmonics, which are subsequently used to obtain the 3-D Cartesian coefficients \({\lambda }_{\xi }={\lambda }_{{\xi }_{1}{\xi }_{2}{\xi }_{3}}\) for the polynomial expansion of the trap potential in the pseudopotential approximation (see above). The Cartesian coefficients are expressed in a coordinate basis with origin defined by ideal micromotion compensation and with axes defined by the principal axes of the pseudopotential. In conjunction with the sensitivities of the zigzag biases C1 and C3 to the λξ coefficients (determined as above from the zigzag potential), we assess the role and magnitude of various electrode deformations in generating bias in the zigzag potential. Assuming that the lowest-order asymmetry is the dominant contribution, the linear bias coefficient for three ions is C1ââââ0.95âλ012. This can arise from a number of different rod and endcap deformations of order 10 μm. The same deformations make contributions to C3 of order 10â3â10â4. They are also reasonably consistent with the linear bias measured for five ions, where C1ââââ7.6âÃâ10â4λ012â+â1.50λ014. For four ions, the linear bias at lowest order of perturbation is C1ââââ1.14âλ013, which is likely due to transverse counter-displacements of the endcaps. Shifts and rotations of the trap potential will induce additional bias at next order of approximation in conjunction with nonlinear terms in the potential.
Data availability
The data presented in this manuscript are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
The code used for data analysis and simulation is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Diedrich, F., Peik, E., Chen, J. M., Quint, W. & Walther, H. Observation of a phase transition of stored laser-cooled ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2931â2934 (1987).
Wineland, D. J., Bergquist, J. C., Itano, W. M., Bollinger, J. J. & Manney, C. H. Atomic-ion Coulomb clusters in an ion trap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2935â2938 (1987).
Birkl, G., Kassner, S. & Walther, H. Multiple-shell structures of laser-cooled 24Mg+ ions in a quadrupole storage ring. Nature 357, 310â313 (1992).
Mitchell, T. B. et al. Direct observations of structural phase transitions in planar crystallized ion plasmas. Science 282, 1290â1293 (1998).
Major, F. G., Gheorghe, V. N. & Werth, G. Charged Particle Traps: Physics and Techniques of Charged Particle Field Confinement (Springer-Verlag, 2005).
Raizen, M. G., Gilligan, J. M., Bergquist, J. C., Itano, W. M. & Wineland, D. J. Ionic crystals in a linear Paul trap. Phys. Rev. A 45, 6493â6501 (1992).
Schiffer, J. P. Phase transitions in anisotropically confined ionic crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 818â821 (1993).
Walther, H. From a single ion to a mesoscopic system - crystallization of ions in Paul traps. Phys. Scr. 1995, 360 (1995).
Dubin, D. H. E. & OâNeil, T. M. Trapped nonneutral plasmas, liquids, and crystals (the thermal equilibrium states). Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 87â172 (1999).
Piacente, G., Schweigert, I. V., Betouras, J. J. & Peeters, F. M. Generic properties of a quasi-one-dimensional classical Wigner crystal. Phys. Rev. B 69, 045324 (2004).
Fishman, S., De Chiara, G., Calarco, T. & Morigi, G. Structural phase transitions in low-dimensional ion crystals. Phys. Rev. B 77, 064111 (2008).
Enzer, D. G. et al. Observation of power-law scaling for phase transitions in linear trapped ion crystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2466â2469 (2000).
Liang, J. & Haljan, P. C. Hopping of an impurity defect in ion crystals in linear traps. Phys. Rev. A 83, 063401 (2011).
Ejtemaee, S. & Haljan, P. C. Spontaneous nucleation and dynamics of kink defects in zigzag arrays of trapped ions. Phys. Rev. A 87, 051401 (2013).
Pyka, K. et al. Topological defect formation and spontaneous symmetry breaking in ion Coulomb crystals. Nat. Commun. 4, 2291 (2013).
Ulm, S. et al. Observation of the Kibble-Zurek scaling law for defect formation in ion crystals. Nat. Commun. 4, 2290 (2013).
Kiethe, J., Nigmatullin, R., Kalincev, D., Schmirander, T. & Mehlstäubler, T. E. Probing nanofriction and Aubry-type signatures in a finite self-organized system. Nat. Commun. 8, 15364 (2017).
Retzker, A., Thompson, R. C., Segal, D. M. & Plenio, M. B. Double well potentials and quantum phase transitions in ion traps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 260504 (2008).
Blatt, R. & Wineland, D. Entangled states of trapped atomic ions. Nature 453, 1008â1015 (2008).
Monroe, C., Meekhof, D. M., King, B. E. & Wineland, D. J. A Schrödinger cat superposition state of an atom. Science 272, 1131â1136 (1996).
Leibfried, D. et al. Creation of a six-atom Schrödinger cat state. Nature 438, 639â642 (2005).
Monz, T. et al. 14-qubit entanglement: creation and coherence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 130506 (2011).
Noguchi, A., Shikano, Y., Toyoda, K. & Urabe, S. Aharonov-Bohm effect in the tunnelling of a quantum rotor in a linear Paul trap. Nat. Commun. 5, 3868 (2014).
Bruzewicz, C. D., Chiaverini, J., McConnell, R. & Sage, J. M. Trapped-ion quantum computing: progress and challenges. Appl. Phys. Rev. 6, 021314 (2019).
Turchette, Q. A. et al. Heating of trapped ions from the quantum ground state. Phys. Rev. A 61, 063418 (2000).
Brownnutt, M., Kumph, M., Rabl, P. & Blatt, R. Ion-trap measurements of electric-field noise near surfaces. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 1419â1482 (2015).
McCormick, K. C. et al. Quantum-enhanced sensing of a single-ion mechanical oscillator. Nature 572, 86â90 (2019).
Cowley, R. A. Soft modes and structural phase transitions. Integr. Ferroelectr. 133, 109â117 (2012).
Shimshoni, E., Morigi, G. & Fishman, S. Quantum zigzag transition in ion chains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 010401 (2011).
Chiara, G. D., del Campo, A., Morigi, G., Plenio, M. B. & Retzker, A. Spontaneous nucleation of structural defects in inhomogeneous ion chains. New J. Phys. 12, 115003 (2010).
Plischke, M. & Bergersen, B. Equilibrium Statistical Physics, 3rd edn. (World Scientific, 2006).
Ejtemaee, S. & Haljan, P. C. 3D Sisyphus cooling of trapped ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 043001 (2017).
Ejtemaee, S., Thomas, R. & Haljan, P. C. Optimization of Yb+ fluorescence and hyperfine-qubit detection. Phys. Rev. A 82, 063419 (2010).
Landa, H., Drewsen, M., Reznik, B. & Retzker, A. Modes of oscillation in radiofrequency paul traps. New J. Phys. 14, 093023 (2012).
Müller-Kirsten, H. J. W. Introduction to Quantum Mechanics, 2nd edn. (World Scientific, 2012).
Douglas, D. J., Glebova, T. A., Konenkov, N. V. & Sudakov, M. Y. Spatial harmonics of the field in a quadrupole mass filter with circular electrodes. Tech. Phys. 44, 1215â1219 (1999).
Filippov, S., Vyurkov, V. & Fedichkin, L. Effect of image charge on double quantum dot evolution. Phys. E: Low.-dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 44, 501â505 (2011).
Wineland, D. et al. Experimental issues in coherent quantum-state manipulation of trapped atomic ions. J. Res. Natl Inst. Stand. Technol. 103, 259 (1998).
Zurek, W. H., Dorner, U. & Zoller, P. Dynamics of a quantum phase transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 105701 (2005).
Home, J. P., Hanneke, D., Jost, J. D., Leibfried, D. & Wineland, D. J. Normal modes of trapped ions in the presence of anharmonic trap potentials. New J. Phys. 13, 073026 (2011).
Gong, Z.-X., Lin, G.-D. & Duan, L.-M. Temperature-driven structural phase transition for trapped ions and a proposal for its experimental detection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 265703 (2010).
Roos, C. F. et al. Nonlinear coupling of continuous variables at the single quantum level. Phys. Rev. A 77, 040302 (2008).
Baltrusch, J. D., Cormick, C., De Chiara, G., Calarco, T. & Morigi, G. Quantum superpositions of crystalline structures. Phys. Rev. A 84, 063821 (2011).
Landa, H., Marcovitch, S., Retzker, A., Plenio, M. B. & Reznik, B. Quantum coherence of discrete kink solitons in ion traps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 043004 (2010).
Timm, L., Rüffert, L. A., Weimer, H., Santos, L. & Mehlstäubler, T. E. Quantum nanofriction in trapped ion chains with a topological defect. Phys. Rev. Res. 3, 043141 (2021).
Zhang, J., Chow, B. T. & Haljan, P. C. Stabilization of ion-trap secular frequencies for a quantum phase transition study. Preprint at http://arXiv.org/abs/2210.14478 (2022).
Wineland, D. et al. Experimental primer on the trapped ion quantum computer. Fortschr. Phys. 46, 363â390 (1998).
Metcalf, H. J. & van der Straten, P. Laser Cooling and Trapping (Springer, 1999).
Di Marco, V. B. & Bombi, G. Mathematical functions for the representation of chromatographic peaks. J. Chromatogr. A 931, 1â30 (2001).
Kaufmann, H. et al. Precise experimental investigation of eigenmodes in a planar ion crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 263003 (2012).
Okun, P. & Burke, K. Uncommonly accurate energies for the general quartic oscillator. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 121, e26554 (2021).
CPO Programs, Available on the web site http://www.electronoptics.com.
Acknowledgements
We thank Haggai Landa for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the Canada Foundation for Innovation Leaders Opportunity Fund (CFI LOF). Jie Zhang acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 12004430, the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province under grant No. 2022RC1194 and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province under grant No. 2023JJ10052.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.E. and P.C.H. designed the initial experiment. All authors contributed to setup, data collection and analysis over the course of the project, and all authors contributed to the preparation of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisherâs note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the articleâs Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the articleâs Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chow, B.T., Ejtemaee, S. et al. Spectroscopic characterization of the quantum linear-zigzag transition in trapped ions. npj Quantum Inf 9, 68 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-023-00741-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-023-00741-5
This article is cited by
-
Tracking the extensive three-dimensional motion of single ions by an engineered point-spread function
Nature Communications (2024)