Tutorial Sheet - 6 (Transistor Amplifier)
Uploaded by
Sulabh KumarTutorial Sheet - 6 (Transistor Amplifier)
Uploaded by
Sulabh KumarBasic Electronic Devices and Circuits (10B11EC211) Tutorial Sheet - 6 (Transistor Amplifier) 1.
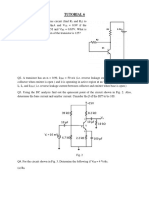
Calculate the base bias voltage (VB ) for the amplifier circuit given in Fig. 1 ( i) !hen the signal source is capacitor"couple# to the circuit as sho!n in Fig. 1 a an# (ii) !hen the signal source is #irectl$ connecte# to the circuit as in Fig. 1b. %Ans. (a) &.'( )* (b) 0.21 )+
(a) Fig. 1
(b)
2. ,n the single"stage amplifier circuit sho!n in Fig. 2 the B-T use# is AC12. !hich has hfe or / 1(0 hie or rin / 1.( 01. 2ra! its ac e3uivalent circuit an# calculate the voltage gain (Vo/Vs) !hen (a) RL is connecte# an# (b) RL is #isconnecte#. %Ans. 4(0 4100+
Fig. 2 3. For the amplifier circuit of Fig. 2 calculate (a) Vo/Vs, if the source resistance is .00 1. (b) Io/Ii, !here Io is the current through the loa# resistor R5 an# Ii is the input current as sho!n. (c) Io/Is !here Is is the ac current supplie# b$ the input voltage source. %Ans. (a) 426* (b) 4'(* (c) 4&6.'+
. ,f in the amplifier circuit of Fig. 2 both R1 an# R2 are 6 01 #etermine the gain of the amplifier. %Ans. 0+ !. 7oint E in Fig. '.8. represents the emitter terminal of a B-T amplifier. Both #c an# ac signal voltages appear at point E. A part of emitter resistance is to be b$passe# b$ a capacitor CE as sho!n in the figure. ,f the amplifier is re3uire# to han#le signals of fre3uenc$ ranging from 2( 9: to 1( 09: #etermine the suitable practical value of the b$pass capacitor. %Ans. 100 ;F+
Fig. 3
Fig.
6. Figure '.8' sho!s a B-T small"signal amplifier !ith a fi<e# bias. The #c beta (=0) of the transistor is 110. The h"parameters of the transistor are hie / 1.1 01 hfe / 100 an# hoe / 2( ;>. Calculate the voltage gain of the amplifier. %Ans. The transistor is in #eep saturation* AV / 0+
You might also like
- BJT Amplifier Sheet: Figure 1: Problem 1No ratings yetBJT Amplifier Sheet: Figure 1: Problem 13 pages
- Btech Eee 3 Sem Analog Electronic Circuits Pel3i102 2018No ratings yetBtech Eee 3 Sem Analog Electronic Circuits Pel3i102 20182 pages
- Unitwise Objective Question With AnswerNo ratings yetUnitwise Objective Question With Answer19 pages
- Analog Electronic Circuits (ECE - 2101) RCSNo ratings yetAnalog Electronic Circuits (ECE - 2101) RCS3 pages
- ANALOG ELECTRONICS CIRCUIT-ELE-ETC-3rd-21-22No ratings yetANALOG ELECTRONICS CIRCUIT-ELE-ETC-3rd-21-222 pages
- 090 «﹝Aditya﹞» PDF Question Bank Chapter 01 BJT & MOSFET AnalysispdfNo ratings yet090 «﹝Aditya﹞» PDF Question Bank Chapter 01 BJT & MOSFET Analysispdf10 pages
- Fall 2023 - Exercise (3) - BJT Amplifiers - EE219No ratings yetFall 2023 - Exercise (3) - BJT Amplifiers - EE2193 pages
- Design A RC Coupled CE Transistor Amplifier100% (3)Design A RC Coupled CE Transistor Amplifier7 pages
- GATEPaper - in - GATE 2014 ECE Video Solutions On Analog Circuits (Analog Electronics)0% (1)GATEPaper - in - GATE 2014 ECE Video Solutions On Analog Circuits (Analog Electronics)7 pages
- 2ee201 Edc Index Ta 2010, Term. Ass.4,5,7,8No ratings yet2ee201 Edc Index Ta 2010, Term. Ass.4,5,7,812 pages
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionFrom EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)5/5 (1)
- Tutorial Sheet - 7 (Feedback Amplifiers)No ratings yetTutorial Sheet - 7 (Feedback Amplifiers)1 page
- Group I (Dilute H SO Group) - CO: (Carbonate), SO (Sulphite), S (Sulphide), NO (Nitrite) : Salt + Dil HNo ratings yetGroup I (Dilute H SO Group) - CO: (Carbonate), SO (Sulphite), S (Sulphide), NO (Nitrite) : Salt + Dil H4 pages
- Tutorial Sheet - 8 (Sinusoidal Oscillators)No ratings yetTutorial Sheet - 8 (Sinusoidal Oscillators)3 pages