Gem Clarity
Gem Clarity
Uploaded by
arunabhatlaCopyright:
Available Formats
Gem Clarity
Gem Clarity
Uploaded by
arunabhatlaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Gem Clarity
Gem Clarity
Uploaded by
arunabhatlaCopyright:
Available Formats
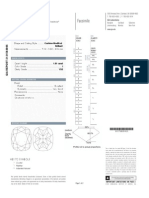
Clarity Scale Extra Fine Quality.
These gems have microscopic inclusions IF which are difficult to slightly difficult to see under a loupe with 10X magnification. Extra Fine Quality. Small pin-pricks are just visible to the VVS1 scrutiny of the close nake eye. However, the beauty of the gem is not diminished in anyway Very Fine Quality. Small pin-pricks are just visible to the VVS2 scrutiny of the close nake eye. However, the beauty of the gem is not diminished in anyway Good Quality. Small pin-pricks and feathers are just visible VS1 to the scrutiny of the close nake eye. However, the overall beauty of the gem is still not diminished Good Quality. These gems have inclusions which are fairly VS2 easy to see to the close naked eye. However the overall beauty of the gem is still high. Good to the medium qualities. Included gems with internal SI1-2 features that range from eye visible to easily seen to the naked eye. Opaque/Translucent Highly included,Translucent
Check list to help you make Gemstone's best buying decision: 1. Always take a gemstones certificate provided by an internationally recognized laboratory. 2. Look for the status of treatment (heated or unheated) carefully in the certificate. 3. Conversion of carat and ratti should be clear. Carat is the international unit for weight of gemstones, calculate and buy in carats. 4. For a genuine purchase decision stay with a professional or a jeweller with serious gemological training. 5. You must take a detailed bill of your purchase; it works as an undisputed future reference document. Conversion from Carat and Ratti to mg 1 Carat = 200 mg 1 Ratti = 121.5 mg (in ayurveda this Rati is used) or 1 Ratti = 182.25 mg
In India people generally buy and sell gemstones according to Rati weight, but it is advised to buy them according to Carat weight because carat is a standard measurement. Ayurvedic Ratti 1 tola = 11.664 gms 1 tola = 12 masha 1 masha = 8 ratti 1 tola = 12 x 8 ratti 1 ratti = 121.5 mg Gold Ratti 1 tola = 16 aane 1 aana = 4 ratti 1 ratti = 182.25 mgm
Diamond Color Basics
What is diamond color?
Most diamonds have hints of color, and subtle color differences have a big impact on diamond prices. Diamonds are actually found in many colors, but the majority of diamonds available will have tints of yellow or brown. Diamond color is a primary quality factor along with the other 4Cs of Diamond Clarity, Diamond Carat Weight, and Diamond Cut.
DIAMOND CLARITY
Clarity refers to the degree to which imperfections are present in a diamond. Diamonds which contain numerous or significant imperfections have less brilliance because the flaws interfere with the path of light through the diamond. In grading a diamond's clarity, the GIA considers the number, size, color, reflectivity, and position of every flaw visible under 10x magnification. Below are the GIA clarity grades and definitions, with further comments from Lumera:
Flawless:
FL
Extremely rare, less than 1 in 5000 jewelry quality No inclusions or blemishes are diamonds are rated FL. visible to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.
Internally Flawless:
IF
FL and IF diamonds appear identical unless viewed No inclusions, only blemishes under 10x magnification by a skilled grader. Less than are visible to a skilled grader 3% of jewelry quality diamonds are rated IF. using 10x magnification.
VVS1 Very, Very Slightly Included:
VVS1 inclusions are typically only visible from the pavilion (bottom), while VVS2 inclusions are visible Inclusions are difficult for a from the crown (top). When viewed with the naked VVS2 skilled grader to see under 10x eye, the diamond appears identical to higher grades. magnification.
VS1 VS2 SI1 SI2
Very Slightly Included:
Inclusions are clearly visible under 10x magnification but can be characterized as minor.
Slightly Included:
Inclusions are not visible to the naked eye. Perhaps 1 in 100 untrained observers can detect VS2 inclusions with the naked eye, on close inspection under ideal conditions.
Inclusions are noticeable to a skilled grader using 10x magnification.
Included:
SI1 is the lowest grade with flaws often invisible to the naked eye. SI2 inclusions are usually visible to the naked eye, although they will require close inspection.
I1
Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification and may affect transparency and brilliance.
I1 diamonds have inclusions that are almost always visible to the naked eye.
Get a complete explanation of Clarity, and the types of imperfections that affect it.
Posted by kenny 1.34 carat H Color Octavia asscher cut diamond
What is the Diamond Color Scale?
There have been methods for grading diamond color since the 1700s. Colorless diamonds have always been valued for their rarity and purity of crystal. Today, diamonds are generally evaluated by a diamond color scale that was developed in the 1950s by GIA's Richard T. Liddicoat. The Color Grading Scale starts with the letter D and ends at Z. D colored diamonds have the least amount of color and Z colored diamonds have the most color in the range of D-Z. Beyond Z color, diamonds are graded as Fancy Color with a separate set of parameters.
GIA
*Fun Fact - When GIA developed the D-Z grading system they avoided A-C because some dealers use A1 to C3 for 'in-house' grading systems.
How is diamond color graded?
Diamond graders assess color by placing a diamond in a lighting unit that simulates daylight. The diamond is positioned face down rather than face up, so the grader can evaluate body color. The diamond will be compared to masterstones of similar color. Masterstones are sets of diamonds that represent the D-Z color scale.
Diamond Color is graded face down
Diamond color and price?
D colored diamonds are the rarest and most expensive of diamonds within the D-Z scale. Certain fancy colored diamonds will command the highest prices overall, and these will be discussed in separate tutorial. Many people enjoy diamonds in the near colorless range G-J, as they find a balance of size, clarity, and price to meet their needs. *Compare diamond prices of different color grades.
Diamond Color - The Nitty Gritty
What causes color in diamonds?
Diamonds are carbon essentially, but most diamonds will have trace impurities that create color. For example, nitrogen impurities cause yellow color. Nitrogen is the most common impurity in diamond, so the majority of diamonds you'll see in the marketplace will have varying degrees of
yellow tint. Brown color in diamond is thought to be caused by internal graining, which results from structural irregularites often in combination with an impurity like nitrogen. Colorless diamonds are very rare, as they contain little to no impurities and are essentially chemically pure. *Stay tuned for our Fancy Color tutorial, where we will discuss cause of color in depth.
Does diamond fluorescence affect color?
Diamond Fluorescence may potentially make a warmer colored stone appear more colorless. About 30% of all diamonds fluoresce blue, and blue will make diamonds with yellow tint generally appear "whiter" than their non-fluroescent counterparts. The effect of fluorescence should be judged on a case-by-case basis, as diamonds will fluoresce to varying degrees.
How does diamond cut affect color?
Well-cut round brilliant diamonds will typically hide their color better than poorly cut stones of the same shape. Also certain fancy shapes like emerald cuts, ovals, and pear cuts will reveal more color, because they typically have broader facet arrangements. The brighter the cut, the less color you will see from the face-up view. However, color will still be visible from the pavillion.
Do different labs have different color grades?
With the exception of AGS Labs numerical color grading scale, most diamond grading labs utilize GIA's D-Z scale. Not all laboratory color grading is equal, as there are differences among the labs. There is a certain amount of subjectivity among human color graders, and labs utilize several graders to assess the final color grade. Click on the links below for different lab color grading methods. GIA Color Grading Scale AGS Labs Numerical Color Grading Scale International Gemological Institute (IGI) EGL USA HRD Antwerp
Ring metals and diamond color
Precious Metals can change the overall apparent color of a diamond. Diamonds reflect light back to the viewers eye, and they also reflect light of surrounding metal. Metal choice is a personal preference, and there are two general schools of thought about diamond color and metal. Some prefer to set warmer colored diamonds in white metal to help them face-up a bit whiter, while others find the contrast of yellow or rose gold and diamond to be desirable. Additionally, some prefer to see warmth in their diamonds, so that should be considered when choosing the color of metal.
People who have LO, NO, OO, SU, WAR, END, ILL, DI, DHI, SAD, MAD letters will have to undergo various problems and turbulence in their life due to negative vibrations. Every man has to check his NAMES that whether they have negative vibrations.
You might also like
- 117-Gemstone IdentificationDocument17 pages117-Gemstone Identificationms_pmNo ratings yet
- Tourmaline Alexandrite Chrysoberyl: Gemstone Name Specific Gravity Mohs Hardness Index of Refraction Gemstone FamilyDocument2 pagesTourmaline Alexandrite Chrysoberyl: Gemstone Name Specific Gravity Mohs Hardness Index of Refraction Gemstone FamilyKhurram Naseem100% (2)
- How Much Are Diamonds Worth?: Diamond Price Chart Actual Diamond PricesDocument8 pagesHow Much Are Diamonds Worth?: Diamond Price Chart Actual Diamond PricesChris.No ratings yet
- Premier Catalog 2010 2011Document112 pagesPremier Catalog 2010 2011Kaity Morris100% (2)
- Vdocuments - MX - Gemological Laboratory Equipment List PDFDocument82 pagesVdocuments - MX - Gemological Laboratory Equipment List PDFJanez Forstnaric100% (1)
- BUYING A DIAMOND - An Impartial Guide: Know Your DiamondsDocument8 pagesBUYING A DIAMOND - An Impartial Guide: Know Your DiamondsSubhash Digambar VisalNo ratings yet
- Diamonds ReportDocument7 pagesDiamonds ReportUsertightNo ratings yet
- Diamond Buying GuideDocument4 pagesDiamond Buying GuideSally AnneNo ratings yet
- Diamonds ChiragDocument22 pagesDiamonds Chiragchirag gavadiya100% (1)
- Diamond Grading ImpDocument4 pagesDiamond Grading Impdrsivaprasad7No ratings yet
- 4cs BrochureDocument2 pages4cs Brochurepink_key711No ratings yet
- Diamond Buyer GuideDocument5 pagesDiamond Buyer GuidetgvnayagamNo ratings yet
- D Lesson 04Document23 pagesD Lesson 04ana_Ştefan_3No ratings yet
- Diamond Charts and Value GuideDocument4 pagesDiamond Charts and Value GuideBrian PringleNo ratings yet
- Gemstone Quality AnalysisDocument10 pagesGemstone Quality AnalysisTharanga Sujeeva MadalakandaNo ratings yet
- Diamond Buying FundamentalsDocument13 pagesDiamond Buying FundamentalsNasim100% (1)
- Chelsea and Synthetic Emerald Filters Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsFrom EverandChelsea and Synthetic Emerald Filters Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Diamond Ring Buying Guide: How to Identify, Evaluate & Select The Best Diamonds & Diamond Jewelry, 8th EditionFrom EverandDiamond Ring Buying Guide: How to Identify, Evaluate & Select The Best Diamonds & Diamond Jewelry, 8th EditionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Refractometers Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsFrom EverandRefractometers Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- SSEF Diamond-Type Spotter and Blue Diamond Tester Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsFrom EverandSSEF Diamond-Type Spotter and Blue Diamond Tester Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsNo ratings yet
- Loupes Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsFrom EverandLoupes Made Easy: The "RIGHT-WAY" Guide to Using Gem Identification ToolsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chalcedony Value, Price, and Jewelry Information - International Gem SocietyDocument8 pagesChalcedony Value, Price, and Jewelry Information - International Gem Societyasset68No ratings yet
- Gemology Diamond Vs MossoniteDocument13 pagesGemology Diamond Vs MossonitezatiNo ratings yet
- Shape: Diamond Grading ChartDocument1 pageShape: Diamond Grading ChartSagar KarvandeNo ratings yet
- D Lesson 14Document17 pagesD Lesson 14Mai Do AsensiNo ratings yet
- Are Diamonds Unbreakable - Royal Coster Diamonds PDFDocument5 pagesAre Diamonds Unbreakable - Royal Coster Diamonds PDFVasile Diana AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Diamond EduDocument6 pagesDiamond EduKong Lay King100% (1)
- Fancy Vivid Purple-Pink DiamondDocument14 pagesFancy Vivid Purple-Pink Diamondhbraga_sruival100% (1)
- Dark Field LoupeDocument4 pagesDark Field Loupesaurabh_acmasNo ratings yet
- ddg16 PrintableDocument39 pagesddg16 PrintablerjvrglhchhqbxflmekNo ratings yet
- Precision Cutting Tools PDFDocument16 pagesPrecision Cutting Tools PDFHoang Truong DinhNo ratings yet
- Fracture Filling of DiamondsDocument12 pagesFracture Filling of DiamondsVaishali JhaveriNo ratings yet
- GIA, How To Purchase The Perfect Diamond Engagement RingDocument5 pagesGIA, How To Purchase The Perfect Diamond Engagement Ringkaveh25100% (1)
- Facsimile: Di A Mond GR A Ding ReportDocument2 pagesFacsimile: Di A Mond GR A Ding ReportJoshColistraNo ratings yet
- The Allnatt Diamond ($3 Million) : JewelersDocument5 pagesThe Allnatt Diamond ($3 Million) : JewelersTomi TodinganNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument67 pagesFinalpersi06No ratings yet
- ddg05 PrintableDocument30 pagesddg05 PrintablerjvrglhchhqbxflmekNo ratings yet
- 2020 Education Catalog: Carlsbad CampusDocument71 pages2020 Education Catalog: Carlsbad CampusLina PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Estimating Cut Grade 0bookletDocument10 pagesEstimating Cut Grade 0bookletSanjay Thakkar100% (1)
- Jodie Diegel, GG, MBA: Graduate Gemologist Gemological Institute of AmericaDocument29 pagesJodie Diegel, GG, MBA: Graduate Gemologist Gemological Institute of AmericarosemaryofpakistanNo ratings yet
- Emerald Cut - IGSDocument8 pagesEmerald Cut - IGSFernandoconectadoNo ratings yet
- Bvlgari Brochure Bridal Row Us 2017Document35 pagesBvlgari Brochure Bridal Row Us 2017Suwichaya TechaNo ratings yet
- Bulgari Fancy Deep-Blue Diamond CatalogueDocument9 pagesBulgari Fancy Deep-Blue Diamond Cataloguehbraga_sruivalNo ratings yet
- D Lesson 03Document23 pagesD Lesson 03ana_Ştefan_3No ratings yet
- GEMSDocument65 pagesGEMSsaopaulo100% (1)
- SSEF TRADE ALERT - Kashmir-Like Sapphires From Madagascar Entering The Gemtrade in Large Sizes andDocument6 pagesSSEF TRADE ALERT - Kashmir-Like Sapphires From Madagascar Entering The Gemtrade in Large Sizes andphtoostar_475335573No ratings yet
- Samuels Jewelers Winter 2008 CatalogDocument32 pagesSamuels Jewelers Winter 2008 CatalogSteve Kirklin100% (1)
- Gem-A CCFDocument4 pagesGem-A CCFAlfonso HarisNo ratings yet
- Study of Gem and Jewellery: Types of Gem Stone Setting #DrneerujainDocument26 pagesStudy of Gem and Jewellery: Types of Gem Stone Setting #DrneerujainDr. Neeru jainNo ratings yet
- Ruby, Pink Sapphire & Padparadscha - Walking The Line - Lotus GemologyDocument23 pagesRuby, Pink Sapphire & Padparadscha - Walking The Line - Lotus Gemologykandhan_tNo ratings yet
- The Diamond 4CsDocument14 pagesThe Diamond 4CsDipak MondalNo ratings yet
- Polymer Impregnated Turquoise PDFDocument3 pagesPolymer Impregnated Turquoise PDF8duke8No ratings yet
- Palladium Brochure Hooverandstrong ComDocument4 pagesPalladium Brochure Hooverandstrong ComWilliam E. Hawkins Jr.No ratings yet
- DDG Cut Grade TableDocument1 pageDDG Cut Grade TablePaul MessinaNo ratings yet
- Materials Refractive IndexDocument2 pagesMaterials Refractive IndexGems N Jewels PakistanNo ratings yet
- Lapidary ProcessDocument35 pagesLapidary ProcessDeus GarciaNo ratings yet
- 2018 GIA London Education Catalog PDFDocument40 pages2018 GIA London Education Catalog PDFSilviu Andone100% (1)
- 1 150134 HRD Cut Grade en WebDocument12 pages1 150134 HRD Cut Grade en Webraj2471No ratings yet
- WFDocument2 pagesWFkas456No ratings yet
- September 1, 2007: Retrieving Hardware InformationDocument1 pageSeptember 1, 2007: Retrieving Hardware InformationarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Ms 000029Document7 pagesMs 000029arunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Apms Recruitment 2012 Roster Wise List of Candidates Allotted TGT - Zone Vi (Venue: Govt. Mahaboobia High School (Girls), Gunfoundry, Hyderbad)Document12 pagesApms Recruitment 2012 Roster Wise List of Candidates Allotted TGT - Zone Vi (Venue: Govt. Mahaboobia High School (Girls), Gunfoundry, Hyderbad)arunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- September 4, 2007: Renaming FilesDocument1 pageSeptember 4, 2007: Renaming FilesarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Gem ClarityDocument7 pagesGem ClarityarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- August 13, 2007: Debugging ScriptsDocument1 pageAugust 13, 2007: Debugging ScriptsarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- August 25, 2007: Memory FragmentationDocument1 pageAugust 25, 2007: Memory FragmentationarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- September 10, 2007: Linux Hints, Tips, and TricksDocument1 pageSeptember 10, 2007: Linux Hints, Tips, and TricksarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- NuDocument8 pagesNuarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgements: Item: Word Input-Output Name Value Simple-Command: Item Simple-Command Item Command: Simple-CommandDocument2 pagesAcknowledgements: Item: Word Input-Output Name Value Simple-Command: Item Simple-Command Item Command: Simple-CommandarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- September 2, 2007: Simple Network Performance TestDocument1 pageSeptember 2, 2007: Simple Network Performance TestarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Fault Handling: Figure 3. UNIX SignalsDocument2 pages3.6 Fault Handling: Figure 3. UNIX SignalsarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Anecdote For FathersDocument1 pageAnecdote For FathersarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Case-Part: Pattern) Command-List Pattern: Word Pattern - Word Else-PartDocument3 pagesCase-Part: Pattern) Command-List Pattern: Word Pattern - Word Else-PartarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Unix 25Document2 pagesUnix 25arunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Unix 22Document2 pagesUnix 22arunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Command SubstitutionDocument2 pages3.3 Command SubstitutionarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Keyword Parameters: 2.10 The Man CommandDocument2 pages3.0 Keyword Parameters: 2.10 The Man CommandarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Control Flow - IfDocument2 pages2.7 Control Flow - IfarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Parameter TransmissionDocument2 pages3.1 Parameter TransmissionarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- The Sequence: 2.8 Command GroupingDocument2 pagesThe Sequence: 2.8 Command GroupingarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Error Handling: Execution of A Command (See Also 3.7) May Fail For Any of The Following ReasonsDocument2 pages3.5 Error Handling: Execution of A Command (See Also 3.7) May Fail For Any of The Following ReasonsarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Control Flow - Case: DoneDocument2 pages2.2 Control Flow - Case: DonearunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- $path: 2.5 The Test CommandDocument2 pages$path: 2.5 The Test CommandarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Here DocumentsDocument2 pages2.3 Here DocumentsarunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Control Flow - For: Who - Grep $1Document2 pages2.1 Control Flow - For: Who - Grep $1arunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Prompting: / Is Convenient For Quoting Single Characters. When More Than One Character Needs Quoting TheDocument2 pages1.7 Prompting: / Is Convenient For Quoting Single Characters. When More Than One Character Needs Quoting ThearunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Input Output Redirection: Ls - L FileDocument2 pages1.3 Input Output Redirection: Ls - L FilearunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- Unix 10Document2 pagesUnix 10arunabhatlaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Unix Shell: 7 Further InformationDocument2 pagesAn Introduction To The Unix Shell: 7 Further InformationarunabhatlaNo ratings yet