0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
263 viewsTides Webquest
Tides Webquest
Uploaded by
api-264090085Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Tides Webquest
Tides Webquest
Uploaded by
api-2640900850 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
263 views3 pagesOriginal Title
tides webquest
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
263 views3 pagesTides Webquest
Tides Webquest
Uploaded by
api-264090085Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Tides Webquest
Part I: Background on Tides
Begin your information search by using your textbook and accessing
http://www.nos.noaa.gov/education/tides/welcome.html
As you read through the tutorial, answer the questions below that correspond to each
section of the tutorial.
What are Tides?
1. What is a basic definition of a tide? The daily rise & fall of Earths
oceans caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and
Sun.
. What is a high tide? What is a low tide? High tide occurs when the
crest of a wave reaches a certain location, while low tide
occurs when the trough reaches a certain location.
!. What is tidal range? The diference between the heights of high
tide & low tide.
What Causes Tides?
". #ides are caused by the gra$itational attraction of what two celestial bodies? The
sun & the Moon
%. What does &ewton's law of uni$ersal gra$itational state? The greater the
ass of the ob!ects and the closer they are to each other,
the greater the gravitational attraction between the.
(. Which celestial body has a greater effect on tidal forces on )arth? The sun
Gravity, Inertia, and the Two Bulges
*. +ow does the moon create a bulge? The oons gravitational pull
e"ceeds #nertia, pulling the water towards the oon.
1,. What causes a bulge to be created on the opposite side of the )arth or the -far
side. from the moon? #nertia e"ceeds the gravitational pull of the
oon, so the water continues to ove in a straight line,
oving away fro the Earth.
Changing ngles and Changing Tides
11. /escribe how changes in the relati$e positions of the moon and sun change in
relation to the )arth? $s their positions change, their gravitational
pull either inially or a"ially decreases.
1. At what point is the sun at its minimum declination and its maximum declination?
%uring the e&uino"es, the sun is at its iniu
declination, during the solstices , the sun is at its a"iu
declination.
!requency o" Tides # The $unar %ay
10. 1ompare and contrast a solar and lunar day. +ow long is a lunar day? The
solar day is '( hrs long, while the )unar day is '( hrs and *+
inutes long.
1". Why do most coastal areas experience two high tides and two low tides?
,ecause the Earth rotates through two tidal bulges every
lunar day.
1%. +ow long does it take for high tide to occur? +ow long is the time between low
and high tide? High tides occur every -' hours and '* inutes,
a.ing the tie n between high tide and low tide / hours
and -'.* inutes.
Tidal &ariations # The In"luence o" Position and %istance
1(. What causes spring tides? What causes neap tides? +ow many spring and neap
tides occur in a lunar month? Spring tides occur when the Earth, Sun,
and oon are aligned, causing the solar tide to have an
additive efect on the lunar tide. $ neap tide occurs when
the oon and sun are at an angle to eachother, causing the
solar tides to partially cancel out the lunar tides. %uring
each )unar onth, two sets of spring tides, and two sets of
neap tides occur.
1*. +ow are tide2generating forces affected when the moon is closest to the )arth 3or
perigee4? when the moon is farthest away from the )arth 3or apogee4? +ow does this
affect the tides that are produced? $t the perigee, tide generating
forces are higher than usual, producing above average
ranges in the tides, while at the apogee, tide generating
forces are lower than usual, producing below average
ranges in the tides.
,. +ow are tide2generating forces affected when the )arth is closest to the sun 3or
perihelion4? when the )arth is farthest from the sun 3or aphelion4? +ow does this
affect the tides that are produced? $t the perihelion, tidal ranges are
enhanced, while at the aphelion, tidal ranges are reduced.
What ""ects Tides in ddition to the 'un and (oon?
1. +ow are the magnitudes of tides affected by shorelines? By mid2ocean islands?
$t a saller scale, the agnitude of tides can be strongly
in0uenced by the shape of the shoreline. Mid1oceanic
islands not near continental argins typically e"perience
very sall tides of - eter or less.
. +ow does a funnel2shaped bay compare to a narrow inlet and shallow water?
2unnel1shaped bays in particular can draatically alter tidal
agnitude.
!. What is the affect of strong tidal ri$ers on tides in estuaries? #n estuaries
with strong tidal rivers, powerful seasonal river 0ows in the
spring can severely alter or as. the incoing tide.
5. What other abiotic factors affect tides? 1ompare and contrast wind and weather
patterns that affect tides. )ocal winds and wind patterns can also
alter tides.
You might also like
- Tides&CurrentsDocument4 pagesTides&CurrentsGriffin Glenn50% (12)
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-265544103No ratings yet
- Seasons WebquestDocument2 pagesSeasons Webquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Solar System Fact CardsDocument2 pagesSolar System Fact CardsSónia Nascimento100% (1)
- Using Daily Aspect Calendars To Time Intraday TradesDocument7 pagesUsing Daily Aspect Calendars To Time Intraday Tradesprasch100% (7)
- The Chinese CalendarDocument3 pagesThe Chinese CalendarDan Van den Berghe100% (1)
- Tides WebquestDocument3 pagesTides Webquestapi-264753403No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-265487375No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-264873863No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-264873508No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-264220457No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument3 pagesTides Webquestapi-264886115No ratings yet
- Tides Webquest 1Document3 pagesTides Webquest 1api-264099015No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-264590160No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-264150929No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument3 pagesTides Webquestapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Tides WebquestDocument3 pagesTides Webquestapi-2642205840% (2)
- Tides WebquestDocument2 pagesTides Webquestapi-264100173No ratings yet
- Tidal Types and CyclesDocument6 pagesTidal Types and CyclesAljohn Mar CanalesNo ratings yet
- Tides: Not Observed Rarely Observed Observed Tidal Ranges Are Often Much Larger Rarely ObservedDocument17 pagesTides: Not Observed Rarely Observed Observed Tidal Ranges Are Often Much Larger Rarely Observedchuchu092010No ratings yet
- Geography (Chapter 13) - Daily Class Notes - Samagra Book Series Batch (Hinglish)Document8 pagesGeography (Chapter 13) - Daily Class Notes - Samagra Book Series Batch (Hinglish)aayushgoswami810No ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument61 pagesOceanographyAbdul skNo ratings yet
- High TideDocument15 pagesHigh TideHồng LêNo ratings yet
- 4. Renewable EnergyDocument53 pages4. Renewable Energyhamza jelaniNo ratings yet
- TIDESDocument2 pagesTIDESjajokox546No ratings yet
- Week 11 TidesDocument36 pagesWeek 11 Tidesczedric25No ratings yet
- TidesDocument3 pagesTidesKeynie Densing VasayNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Describe The Basic Theory of TidesDocument16 pages5.1 Describe The Basic Theory of TidesAley Nabi RizviNo ratings yet
- 5 TidesDocument5 pages5 TidesJonas CabacunganNo ratings yet
- TidesDocument67 pagesTidesmonsur ahmedNo ratings yet
- Basics of TidesDocument11 pagesBasics of TidesHarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Navigation NAU 102 Lesson 25Document37 pagesNavigation NAU 102 Lesson 25Daniel EnglandNo ratings yet
- Oceanography Slides SHB Chapter8Document21 pagesOceanography Slides SHB Chapter8Kogulan MuruganNo ratings yet
- Water Waves GLDocument4 pagesWater Waves GLnaturevideovlogNo ratings yet
- 001 CombineDocument23 pages001 CombineMahmoud Magdy RizkNo ratings yet
- Eas/Bioee 154 Introduction To Oceanography: TidesDocument3 pagesEas/Bioee 154 Introduction To Oceanography: TidesagungpriyantoNo ratings yet
- Physics WrittenDocument18 pagesPhysics WrittenMikey IrwinNo ratings yet
- Tide ObservationsDocument39 pagesTide ObservationsJeffpedidaNo ratings yet
- Ovements OF Cean AterDocument6 pagesOvements OF Cean AterAjit BandgarNo ratings yet
- Port Engineering-04Document27 pagesPort Engineering-04Rhezader AgNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q1 Melc 17Document14 pagesEarth and Life Science Q1 Melc 17candidocorpuz05No ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument21 pagesOceanographyOmar MianNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Currents, Waves & Tides - EHowDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Currents, Waves & Tides - EHowicemage1991No ratings yet
- Tides DocumentDocument5 pagesTides DocumentOlivia JamesNo ratings yet
- Tides-2015 LectureDocument17 pagesTides-2015 Lectureapi-169639475No ratings yet
- Harbour Engineering PPT Part 2.1Document101 pagesHarbour Engineering PPT Part 2.1Shreya SinhaNo ratings yet
- HW09, OceansDocument2 pagesHW09, Oceansjohnny_kim_10No ratings yet
- Tides in Astronomy RevisedDocument8 pagesTides in Astronomy RevisedaimeexianeramosaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.1 Waves-OceanographyDocument10 pagesLesson 4.1 Waves-OceanographyMary Jean AmparoNo ratings yet
- COASTSDocument45 pagesCOASTSshwethaaaNo ratings yet
- 22 Coastal ZonesDocument15 pages22 Coastal ZonesLuisa LouisaNo ratings yet
- 2014 Exam #3 Study GuideDocument7 pages2014 Exam #3 Study Guidehairey947594No ratings yet
- Tides Lecture 2 26092023 013020amDocument9 pagesTides Lecture 2 26092023 013020amس ہ ی لNo ratings yet
- TIDES Handout 2022 (Final) PDFDocument6 pagesTIDES Handout 2022 (Final) PDFArsh100% (1)
- Waves Move Through Oceans.: How Does Wave Motion Change With Depth?Document5 pagesWaves Move Through Oceans.: How Does Wave Motion Change With Depth?yanickdouce5408No ratings yet
- Group 5 TidesDocument23 pagesGroup 5 TidesJayson ReyNo ratings yet
- Tides and Currents: Week 1 & 2Document40 pagesTides and Currents: Week 1 & 2Seth MurilloNo ratings yet
- Moon and TidesDocument5 pagesMoon and Tidesvr_talleiNo ratings yet
- Tidal EnergyDocument122 pagesTidal EnergySandeep Badarla50% (2)
- Tides and Lunar PhasesDocument16 pagesTides and Lunar Phasesapi-291717107No ratings yet
- I. Introduction To Wave Energy and Motion: Chapter 4 Outline - Waves and TidesDocument4 pagesI. Introduction To Wave Energy and Motion: Chapter 4 Outline - Waves and TidesRyan SolomonNo ratings yet
- Ocean Tides and Tsunamis - Nature Book for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandOcean Tides and Tsunamis - Nature Book for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy WebquestDocument4 pagesRenewable Energy Webquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Severe Weather WebquestDocument5 pagesSevere Weather Webquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Climate Notes Glencoe 14 1 14 2Document3 pagesClimate Notes Glencoe 14 1 14 2api-264090085No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDocument2 pagesAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Lorax Truax QuestionsDocument2 pagesLorax Truax Questionsapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Tsunami WebquestDocument3 pagesTsunami Webquestapi-264090085No ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 2Document3 pagesRocks and Minerals Webquest 2api-264090085No ratings yet
- Module 3 and 4Document9 pagesModule 3 and 4michael sto domingoNo ratings yet
- Air Force Education Center by SlidesgoDocument48 pagesAir Force Education Center by SlidesgoIqsaNo ratings yet
- Angler PDFDocument6 pagesAngler PDFabdelaziz hmidatNo ratings yet
- Group 4-GM-The Casting of Dove Soap in Ugly WudiDocument55 pagesGroup 4-GM-The Casting of Dove Soap in Ugly WudiLutfi HergitasariNo ratings yet
- 11.8 Journey Into Space Year 5Document28 pages11.8 Journey Into Space Year 5falmubarak RnoNo ratings yet
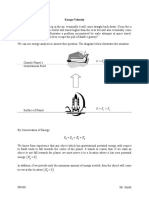
- Escape Velocity PDFDocument5 pagesEscape Velocity PDFRatriNo ratings yet
- Earths Interior WebquestDocument5 pagesEarths Interior Webquestapi-263644974No ratings yet
- Modul Set ADocument9 pagesModul Set AZuraihan Yusof75% (16)
- Basic Chemistry For Pre KDocument63 pagesBasic Chemistry For Pre Kwahyu2azhar20030501No ratings yet
- Navgraha SlokamDocument2 pagesNavgraha Slokammythili.rNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Universe Term PaperDocument24 pagesUnderstanding The Universe Term PaperChooniTayNo ratings yet
- Space - Planet Fact CardsDocument4 pagesSpace - Planet Fact CardsJames KeruNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth in The Solar SystemjfgsdhfshNo ratings yet
- UPSC Essentials by The Indian Express UPSC Essentials Vol IDocument80 pagesUPSC Essentials by The Indian Express UPSC Essentials Vol IAnonymous PoUQsfecsUNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere - TestDocument5 pagesAtmosphere - Testmerdicamae29No ratings yet
- Taxi Infographics by SlidesgoDocument35 pagesTaxi Infographics by SlidesgoLuc AgboblakaNo ratings yet
- Naming: Asteroids AreDocument22 pagesNaming: Asteroids AreBen NuariNo ratings yet
- Case of AmputationDocument8 pagesCase of Amputationsaptarishis astrologyNo ratings yet
- Is Mercury A:: Natural Benefic or Natural Malefic?Document1 pageIs Mercury A:: Natural Benefic or Natural Malefic?STELLA MALLIOTAKINo ratings yet
- International Civil Aviation Day by SlidesgoDocument57 pagesInternational Civil Aviation Day by Slidesgomakichu12No ratings yet
- World Autism Awareness Day by SlidesgoDocument63 pagesWorld Autism Awareness Day by Slidesgoغغ خخNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument13 pagesEarthAmani A. YusefNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerMARILYN ANTONIO ONGKIKONo ratings yet
- Gravitational Force WorksheetDocument4 pagesGravitational Force WorksheetAnjela AprilNo ratings yet
- Crne RupeDocument16 pagesCrne RupeMei Đulabić ChalfeNo ratings yet
- Notes The Living World L1 2023Document3 pagesNotes The Living World L1 2023nandukr.8083No ratings yet
- Division 4 and 5 Fire CodeDocument43 pagesDivision 4 and 5 Fire CodePauline Alexandrei VuelbanNo ratings yet