0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 viewsInternal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber
Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber
Uploaded by
PejuangHatiA gas turbine is an internal combustion engine that uses air instead of water like a steam power plant. It has a rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine with a combustion chamber in between. The air is compressed in the compressor, fuel is added and ignited in the combustion chamber to generate high-temperature gas, which expands through the turbine to power the compressor and devices like an electric generator connected to the shaft. Depending on its purpose, a gas turbine is designed to maximize either the temperature or velocity of the exhaust gases. Gas turbines are commonly used to power aircraft, trains, ships, generators, and even tanks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber
Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber
Uploaded by
PejuangHati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views1 pageA gas turbine is an internal combustion engine that uses air instead of water like a steam power plant. It has a rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine with a combustion chamber in between. The air is compressed in the compressor, fuel is added and ignited in the combustion chamber to generate high-temperature gas, which expands through the turbine to power the compressor and devices like an electric generator connected to the shaft. Depending on its purpose, a gas turbine is designed to maximize either the temperature or velocity of the exhaust gases. Gas turbines are commonly used to power aircraft, trains, ships, generators, and even tanks.
Original Description:
a
Original Title
Gas Turbine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
A gas turbine is an internal combustion engine that uses air instead of water like a steam power plant. It has a rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine with a combustion chamber in between. The air is compressed in the compressor, fuel is added and ignited in the combustion chamber to generate high-temperature gas, which expands through the turbine to power the compressor and devices like an electric generator connected to the shaft. Depending on its purpose, a gas turbine is designed to maximize either the temperature or velocity of the exhaust gases. Gas turbines are commonly used to power aircraft, trains, ships, generators, and even tanks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views1 pageInternal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber
Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber
Uploaded by
PejuangHatiA gas turbine is an internal combustion engine that uses air instead of water like a steam power plant. It has a rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine with a combustion chamber in between. The air is compressed in the compressor, fuel is added and ignited in the combustion chamber to generate high-temperature gas, which expands through the turbine to power the compressor and devices like an electric generator connected to the shaft. Depending on its purpose, a gas turbine is designed to maximize either the temperature or velocity of the exhaust gases. Gas turbines are commonly used to power aircraft, trains, ships, generators, and even tanks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
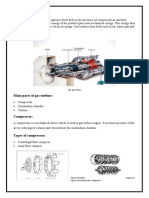
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine,
is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an
upstream rotatingcompressor coupled to a
downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in
between.
The basic operation of the gas turbine is similar to
that of the steam power plant except that air is
used instead of water. Fresh atmospheric air flows
through a compressor that brings it to higher
pressure. Energy is then added by spraying fuel
into the air and igniting it so the combustion
generates a high-temperature flow. This hightemperature high-pressure gas enters a turbine,
where it expands down to the exhaust pressure,
producing a shaft work output in the process.
The turbine shaft work is used to drive the
compressor and other devices such as an electric
generator that may be coupled to the shaft. The
energy that is not used for shaft work comes out in
the exhaust gases, so these have either a high
temperature or a high velocity. The purpose of the
gas turbine determines the design so that the most
desirable energy form is maximized. Gas turbines
are used to power aircraft, trains, ships, electrical
generators, or even tanks.[1]
You might also like
- EEC 122 CompleteDocument34 pagesEEC 122 CompleteAdeniji OlusegunNo ratings yet
- Report Roller ChainDocument11 pagesReport Roller ChainPejuangHati100% (1)
- Gas Turbine: Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber Steam Power Plant Compressor EnergyDocument6 pagesGas Turbine: Internal Combustion Engine Compressor Turbine Combustion Chamber Steam Power Plant Compressor EnergyNicko Jay BajaoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. Objectivefarah nazNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment No.5 To Study The Simple Gas Turbine Engine. Objectivefarah nazNo ratings yet
- Simple Gase Turbine and Diesel Power PlantDocument9 pagesSimple Gase Turbine and Diesel Power Plantdaniel298957No ratings yet
- Automotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Document48 pagesAutomotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Santanu ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Prime Mover Refers To A Machine or Device That ConvertsDocument8 pagesPrime Mover Refers To A Machine or Device That ConvertsАбдельнасир АбдельрахманNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine: Principles of OperationDocument1 pageJet Engine: Principles of Operationa.wNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Powerplant: Turbine EngineDocument18 pagesAircraft Powerplant: Turbine Enginejohn collinsNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Gas Turbine ConstructionDocument4 pagesFigure 1: Gas Turbine ConstructionSyed Anas Sohail100% (2)
- Chapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument21 pagesChapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantBiniam Nega100% (1)
- Working Principle Gas Turbine and Combined Cycles, Auxiliary SystemsDocument27 pagesWorking Principle Gas Turbine and Combined Cycles, Auxiliary SystemsRey Danielle Navea100% (3)
- Gas Turbine Working and TypesDocument4 pagesGas Turbine Working and TypesGopi Kiran NaikNo ratings yet
- Eoa Module 3Document34 pagesEoa Module 3Music vinesNo ratings yet
- A Gas Turbine UnitDocument9 pagesA Gas Turbine UnitTITU NATHNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure - The Pressure of A Fluid On A Body When The Body Is at Rest Relative To The FluidDocument4 pagesStatic Pressure - The Pressure of A Fluid On A Body When The Body Is at Rest Relative To The FluidJhiGz Llausas de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- How A Jet Engine WorksDocument7 pagesHow A Jet Engine WorksJesús Juan Ignacio BornicesNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine Types, Functions and ConstructionDocument10 pagesJet Engine Types, Functions and ConstructionTushar ShingadeNo ratings yet
- Bhel TrainingDocument41 pagesBhel TrainingArun AroraNo ratings yet
- 2019-Me-111 (Jet Engine)Document9 pages2019-Me-111 (Jet Engine)touqeerahmad 9058No ratings yet
- Introduction To TurbineDocument24 pagesIntroduction To TurbineEngr Mujahid MehdiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument16 pagesUntitledMuhammad AbidNo ratings yet
- Turbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItDocument10 pagesTurbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument13 pagesGas TurbineCleng LaynesNo ratings yet
- Turbojet EngineDocument14 pagesTurbojet EngineYaswanth saiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Jet and Fan Engine Operation - 20141012 - SDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Jet and Fan Engine Operation - 20141012 - SGurunath AeroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas Turbine:: Land Based Gas Turbines Are of Two TypesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Gas Turbine:: Land Based Gas Turbines Are of Two TypesTahir MuneebNo ratings yet
- Jet PropulsionDocument45 pagesJet PropulsionPranay SahuNo ratings yet
- Small Gas Turbines by Ian F BennettDocument78 pagesSmall Gas Turbines by Ian F Bennettbmc.summer.2023No ratings yet
- Engr. Gerald S.: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument9 pagesEngr. Gerald S.: Submitted To: Submitted byReonArandaSanPedro100% (1)
- BCMEDocument9 pagesBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyNo ratings yet
- TurbojetDocument2 pagesTurbojetJose Luis MNo ratings yet
- Basic's of Aircraft EnginesDocument5 pagesBasic's of Aircraft Enginesvenu991No ratings yet
- TurbineDocument1 pageTurbineIonuț Laurențiu StănescuNo ratings yet
- 1 DirtyDozenWeb TraducidoDocument77 pages1 DirtyDozenWeb TraducidoKevin Arteaga100% (1)
- Turbo MachineryDocument16 pagesTurbo MachineryAhmed Abu ZnaitNo ratings yet
- Lab 404Document10 pagesLab 404Wasee AbNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant 1Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant 1ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Assignment On Aircraft EnginesDocument14 pagesAssignment On Aircraft EnginesSimran TyagiNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument14 pagesGas TurbineLarry SmithNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Gas Turbine EngineDocument16 pagesAircraft Gas Turbine EngineAnupNo ratings yet
- DokumenDocument1 pageDokumenNufusNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument6 pagesGas Turbineusama shehrozNo ratings yet
- Collected SampleDocument4 pagesCollected SampleNaftali OmuhandeNo ratings yet
- Jet EngineDocument19 pagesJet EngineSamarth SNo ratings yet
- Jet EnginesDocument11 pagesJet EnginesKrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument23 pagesChapter Five Gas Turbine Power PlantBese Mat100% (2)
- How Gas Turbine Power Plants WorkDocument6 pagesHow Gas Turbine Power Plants Workchella2705100% (2)
- Jet Engines - Introduction To TurbojetsDocument4 pagesJet Engines - Introduction To TurbojetsWaqasNo ratings yet
- Jet PropulsionDocument20 pagesJet Propulsionruthvik mocharlaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory EquipmentDocument9 pagesLaboratory EquipmentFaiq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Jet EngineDocument2 pagesJet EnginebackupdatadevNo ratings yet
- Powerplant2 PPT 9 (Operating Principles)Document28 pagesPowerplant2 PPT 9 (Operating Principles)Zion CabilanganNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering: Seminar Presentation ONDocument18 pagesMechanical Engineering: Seminar Presentation ONPankaj RathoreNo ratings yet
- تقرير (Recovered)Document13 pagesتقرير (Recovered)همسة كاملNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument3 pagesTheoryimmacoolcatNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportPejuangHatiNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Harris Ashraf Bin Hassan: Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesMuhammad Harris Ashraf Bin Hassan: Career ObjectivePejuangHatiNo ratings yet
- 2 Stage Gas Turbine Cycle With Reheat: Turbines Vapor BoilerDocument1 page2 Stage Gas Turbine Cycle With Reheat: Turbines Vapor BoilerPejuangHatiNo ratings yet
- Report Jf303 Tunstern Inert Gas (Tig)Document12 pagesReport Jf303 Tunstern Inert Gas (Tig)aizatulasmira60% (5)
- Notch Weir (V-Norch)Document6 pagesNotch Weir (V-Norch)PejuangHatiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 (Case Study 3 Report)Document11 pagesThermodynamics 1 (Case Study 3 Report)PejuangHatiNo ratings yet
- Manual de CNC TornoDocument147 pagesManual de CNC TornoAbraham Pool100% (1)
- MechschDocument11 pagesMechschvasavik.eeeNo ratings yet
- Phys 3105Document9 pagesPhys 3105myo htetNo ratings yet
- Blasting ParametersDocument1 pageBlasting ParametersZola1stNo ratings yet
- History SBADocument10 pagesHistory SBAShakima Brittany Perez0% (1)
- COMMUNIQUÉ of The 19th AMECEA Plenary Assembly Held in in Addis AbabaDocument10 pagesCOMMUNIQUÉ of The 19th AMECEA Plenary Assembly Held in in Addis AbabajadwongscribdNo ratings yet
- The Initial Stall in Span Wise DirectionDocument8 pagesThe Initial Stall in Span Wise DirectionpareshnathNo ratings yet
- Hotel Business Plan SampleDocument26 pagesHotel Business Plan SamplePAOLA CASTRONo ratings yet
- SCR - 5 - Cleaning and Shaping of Root Canal System.Document12 pagesSCR - 5 - Cleaning and Shaping of Root Canal System.براءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- HP CP6015, CM6040, CM6030 PQ Defect Guide, v1.0Document40 pagesHP CP6015, CM6040, CM6030 PQ Defect Guide, v1.0Kārlis Spreslis0% (1)
- Introduction To Communication SkillsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Communication SkillsNeo AndersonNo ratings yet
- BNP Paribas Uk-Student-Housing-Market-Update - Compressed-1Document2 pagesBNP Paribas Uk-Student-Housing-Market-Update - Compressed-1hamza3iqbalNo ratings yet
- Physics Intro & KinematicsDocument7 pagesPhysics Intro & KinematicsEnger AlingasaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Dromedarian CamelDocument127 pagesAnatomy of The Dromedarian CamelAnanda afu BwNo ratings yet
- PESSIMISM - TO - OPTIMISM - REHEARSAL - WORKSHEET (Fillable)Document2 pagesPESSIMISM - TO - OPTIMISM - REHEARSAL - WORKSHEET (Fillable)Harry AyangcoNo ratings yet
- Reliance Jaiprakash Hydro Propsosed Acquisition AnalysisDocument4 pagesReliance Jaiprakash Hydro Propsosed Acquisition AnalysisAbhilash ShahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument73 pagesCardiovascular DiseaseAli SherNo ratings yet
- TSL 570 Adaptation Project - Arachne: The First SpiderDocument21 pagesTSL 570 Adaptation Project - Arachne: The First SpidernajihahyusofNo ratings yet
- Csat-4 QPDocument13 pagesCsat-4 QPsrinivas bhukyaNo ratings yet
- HIPAADocument3 pagesHIPAAGrace CotesNo ratings yet
- Vital Statistics of The United States 1961 - Vol. 1 - Natality - PG 231 - Race and ColorDocument246 pagesVital Statistics of The United States 1961 - Vol. 1 - Natality - PG 231 - Race and ColorObamaRelease YourRecordsNo ratings yet
- Transforming Healthcare: Integrating Large-Scale Language Modelling in To Chatbot Systems For Instant Medical InformationDocument9 pagesTransforming Healthcare: Integrating Large-Scale Language Modelling in To Chatbot Systems For Instant Medical InformationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- ME Soft ComputingDocument6 pagesME Soft Computingmarshel007No ratings yet
- 1 Listening Test 1Document6 pages1 Listening Test 1Anabel GonzalezNo ratings yet
- BURNS AND SCALD - Doctor SahibDocument36 pagesBURNS AND SCALD - Doctor SahibkhojalkhelNo ratings yet
- Biology 2201 - Respiratory System Notes PDFDocument11 pagesBiology 2201 - Respiratory System Notes PDFVishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Fce Writing 4schoolsDocument26 pagesEbook Fce Writing 4schoolsmorag robertsNo ratings yet
- Umg 604 Janitza PDFDocument80 pagesUmg 604 Janitza PDFdelboteNo ratings yet
- Team Building For Youth Organization: CWTS - Civic Welfare Training Service Units: 3.0Document4 pagesTeam Building For Youth Organization: CWTS - Civic Welfare Training Service Units: 3.0Jon Aragasi100% (1)
- English Paper I - Trial '10Document4 pagesEnglish Paper I - Trial '10Roshan P NairNo ratings yet