6w Concept Map
6w Concept Map
Uploaded by
api-314635911Copyright:
Available Formats
6w Concept Map
6w Concept Map
Uploaded by
api-314635911Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
6w Concept Map
6w Concept Map
Uploaded by
api-314635911Copyright:
Available Formats
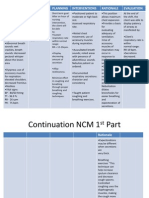
Nursing
Diagnosis
I
Ineffective
airway
clearance
r/t
bronchial
inflammation
AEB
abnormal
breath
sounds
and
changes
in
respiration
rate
and
depth.
Outcome:
PS
will
maintain
patent
airway
with
breath
sounds
clear
or
clearing
and
decreased
work
of
breath
by
end
of
shift
on
9/23
Evaluation:
Goal
met.
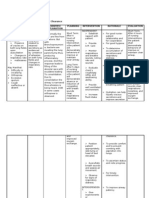
Nursing
Diagnosis
II
Activity
intolerance
r/t
imbalance
between
activity
supply
and
demand
AEB
reports
of
fatigue
and
exertional
dyspnea.
Outcome:
PS
will
report/demonstrate
an
increase
in
tolerance
to
activity
with
decreased
dyspnea
and
vital
signs
within
normal
range
by
end
of
shift
on
9/23
Evaluation:
Goal
not
met.
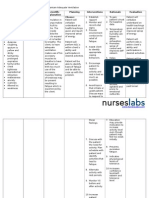
Nursing Diagnosis III
Deficient knowledge r/t condition,
treatment, and discharge needs AEB
requests for information and
recurrence of disease.
Outcome:
PS will verbalize disease process
(using pediatric terminology) and
discharge goals, and participate in
treatment plan by end of shift
on 9/23
Evaluation: Goal partially met.
ND
I
Interventions
1.
Auscultate
lung
fields/breath
sounds.
Determines
the
presence
of
abnormal
breath
sounds
(crackles,
wheezing).
Fine
crackles
at
bases
may
clear
with
deep
breathing,
wheezing
is
a
sign
of
airway
obstruction,
and
requires
intervention.
2.
Assess
the
rate
and
depth
of
respirations.
Tachypnea,
shallow
respirations,
and
asymmetric
chest
movement
are
frequently
present
because
of
discomfort
of
moving
chest
wall
and/or
fluid
in
lung.
3.
Teach
patient
to
perform
deep
breathing
with
coughing
exercises
q1
(at
least
q2).
Deep
breathing
promotes
maximum
expansions
of
the
lungs
and
smaller
airways.
Coughing
exercises
help
clear
airways
of
secretions.
Objective
Data
-lungs
sounds
diminished
in
bases;
expiratory
wheezing
-RR
42,
HR
137;
abdominal
breathing
-non-productive
cough
with
deep
breathing
when
using
incentive
spirometer
-CXR:
white
areas
in
bases
Objective
Data
-increased
WOB
&
RR
when
ambulating
-O2
saturations
90%
after
ambulating
to
bathroom.
-PS
reported
feeling
tired
after
ambulating
ND
II
Interventions
1.
Determine
PSs
response
to
activity.
Note
reports
of
dyspnea,
increased
weakness
and
fatigue,
and
changes
in
vitals
during
and
after
activities.
Established
patients
capabilities
and
needs
and
facilitates
choice
of
interventions.
2.
Explain
importance
of
rest
in
treatment
plan
and
necessity
for
balancing
activities
with
rest.
Bedrest
is
maintained
during
acute
phase
to
decrease
metabolic
demands,
thus
conserving
energy
for
healing.
3.
Assist
with
self-care
activities
as
necessary.
Minimizes
exhaustion
and
helps
balance
oxygen
supply
and
demand.
Objective
Data
-PS
asking
when
he
will
be
able
to
go
back
to
school.
-PS
and
Mom
asking
what
medication
will
he
need
to
take
at
home.
Subjective
Data
-Dad
stated
he
was
having
a
hard
time
breathing
after
soccer
-Dad
stated
I
could
see
him
breathing
from
his
stomach
Pneumonia
Weight
Data
33.1kg
ND
III
Interventions
1.
Discuss
aspects
of
disease
and
recovery
expectations.
Identify
self-care
needs.
Information
can
enhance
coping
and
help
reduce
anxiety/excessive
concern.
Respiratory
symptoms
may
be
slow
to
resolve,
and
fatigue
and
weakness
may
persist
for
an
extended
period.
2.
Reinforce
importance
of
continu8e
deep
breathing
and
coughing
exercises.
During
initial
6-8wk
of
discharge
patient
is
at
greatest
risk
for
recurrence.
3.
Emphasize
necessity
for
continuing
antibiotic
therapy
for
prescribed
period.
Early
discontinuation
may
result
in
recurrence.
Medications
-
ampicillin
(Omnipen)
1700mg
IV,
q6;
T.R.
1241.3-1655mg
IV,
q6
-prednisolone
(Orapred)
20
mg
PO
solution
BID;
T.R.
1.66-33.1mg
BID
-albuterol
(Proventil)
5mg
nebulizer,
q2h;
T.R.
4.97mg,
every
1-4h
Concept Map Key
Developmental
Data
Erikson
Industry
vs.
Inferiority
In
this
developmental
stage,
PS
is
concerned
with
school
and
social
interactions.
Through
these
interactions
children
begin
to
develop
a
sense
of
pride
and
accomplishment.
PS
strives
to
master
new
tasks
as
seen
when
he
was
taught
to
use
an
incentive
spirometer.
PS
sought
praise
when
he
was
using
the
IS.
Children
who
are
praised
and
encouraged
by
their
parents
and
teachers
develop
a
sense
of
accomplishment.
Care
Concept
Nursing
Diagnosis/
Outcomes
Interventions
Evaluation
Assessment
Data
Developmental
Data
Weight
Data
Sarah
Brockman
NUR
4115P
6W
Concept
Map
You might also like
- ANSWER KEY-RESPIRATORY Assessment and ReasoningDocument9 pagesANSWER KEY-RESPIRATORY Assessment and ReasoningMaryAnn Tiburcio Cuevas100% (1)
- Case Study (Asthma)Document3 pagesCase Study (Asthma)AIM50% (4)
- 2020 Midyear Little Jellycat CatalogDocument88 pages2020 Midyear Little Jellycat CatalogJayNo ratings yet
- Session 5Document3 pagesSession 5Sistine Rose Labajo100% (3)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- Concept Map Finished 2Document6 pagesConcept Map Finished 2api-352785497100% (1)
- JCB - 3dx Kirloskar EngineDocument1 pageJCB - 3dx Kirloskar EngineDhru TiNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Asthma)Document3 pagesCase Study (Asthma)AIM100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- Unit 14Document21 pagesUnit 14jcrd7vdmksNo ratings yet
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- School of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: Holy Angel UniversityDocument19 pagesSchool of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: Holy Angel UniversityMonica BorjaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma NCPDocument6 pagesBronchial Asthma NCPRacelle DelesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKoleen KirstenNo ratings yet
- Nursing 1Document3 pagesNursing 1israjaved19No ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument3 pagesNCP ErPensayo, Stephanie Keith V.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument22 pagesNursing Care Planaln00550% (2)
- Efficacy of Pursed-Lips Breathing: A Breathing Pattern Retraining Strategy For Dyspnea ReductionDocument8 pagesEfficacy of Pursed-Lips Breathing: A Breathing Pattern Retraining Strategy For Dyspnea ReductionGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Study Based On Actual PatientDocument6 pagesSample Case Study Based On Actual PatientRamalingam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- NCP SDocument8 pagesNCP SMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 26Document9 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems 9e Chapter 26sarasjunkNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Comprehensive ExaminationDocument8 pagesComprehensive ExaminationAnonymous dquW2YmO7No ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- TriageDocument20 pagesTriage39 femina pcNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0885392419300429 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0885392419300429 MainEndhy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Ncp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONDocument4 pagesNcp's FOR PLEURAL EFFUSIONHania Polangi100% (1)
- Triage 2Document21 pagesTriage 239 femina pcNo ratings yet
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 pagesNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- DX Asthma PDFDocument6 pagesDX Asthma PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 031.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter - 031.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersJackie JuddNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Master Shyne With AllDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan For Master Shyne With AllsreekalaNo ratings yet
- Chap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsDocument13 pagesChap 26 To 38 Case Study Answers To QuestionsElaine Jean UayanNo ratings yet
- A Study of Efficiency of Breathing Exercises To Improve Pulmonary FX in SCi PtsDocument6 pagesA Study of Efficiency of Breathing Exercises To Improve Pulmonary FX in SCi PtsMarion AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 01 Pediatric Clinics - February2009Document291 pages01 Pediatric Clinics - February2009Tessa CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug StudyDocument11 pagesNCP and Drug StudyTonio PagaoNo ratings yet
- AssesmentDocument9 pagesAssesmentmizrypNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlansClaire Alcantara50% (2)
- Assessing Respiration: Fundamentals of Nursing Practice, RleDocument2 pagesAssessing Respiration: Fundamentals of Nursing Practice, RleMONIQUE GONZALES0% (1)
- Nursing Careplan #1Document15 pagesNursing Careplan #1aninNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Plan of Care 1Document7 pagesRunning Head: Plan of Care 1api-348816412No ratings yet
- Ahmed Copd Case StudyDocument6 pagesAhmed Copd Case StudyAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- PTB NCPDocument12 pagesPTB NCPNiel LeeNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument5 pagesConcept Mapapi-662323379No ratings yet
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPBeverLyNo ratings yet
- Asthma FatigueDocument2 pagesAsthma FatigueSuriani Abd RahimNo ratings yet
- Programme: High Diploma in NursingDocument7 pagesProgramme: High Diploma in NursingYeesze ChanNo ratings yet
- Postural DrainageDocument6 pagesPostural DrainageKit Alizon Barredo0% (1)
- NCPDocument17 pagesNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Chest Physical TherapyDocument25 pagesChest Physical TherapySeptyAuliaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pendukung GADARDocument8 pagesJurnal Pendukung GADARdavaNo ratings yet
- ASKEP OKSIGENASiDocument11 pagesASKEP OKSIGENASiAgus Indra 2109No ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- Myrna CruzDocument3 pagesMyrna CruzChris Opal NamocatcatNo ratings yet
- Emphysema Case Study AnalysisDocument10 pagesEmphysema Case Study AnalysisEfren VisteNo ratings yet
- PARKINSON's DISEASE Nursing ManagementDocument67 pagesPARKINSON's DISEASE Nursing ManagementDr.Alan John N.ChandarNo ratings yet
- NUR240 Nursing Care Plan Forms: Suffolk County Community CollegeDocument10 pagesNUR240 Nursing Care Plan Forms: Suffolk County Community CollegeJennifer AltenburgNo ratings yet
- MedicationDocument11 pagesMedicationShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- Almaarefa College Adult Nursing Care Practice II Weekly Report Name of Student: Najwa Thawab - Day/DateDocument2 pagesAlmaarefa College Adult Nursing Care Practice II Weekly Report Name of Student: Najwa Thawab - Day/DateNajwa1991No ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Assessment: Respiratory System Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionDocument9 pagesChapter 25: Assessment: Respiratory System Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionKrishna RamaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care for Healthcare ProvidersFrom EverandNeonatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care for Healthcare ProvidersNo ratings yet
- The Astronomy of Chitzen-ItzaDocument20 pagesThe Astronomy of Chitzen-Itzaamarch619No ratings yet
- Unit-5: The Link Layer and Local Area NetworksDocument38 pagesUnit-5: The Link Layer and Local Area NetworksJinkal DarjiNo ratings yet
- Toyota Powered Stacker Trucks: The BT Staxio RangeDocument16 pagesToyota Powered Stacker Trucks: The BT Staxio RangeFrancisco MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Piping & Instrumentation DiagramDocument20 pagesPiping & Instrumentation DiagramOladayo Siyanbola100% (2)
- Operation Arctic FoxDocument4 pagesOperation Arctic FoxAndrea MatteuzziNo ratings yet
- CH-7 InsulatorDocument13 pagesCH-7 InsulatorMerera TaresaNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry Research Program: Melkassa Agricultural Research CenterDocument6 pagesFood Chemistry Research Program: Melkassa Agricultural Research CenterasresNo ratings yet
- PresentationsmjjDocument18 pagesPresentationsmjjgaju619No ratings yet
- Exercises Present SimpleDocument3 pagesExercises Present SimpleВика ЕвтушенкоNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Sprayer Machine: Major Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfilment For The Award ofDocument24 pagesBicycle Sprayer Machine: Major Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfilment For The Award ofashi ashiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Crop Water RequirementDocument75 pagesUnit 1 Crop Water RequirementvizhideepaNo ratings yet
- PHYS131 Fall 2019 JamalDocument3 pagesPHYS131 Fall 2019 JamalMujahed BrijieahNo ratings yet
- Lab Session 03 UptadeDocument7 pagesLab Session 03 UptadeAbdullah SahirNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7-10SnowLoadProvisionsJuly2012Document49 pagesASCE 7-10SnowLoadProvisionsJuly2012Mike Junior0% (1)
- X Science SQP 2018-19Document6 pagesX Science SQP 2018-19muthu100% (1)
- Beneview T8: Consecutivos: 12, 15, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111 Y 112Document192 pagesBeneview T8: Consecutivos: 12, 15, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111 Y 112Ventas IPSUM Soluciones HospitalariasNo ratings yet
- Case Study MCDDocument16 pagesCase Study MCDJohn kananamanNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu ASYB18LDC - AOYS18LDCDocument19 pagesFujitsu ASYB18LDC - AOYS18LDCPablos Augoustis100% (1)
- Fuel Briquetting (Based On Agri. Waste & Municipal Solid Waste)Document12 pagesFuel Briquetting (Based On Agri. Waste & Municipal Solid Waste)Sabhaya ChiragNo ratings yet
- Fpb1a3030s13w CCT Led Panels ManualDocument16 pagesFpb1a3030s13w CCT Led Panels Manualnosas4gNo ratings yet
- Midshire Business Systems - Riso RZ1070 BrochureDocument12 pagesMidshire Business Systems - Riso RZ1070 BrochureadietoppingNo ratings yet
- Determination of Heat of Combustion of Biodiesel Using Bomb CalorimeterDocument3 pagesDetermination of Heat of Combustion of Biodiesel Using Bomb CalorimeterIsmail RahimNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Motores de ArranqueDocument19 pagesEspecificaciones Motores de ArranqueVictor LuqueNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis GuideDocument19 pagesSWOT Analysis GuideNelle DelanteNo ratings yet
- Merowe DamDocument38 pagesMerowe DamAmgad_S100% (1)
- Fanfic StuffborigDocument42 pagesFanfic StuffborigtresesantaNo ratings yet
- Sample Radiobroadcasting ScriptDocument3 pagesSample Radiobroadcasting ScriptMervin BauyaNo ratings yet
- Naca Duct RMDocument47 pagesNaca Duct RMGaurav GuptaNo ratings yet