Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems
Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems
Uploaded by
Ebony GoodCopyright:
Available Formats
Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems
Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems
Uploaded by
Ebony GoodCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems
Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems
Uploaded by
Ebony GoodCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Name: Ebony Goodridge Due Date: 18/11/2010
Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities
Blog resource: http://tinyurl.com/249fd5a
Cite all sources using the CSE method (or ISO 690 Numerical in Word). The first example has been done for you.
Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid printing this if possible.
1. Define the following terms:
Species: A group of organisms that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring. [ CITATION
Ste09 \l 1033 ]
Habitat: The habitat in which a species usually lives in
Population: A group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time.
Community: A group of populations living and interacting with each other.
Ecosystem: A community and its a biotic (non-living) environment.
Ecology: the study of relationships between living organisms and between organisms and their
environment.
Niche: the relational position of a species or population in its ecosystem to each other.
Biodiversity: the diversity of plant and animal life in a particular habitat.
Trophic level: the position an organism occupies on the food chain.
2. Complete the tree below with definitions and examples of each type of feeding strategy.
Distinguish between the feeding strategies at each level of the diagram.(Answers at bottom)
Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Student Name: Ebony Goodridge Due Date: 18/11/2010
Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities
ANSWER TO 2.
Autotrophy: self feeding, organisms which produce their own food from organic molecules.
Heterotrophy: other source feeding, organisms which derive energy from other living
organisms.
Producers: a) Photo autotrophy: photosynthesis (gets energy from the sun), green plants,
phytoplankton, and algae.
b) Chemo autotrophy: chemosynthesis( collect energy from certain chemicals),
deep see chemosynthetic bacteria.
Consumers: ingest organic matter which is living or recently killed.
a) Primary consumers eat producers (herbivores)
b) Secondary consumers eat other consumers (carnivores, omnivores)
Decomposers: derive energy from non-living organic matter. (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen make
up organic matter.)
a) Detrivores ingest non-living organic matter (earthworms, woodlice)
b) Saprotrophs live in or on non-living organic matter, secreting digestive enzymes
into it and absorbing digestive products (bacteria and fungi)
3. Food chains represent the flow of energy and nutrients in a series of feeding relationships.
Give one example of a marine food chain (min. 4 organisms)
Phytoplankton --> Zooplankton --> Krill --> Whale
Give one example of a terrestrial food chain (min. 4 organisms)
Arctic Willow --> Lemming --> Snowy Owl --> Arctic Wolf
Give one other example of a food chain (min. 4 organisms)
Saw Grass --> Freshwater Fungi --> Crickets --> Toad --> Banded Water Snake
4. Describe what is meant by a food web.
Food webs show all of the feeding relationships within a habitat.
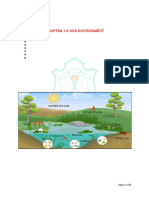
5. The food web below shows some coral reef feeding relationships;
Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Student Name: Ebony Goodridge Due Date: 18/11/2010
Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities
a. Identify species in the following trophic levels:
i. Producers: phytoplankton and algae
ii. Primary consumers: sea whip, parrot fish, turtles, marine invertebrates.
iii. Secondary consumers: reef sharks, snappers, groupers.
6. On a separate sheet, construct a freshwater food web based on the following information:
Organism Energy sources
Water crowfoot Sunlight
Cased caddisfly larva Micro-plants, algae, particles of dead plants and animals
Damselfly nymph Micro-plants, algae, particles of dead plants and animals
Mayfly nymph Micro-plants, algae, particles of dead plants and animals
Dragonfly Other adult insects and small flies
Duck All nymphs, all plants, snails, tadpoles, young frogs
Freshwater Shrimp Particles of dead plants and animals
Water vole Plants
Algae Sunlight
Otter Fish, frogs and newts
Water starwort Sunlight
Pond snail Microplants, all water plants and algae
Alderfly nymph Micro-plants, algae, particles of dead plants and animals
Pond skater Particles of dead plants and animals
Frog Mayfly, midge larvae, pond skater, caddisfly, small flies
Tadpole Micro-plants, algae
Micro-plants Sunlight
Great diving beetle Water flea, snails, tadpole, all nymphs
Bullhead fish Diving beetle, tadpole, all nymphs, water flea, snail, midge larvae
Adapted from: http://www.cornwallriversproject.org.uk/education/education_pack.htm
Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Student Name: Ebony Goodridge Due Date: 18/11/2010
Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities
7. For the food web created above:
a. Identify organisms in each of the trophic levels.
Producers: water crowfoot, micro plants, water starwort, algae.
Primary Consumer: pond snail, tadpole, shrimp, mayfly nymph.
Secondary Consumer: Great diving beetle, dragonfly.
Tertiary Consumer: Otter, Duck, Bullhead Fish.
b. Identify organisms that fit more than one trophic level.
Shrimp and Tadpole.
c. Identify those which could be classed as detritivores
8. Suggest why it is sometimes difficult to classify organisms into trophic levels.
It is sometimes difficult to classify organisms into trophic levels because they sometimes fit
more than one category and therefore you have to decide which trophic level is the best fit.
9. Outline why numbers of organisms are smaller at higher trophic levels.
The numbers of organisms are smaller at higher trophic levels because not many organisms
survive to eat other ones. You have to be at the top of the food chain to be able to survive and
reach higher trophic levels because no other organism can eat you.
10. State the original source of energy for almost all communities.
The original source of energy for almost all communities is the sun.
11. Explain how energy flows through a community, including why energy transfers are never 100%
efficient.
Sunlight is the main source of energy and it starts flowing through the community when the
Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
Student Name: Ebony Goodridge Due Date: 18/11/2010
Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities
producer absorbs the energy and the energy is than passed up along the food chain once the
animal gets eaten. Energy transfers are never 100% efficient because every time the energy
flows through the food chain, energy is being lost at each stage due to respiration and nutrients
being recycled.
12. State the function of a pyramid of energy.
The function of a pyramid of energy is to be a graphic representation of the amount of energy
that is in each different trophic level of the food chain.
13. Give an example of a unit of measurement used in a pyramid of energy, giving a description of
each component.
An example of a unit of measurement used in a pyramid of energy is KJ which stands for kilo
joules.
14. “Energy flows through an ecosystem, nutrients are recycled.”
Explain this statement with the aid of a flow chart. Include the roles of saprotrophic bacteria and fungi
Nutrients are being recycled because they need to conserve the energy that the producer gets from the
sunlight and give it to the other organisms. For example, between the saprotrophic bacteria and fungi;
get their nutrients from dead organic matter, which would than mean that the nutrients are being
recycled.
15. Outline three examples of cycles of inorganic nutrients. For each, outline the uses of the
nutrients in living organisms, its method of transfer into and through the food chain and how it
is returned to the inorganic nutrient pool.
a. Carbon-
b. Nitrogen-
c. Calcium-
Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com
You might also like
- Year 9 Ecology Revision SolutionsDocument10 pagesYear 9 Ecology Revision SolutionsHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- Ecology Notes!!Document10 pagesEcology Notes!!Raudha Athif100% (3)
- Yacomine - Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems - 181110Document5 pagesYacomine - Essential Biology 05.1 Communities and Ecosystems - 181110joeyacomineNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities: Group of Organisms That Can Interbreed To Produce Fertile OffspringDocument5 pagesEssential Biology 5.1: Ecosystems & Communities: Group of Organisms That Can Interbreed To Produce Fertile OffspringChloe Troulan100% (1)
- 5.1 Communities and Ecosystems WORDDocument6 pages5.1 Communities and Ecosystems WORDCaitlin BarrettNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Communities and Ecosystems/ YokDocument10 pages5.1 Communities and Ecosystems/ YokxX69M3XxNo ratings yet
- Grade 10. Food Chain - Food Webs.Document39 pagesGrade 10. Food Chain - Food Webs.fearondejonae5No ratings yet
- Food Web 2019Document32 pagesFood Web 2019Ade GratiaNo ratings yet
- A.A Basic Concepts of EcologyDocument67 pagesA.A Basic Concepts of Ecologyrieann leonNo ratings yet
- Hwa Chong Institution Prepared by Tanky and Nada 2011Document10 pagesHwa Chong Institution Prepared by Tanky and Nada 2011Tonald DrumpNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMSDocument8 pagesECOSYSTEMSammarahn0No ratings yet
- STD 7 chp4 Notes NewDocument4 pagesSTD 7 chp4 Notes Newrahulbd4uNo ratings yet
- Unit # 16 Bio Class 10Document42 pagesUnit # 16 Bio Class 10Muhammad Owais FayazNo ratings yet
- Ecology1 PPTDocument56 pagesEcology1 PPTAiza CahiligNo ratings yet
- ANSWER KEY ASK 8 PacketDocument24 pagesANSWER KEY ASK 8 PacketneeromodeNo ratings yet
- Ecology DiscussionDocument31 pagesEcology DiscussionAl Marjorie Abrasaldo TatingNo ratings yet
- Module 5BDocument18 pagesModule 5BRatay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 10 Lesson Plan Oct 2-14Document5 pagesBiology Grade 10 Lesson Plan Oct 2-14Nicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization With QUIZDocument55 pagesLevels of Organization With QUIZdavid jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document33 pagesChapter 2Mimiento SearNo ratings yet
- Organisms and Their Environment Lecture 1Document46 pagesOrganisms and Their Environment Lecture 1amanirameez84No ratings yet
- PEE M1 and M2Document13 pagesPEE M1 and M2Jhon Marvin Arienza100% (2)
- Study Guide The Diversity and Relationships of LifeDocument6 pagesStudy Guide The Diversity and Relationships of LifemikeschallraNo ratings yet
- Cheaper 12 NotesDocument7 pagesCheaper 12 NotessenthilkumarharishragavNo ratings yet
- 4.1 To 4.4 Ecosystems, Energy & Carbon Cycle (2023)Document147 pages4.1 To 4.4 Ecosystems, Energy & Carbon Cycle (2023)riorivfunNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology Revision Guide AnswersDocument36 pagesCSEC Biology Revision Guide AnswersShaquan FullertonNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Web Presentation PDFDocument37 pagesFood Chain and Web Presentation PDFScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Ecology LectureDocument93 pagesEcology LectureJeffrey Ells0% (1)
- Environmental DisatersDocument300 pagesEnvironmental DisatersFaith RiderNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document23 pagesUnit 2kirankatila99No ratings yet
- ch.3 EcosystemDocument6 pagesch.3 Ecosystemrounak.panja83No ratings yet
- Principles of EcologyDocument11 pagesPrinciples of EcologyRopelson Rabino100% (1)
- Unit 2 Ecosystem - 2Document52 pagesUnit 2 Ecosystem - 2Shreya 11-DNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity # 2 Energy Flow in Ecosystems: The Trophic Pyramids IntroductonDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity # 2 Energy Flow in Ecosystems: The Trophic Pyramids IntroductonMAY UNIDANo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 Module5 (Week6-7)Document36 pagesScience7 Q2 Module5 (Week6-7)nona wayne dela peñaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q2 Module 9 EcosystemsDocument21 pagesEarth and Life Science Q2 Module 9 EcosystemsMarc Joseph NillasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - EcologyDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 2 - EcologynnchlntkazeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ScienceDocument13 pagesIGCSE ScienceOOI WEN SHI MoeNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems and BiodiversityDocument25 pagesEcosystems and BiodiversityRahul67% (3)
- 11-1 The Science of EcologyDocument14 pages11-1 The Science of Ecologyapi-265907602No ratings yet
- 10 Chp 13 Our Environment 2024-25Document8 pages10 Chp 13 Our Environment 2024-255205prachiNo ratings yet
- CK-12 Biology Chapter 11 WorksheetsDocument23 pagesCK-12 Biology Chapter 11 WorksheetsmaleskunNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument8 pagesEcosystemArts NEFNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems CambDocument20 pagesEcosystems CambarmvelNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Ecology TutorialDocument6 pagesWelcome To The Ecology TutorialmariareanaNo ratings yet
- 2module in Environmental Science 2Document6 pages2module in Environmental Science 2I'm YouNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Important Questions: Our EnvironmentDocument6 pagesClass 10 Science Important Questions: Our EnvironmentGaurav YadavNo ratings yet
- Classwork Food Chains and Food WebsDocument5 pagesClasswork Food Chains and Food Websapi-272124446No ratings yet
- Multi - Section Test 2Document7 pagesMulti - Section Test 2api-314229616No ratings yet
- Module 2 Environmental ScienceDocument23 pagesModule 2 Environmental ScienceMarivic SolomonNo ratings yet
- Ecology HandoutDocument6 pagesEcology HandoutGabrielle Morgan100% (1)
- Chapter 1 EcologyDocument38 pagesChapter 1 EcologyRamil NacarioNo ratings yet
- Biology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsDocument92 pagesBiology VII Section 1 Lesson 2 Variety of Living OrganismsGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Biology - Note 1Document5 pagesEnvironmental Biology - Note 1Rithaj HarunNo ratings yet
- Organisms and Their Environment Lecture 1Document46 pagesOrganisms and Their Environment Lecture 1amanirameez84No ratings yet
- Ecology and PrinciplesDocument34 pagesEcology and PrinciplesMureed KazimNo ratings yet
- MST 101 Environmental Science Asynchronous Activity 2: Submitted byDocument8 pagesMST 101 Environmental Science Asynchronous Activity 2: Submitted byDexter TubioNo ratings yet
- 230-37884 2Document16 pages230-37884 2adriana arangoNo ratings yet
- How Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandHow Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Biology Data Based QuestionsDocument2 pagesBiology Data Based QuestionsEbony Good100% (1)
- Communities and Ecosystems 5.1Document15 pagesCommunities and Ecosystems 5.1Ebony GoodNo ratings yet
- Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect: Due Date: Student Name: Candidate Number: 002171-xxxDocument7 pagesEssential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect: Due Date: Student Name: Candidate Number: 002171-xxxEbony GoodNo ratings yet
- Biology Food Chains and Food WebDocument8 pagesBiology Food Chains and Food WebEbony GoodNo ratings yet
- SITE PLANNING & SELECTION v1.0Document58 pagesSITE PLANNING & SELECTION v1.0Alex AnderNo ratings yet
- National Marine Fisheries Service - Working Draft, April 2015Document66 pagesNational Marine Fisheries Service - Working Draft, April 2015ariya.stark14No ratings yet
- Na Level Ii PDFDocument1 pageNa Level Ii PDFm8r-wgow8mNo ratings yet
- (Ebooks PDF) Download Cambridge International As and A Level Geography Second Edition Garrett Nagle Full ChaptersDocument62 pages(Ebooks PDF) Download Cambridge International As and A Level Geography Second Edition Garrett Nagle Full Chaptersspatarlamkaj100% (14)
- Đề Số 10.doc - Google Tài LiệuDocument3 pagesĐề Số 10.doc - Google Tài LiệuLinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mangroves and Coral ReefsDocument22 pagesMangroves and Coral ReefsnarmadhaldNo ratings yet
- Millions in Enhancements Proposed For A&M Athletic FacilitiesDocument196 pagesMillions in Enhancements Proposed For A&M Athletic FacilitiesKBTXNo ratings yet
- The Tragedy of The High Seas - The EconomistDocument3 pagesThe Tragedy of The High Seas - The EconomistFantastic DragonNo ratings yet
- Note Bio Siap!!!Document1 pageNote Bio Siap!!!naninoNo ratings yet
- Marine BenthosDocument23 pagesMarine BenthosDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Turbidity TestDocument3 pagesTurbidity TestAnis NurdiniNo ratings yet
- Climatic RegionsDocument53 pagesClimatic RegionsPrakhar Roy100% (1)
- Okomfo Anokye and Other Prominent Traditional Past LeadersDocument7 pagesOkomfo Anokye and Other Prominent Traditional Past LeadersJoshua AnnanNo ratings yet
- Jurutera August 2014Document28 pagesJurutera August 2014Edison LimNo ratings yet
- Technical Report Series: Central Ground Water BoardDocument23 pagesTechnical Report Series: Central Ground Water BoardAnonymous QZwgOjEx3No ratings yet
- Technological University of The Philippines: ManilaDocument7 pagesTechnological University of The Philippines: ManilapauliNo ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument3 pagesObjectiveJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution and Control - DocxppDocument26 pagesWater Pollution and Control - DocxppGraphic DesignerNo ratings yet
- Industrial Waste Water Treatment - Unit 1Document27 pagesIndustrial Waste Water Treatment - Unit 1bonaveenNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources Important Questions 2022-23Document27 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources Important Questions 2022-23S MNo ratings yet
- Article PublicationDocument7 pagesArticle Publicationgraphic designerNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Who Cares?Document62 pagesBiodiversity: Who Cares?ashraful HoqueNo ratings yet
- Environmental Quality Standards For Water and Effluent Standards WEPADocument13 pagesEnvironmental Quality Standards For Water and Effluent Standards WEPApeguy diffoNo ratings yet
- Basin Hydrology and Wetland Dynamics of Agusan MarshDocument44 pagesBasin Hydrology and Wetland Dynamics of Agusan MarshKalambuan Foundation, Inc.No ratings yet
- Environmental Education Syllabus in B.Ed. of 11 Indian UniversitiesDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Education Syllabus in B.Ed. of 11 Indian Universitiesvinodpr111No ratings yet
- What Is Environment - StudentsDocument21 pagesWhat Is Environment - StudentsCharlesNo ratings yet
- Part IiDocument7 pagesPart IiQuỳnh HoaNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Department: Government of KeralaDocument2 pagesIrrigation Department: Government of KeralashivanandarcotNo ratings yet
- Groundwater VulnerabilityDocument20 pagesGroundwater VulnerabilityPeter NathanielNo ratings yet
- Distribution System QuestionsDocument10 pagesDistribution System QuestionsEdu4civil EngineeringNo ratings yet