Patho Dengue
Patho Dengue
Uploaded by
Lindy Shane BoncalesCopyright:
Available Formats
Patho Dengue
Patho Dengue
Uploaded by
Lindy Shane BoncalesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Patho Dengue
Patho Dengue
Uploaded by
Lindy Shane BoncalesCopyright:
Available Formats
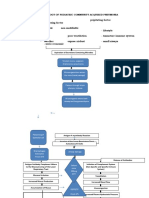
PREDISPOSING FACTOR -Geographical area -Race -Gender -Socioeconomic -Genetic
DENGUE PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Aedes Aegypti/ Aedes albopictus (dengue virus carrier) (8-12 days of viral replication on mosquito salivary glands
PRECIPITATING FACTOR -Environmental Condition -Immunocompromise -Mosquito carrying dengue -Sweaty Skin
Bite from mosquito (portal of entry in the skin)
Allowing dengue virus to be inoculated towards the circulation (incubation period of 3-14 days)
Virus disseminated rapidly into the blood
Virus will present in the circulation
Stimulates WBC inducing B lymphocytes
Viremia
Secrets immunoglobulin (antibodies) and monocytes (macrophages, neutrophils)
Antibodies attack to the viral antigen
Monocytes/macrophages will perform phagocytosis through FC receptors w/in the cell
Dengue replicates w/in the cell Entry to spleen Entry to lymphnode Entry to bone marrrow
Recognition of dengue viral antigen on infected monocytes
Stays in the area
Inflammation Release of cytokine w/c consists of vasoactive agents (urokinase and platelet activating factor) NURSING DIAGNOSIS (FOR COUGH) -Ineffective airway clearance r/t to unproductive cough -Monitor V/S -Encourage to increase fluid intake -Encourage to expectorate sputum -Perform deep breathing SIGNS & SYMPTOMS -Diaphoresis -Warm Skin -Flushed -Headache -Body Weakness -Vomiting -Cough -Nausea -Fever (Intermittent) -Swollen Lymph
Stimulates WBC and Pyrogen release
DENGUE FEVER
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT -Intravenous Fluid -Administer Sulbactam
Virus ultimately target the liver and spleen
Cellular direct destruction
Inflammation
Infection in RBC marrow and shortened platelet count DIAGNOSTIC EXAMINATION -Hematologic Test -Decreased platelet count -41 k/uL (150-450 k/uL)
Apoptosis/Cell Death MEDICAL MANAGEMENT -Intravenous Fluid -Administer Cimetidine SIGNS & SYMPTOMS -Abdominal Pain -Accompanied with vomiting Hepatosplenomegaly
Thrombocytopenia
DENGUE HEMORRHAGIC FEVER SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS -Red sclera on both eyes -Petechiae -Bruises
NURSING DIAGNOSIS -Pain r/t to possible hepatosplenomegaly secondary to DHF
Increase size and number of pores in the capillaries
Increase capillary permeability
Fluid shifting from blood to interstitial fluid
Fluid accumulation in the lungs Coagulopathy Increase amount of fluid that can impair breathing SIGNS & SYMPTOMS -Nonproductive cough with white sputum -Difficulty in breathing
Leakage in the plasma
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Hypovolemia Low BP Tachycardia Tachypnea
PLEURAL EFFUSION
Shock Bleeding
Severe Bleeding
Death MEDICAL MANAGEMENT -Platelet/ Blood Transfusion -Administer Tranexamic Acid -Intravenous solution -ORESOL -CBC urinalysis, fecalysis lab test -Administer Cimitidine NURSING DIAGNOSIS -Risk for shock r/t increase capillary permeability secondary to DHF NURSING MANAGEMENT -monitor V/S every 10 minutes Or earlier -Apply ice cap -Elevate the head -Protect the patient from sudden accidents -Monitor IVF -Stop the activity of the client immediately -Give time to rest -Use soft bristle toothbrush -Encourage avoid dark colored foods SIGNS & SYMPTOMS -Epistaxis -Melena -Hematemesis -Headache -Bruising -Abdominal Pain -Chest pain -Petechiae -Low BP -Clammy Skin -Paleness -SOB -Weakness
LEGEND: y Those that are highlighted have been manifested by the client.
You might also like
- Pancreatitis Case StudyDocument11 pagesPancreatitis Case Studysunny kumarNo ratings yet
- POTTs Disease PathoDocument3 pagesPOTTs Disease PathoEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Patho DengueDocument3 pagesPatho DengueKayshey Christine ChuaNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Pcap PathoDocument2 pagesPcap PathoLardel CarayNo ratings yet
- Final Bsn2f 2c Pcap Case Pres 1Document54 pagesFinal Bsn2f 2c Pcap Case Pres 1Rod Reynon BorceNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop IncisionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop IncisionCharry de VeraNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PsoriasisDocument1 pageConcept Map PsoriasisEran Mark RojasNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiologyaprilkow07No ratings yet
- Case CholeDocument23 pagesCase CholeLailani Rose Gulinao-DorupaNo ratings yet
- Age - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing MicrobesDocument4 pagesAge - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing Microbeslouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- D. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesD. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaBill Clinton Lamira BabanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Group 1Document1 pageConcept Map Group 1eric macabiog100% (1)
- Normal Values of CBCDocument1 pageNormal Values of CBCCherr NollNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of TetanusDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of TetanusAnitha SuprionoNo ratings yet
- Rubella (German Measles) : Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDDocument2 pagesRubella (German Measles) : Sabah Mohsin Al-Maamuri MDnadyaszahraaaaNo ratings yet
- Ascariasis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifesta7ons and TreatmentDocument9 pagesAscariasis: Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifesta7ons and TreatmentJUAN CAMILO GARCIA ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramDocument4 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic Fever Pathophysiology DiagramAni MarlinaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 National Immunization Program (Npi) - MihpDocument15 pagesModule 2 National Immunization Program (Npi) - MihpNurhaifa Mocadema100% (1)
- Bacolod, Queen Elizabeth G. Bsn3A ESSAY About Community Health Network System in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesBacolod, Queen Elizabeth G. Bsn3A ESSAY About Community Health Network System in The PhilippinesQueenie BacolodNo ratings yet
- TOF (Pathophysiology)Document4 pagesTOF (Pathophysiology)Doreen Claire M. WallangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisDocument9 pagesPathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
- TB PathoPhysiologyDocument6 pagesTB PathoPhysiologyChloé Jane HilarioNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PathoDocument2 pagesPneumonia PathoDerick Nyl PascualNo ratings yet
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument17 pagesAcute TonsillopharyngitisRachel Haide NaravalNo ratings yet
- CHOLANGITISDocument1 pageCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresNo ratings yet
- Coxa Plana PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCoxa Plana Pathophysiologymiss RN100% (4)
- ALMOETE Bullous ImpetigoDocument4 pagesALMOETE Bullous ImpetigoGail NamangdanNo ratings yet
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Health Allied Sciences College of NursingDocument43 pagesPamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Health Allied Sciences College of NursingSofea MustaffaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pressure UlcersDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pressure UlcersSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiDocument12 pagesCase Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiHarlene Joyce ReyNo ratings yet
- LeptospirosisDocument3 pagesLeptospirosisJessie Cauilan Cain100% (1)
- PathophyDocument1 pagePathophydianna_espirituNo ratings yet
- Case Pres A1-RhdDocument11 pagesCase Pres A1-RhdCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumothorax PDFDocument2 pagesTension Pneumothorax PDFClarissa Aileen Caliva AdoraNo ratings yet
- Annotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1Document30 pagesAnnotated Group 2 Impetigo Concept Mapping 1DHANE ANN CAMPOSANONo ratings yet
- JRMMC - Patho of Ruptured AppendicitisDocument3 pagesJRMMC - Patho of Ruptured Appendicitis9632141475963No ratings yet
- Ortho NCPDocument3 pagesOrtho NCPMarshin Thea CelociaNo ratings yet
- PathophyDocument2 pagesPathophymharz_astilloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology (Client Base) :: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factorsleslie_macasaetNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsDocument1 pageMycobacterium Tuberculosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorsYoko Mae Yano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology (Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery)Document2 pagesPathophysiology (Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery)Jose Bryan NacillaNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching For A Pregnant WomanDocument33 pagesHealth Teaching For A Pregnant WomanFrancia ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument6 pagesLiver AbscessKenneth SunicoNo ratings yet
- Respi SystemDocument65 pagesRespi Systemapi-373599567% (3)
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoNo ratings yet
- Republic ActDocument36 pagesRepublic ActjanNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument12 pagesPleural EffusionWan HafizNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Multiple Myeloma OkRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument4 pagesDischarge Plan of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDenise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Geographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaDocument1 pageGeographical Area - Tropical Islands in Thepacific (Philippines) and AsiaGenevang SeaweedsNo ratings yet