Sal But Amol
Sal But Amol
Uploaded by
Kay MirandaCopyright:
Available Formats
Sal But Amol
Sal But Amol
Uploaded by
Kay MirandaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Sal But Amol
Sal But Amol
Uploaded by
Kay MirandaCopyright:
Available Formats
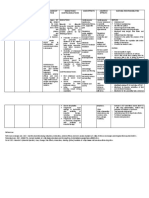
DRUG NAME GENERIC:
Albuterol
CLASSIFICATION
Bronchodilator (therapeutic); adrenergics (pharmacologic)
ACTION/INDICATION Actions :
It relieves nasal
DOSAGE/ROUTE/FREQUENCY
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
EVALUATION
PO (Adults and Children more than 12 years): 2-4 mg 3-4 times a day or 4-8 mg of extended dose tablets twice a day. PO (Geriatric Patients): initial dose should not exceed 2 mg 3-4 times a day and may be increased carefully up to 32 mg/day Inhalation (Adults and children more than 4 years of age): 2 inhalations every 4-6 hours Inhalation (Children 2-12 years old): 0.1-0.15 mg/kg/dose 3-4 times a day
1.
Assess lung sounds, PR and BP before drug administration and during peak of medication.
BRAND:
Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, airet, Novo-Salbutamol, Proventil HFA, Gensalbutamol, Ventodisk, Ventolin HFA, Volmax, VoSpira ER
congestion and reversible bronchospasm by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bronchioles. The relief from nasal congestion and bronchospasm is made possible by the following mechanism that takes place when Salbutamol is administered. 1. First, it binds to the beta2-adrenergic receptors in the airway of the smooth muscle which then leads to the activation of the adenyl cyclase and increased levels of cyclic- 35-adenosine monophosphate 2. (cAMP). When cAMP increases, kinases are activated. 3. Kinases inhibit the phosphorylation of myosin and decrease intracellular calcium. 4. Decreased in
The client is relieved from nasal congestion and bronchospasm.
2.
Observe fore paradoxical spasm and withhold medication and notify physician if
3.
condition occurs. Administer PO medications with meals to minimize gastric
4.
irritation. Extended-release tablet should be swallowedwhole. It should not be
5.
crushed or chewed. If administering medication through inhalation, allow at least 1 minute between inhalation of aerosol
6.
medication. Advise the patient to rinse mouth with water after each inhalation to
7.
minimize dry mouth. Inform the patient that Albuterol may cause an unusual or bad taste.
DRUG NAME
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION/INDICATION
intracellular calcium will result to the relaxation of the smooth muscle airways.
DOSAGE/ROUTE/FREQUENCY
NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
EVALUATION
Indications 1. To control and prevent reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder 2. 3. (COPD) Quick relief for bronchospasm For the prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm 4. Long-term control agent for patients with chronic or persistent bronchospasm
You might also like
- ATI Repiratory Questions - Answer KeyDocument11 pagesATI Repiratory Questions - Answer KeyLeelee SheppardNo ratings yet
- Albuterol Sulfate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesAlbuterol Sulfate Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz100% (1)
- SalbutamolDocument2 pagesSalbutamolMarck Vincent Garcia OngNo ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - OBDocument10 pagesDrug Study - OBArdhel LoslosoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument5 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing InterventionsYvonne AgathaNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsy Discharge Planningjints poterNo ratings yet
- Tamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument23 pagesTamsulosin - Drug Information - UpToDateGénesis GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Drug Profile NebivololDocument6 pagesDrug Profile NebivololKrista ColeNo ratings yet
- GUAIFENESINDocument1 pageGUAIFENESINAngel CatalanNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHerwincayeNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument8 pagesDRUG StudyLou-Lou HadaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Drug Study & 1 NCPDocument4 pages3 Drug Study & 1 NCPAnnie Christine RiveraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ready TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ready TramadolCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy Itopride (Ganaton)Document2 pagesDrugStudy Itopride (Ganaton)jean19.go100% (1)
- SalmeterolDocument2 pagesSalmeterolapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Therabloc DrugDocument2 pagesTherabloc DrugMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- Feu-Nrmf (Drug Study)Document7 pagesFeu-Nrmf (Drug Study)Kaye LaraganNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument1 pageATORVASTATINSHEILA MAE SACLOT100% (1)
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLDocument5 pagesNoradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLBrian RelsonNo ratings yet
- LOVASTATINDocument2 pagesLOVASTATINAngel CatalanNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument6 pagesDRUG StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)Document5 pagesLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)CHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study PantoprazoleIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug Study OmeprazoleBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Florinef (Fludrocortisone)Document3 pagesFlorinef (Fludrocortisone)E100% (1)
- CarvedilolDocument2 pagesCarvedilolKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- A: Hydrolyzed To Active Drug: Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageA: Hydrolyzed To Active Drug: Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug StudyMaki Dc100% (1)
- PREGABALINDocument5 pagesPREGABALINJojenelle R. TepaitNo ratings yet
- GAT NCP Surgery WardDocument4 pagesGAT NCP Surgery WardDon Richard0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyRizzi DeveraNo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Para Iterax XylogelDocument2 pagesPara Iterax XylogelArchie PunzalanNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- Ds Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDs Pedia WardRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FDocument3 pagesDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasNo ratings yet
- CombiventDocument1 pageCombiventDherick Rosas0% (1)
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMae Navidas DigdiganNo ratings yet
- Xii. Drug StudyDocument2 pagesXii. Drug StudyAela Maive MontenegroNo ratings yet
- F&E Drug StudyDocument2 pagesF&E Drug Studychelle_asenjoNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning DengueDocument2 pagesDischarge Planning DengueChyNo ratings yet
- Stress TabsDocument2 pagesStress TabsPamela Joy PacanaNo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy ZineDocument2 pagesHydroxy ZineSharmaine Grace FlorigNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cap RHPDocument7 pagesDrug Study Cap RHPJan DeeNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document1 pageDrug Study 2Blitz KriegNo ratings yet
- The Format of This Leaflet Was Determined by The Ministry of Health and Its Content Was Checked and Approved by It On February 2016Document10 pagesThe Format of This Leaflet Was Determined by The Ministry of Health and Its Content Was Checked and Approved by It On February 2016ddandan_2No ratings yet
- Omeprazole - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOmeprazole - Drug StudyJun Gilbuena100% (1)
- Furosemide ChlorthalidoneDocument5 pagesFurosemide ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Amlodipine BesylateDocument2 pagesAmlodipine BesylateYakumaNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument1 pageSalbutamolMonica Lyka BancaleNo ratings yet
- SalbutamolDocument5 pagesSalbutamolFildehl Janice Bomediano CatipayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory NCLEX Questions Asthma and More Flashcards QuizletDocument1 pageRespiratory NCLEX Questions Asthma and More Flashcards QuizletJannah TangonNo ratings yet
- XopenexDocument1 pageXopenexKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaTuna AhsanNo ratings yet
- EquinehalerDocument2 pagesEquinehalerNicoleta BratosinNo ratings yet
- RFDS Western Operations HEA16 - V3.0 Clinical ManualDocument28 pagesRFDS Western Operations HEA16 - V3.0 Clinical ManualJoed BiasonNo ratings yet
- Flowchart For AEBA Using Spacer - Revised 7-4-2020Document2 pagesFlowchart For AEBA Using Spacer - Revised 7-4-2020Noreen Ooi Zhi MinNo ratings yet
- Review PharmacologyDocument137 pagesReview PharmacologyGeronimo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument18 pagesDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Nutrient DepletionDocument4 pagesDrug-Induced Nutrient DepletionVictoria HristovaNo ratings yet
- Brief Outline Questions To Ask: Acute AsthmaDocument15 pagesBrief Outline Questions To Ask: Acute AsthmaLevina AudreyNo ratings yet
- Beta2 Adrenergic AgonistDocument3 pagesBeta2 Adrenergic AgonistУдшфиАгутеуыNo ratings yet
- Drug TabulationDocument6 pagesDrug TabulationKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- 14 Drug TAbulationDocument6 pages14 Drug TAbulationbrantNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Elaborate Drug StudyDocument16 pagesModule 7 Elaborate Drug StudyDagooc, Alleya Mesha M.No ratings yet
- Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) : Emergency MedicationsDocument3 pagesMethylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) : Emergency MedicationsKdamnzNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Status AsmatikusDocument8 pagesJurnal Status AsmatikusIrani VianzaNo ratings yet
- Case 10 Hiv-AidsDocument47 pagesCase 10 Hiv-AidsErikah Eirah BeloriaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNeri ChavezNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Terbutaline Drug Class and MechanismDocument4 pagesGENERIC NAME: Terbutaline Drug Class and MechanismAngel DamoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory Organs Function - 1drugs Acting On The Respiratory Organs Function - 2Document49 pagesDrugs Acting On The Respiratory Organs Function - 1drugs Acting On The Respiratory Organs Function - 2Mihalachi-Anghel MariaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Short Review: OM Nursing Academy Anil Kantiwal GudhaDocument5 pagesPharmacology Short Review: OM Nursing Academy Anil Kantiwal GudhaNEHA PANDEYNo ratings yet
- 10 Adrenergic Agonists (Notes) AtfDocument13 pages10 Adrenergic Agonists (Notes) AtfFeven AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Ipratropium BromideDocument20 pagesIpratropium BromideAngelique Ramos PascuaNo ratings yet
- 1 Pharmacy Practice Therapeutics OTC Drugs Q&A Content Ver1Document123 pages1 Pharmacy Practice Therapeutics OTC Drugs Q&A Content Ver1bhaveshnidhi64100% (1)
- Drugs in Treatment of Bronchial AsthmaDocument46 pagesDrugs in Treatment of Bronchial AsthmaNikita JangraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Adult: ChildDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Adult: ChildKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Frequently Prescribed DrugsDocument47 pagesFrequently Prescribed DrugsMahogony ScottNo ratings yet